The Perfect Desktop - Fedora 17 - Page 2
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
On this page
3 Update The System
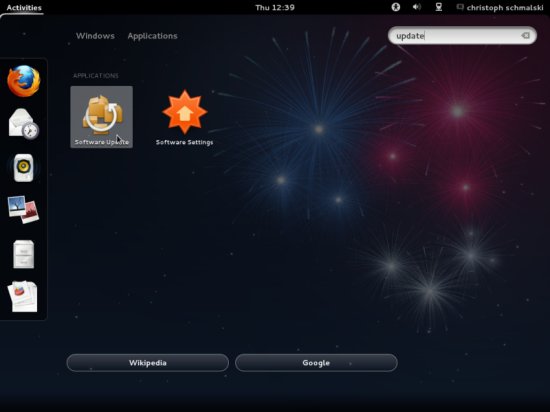
Now it's time to check for updates and install them. This is done using Software Update. Start it from Activities > Applications > Update Manager:
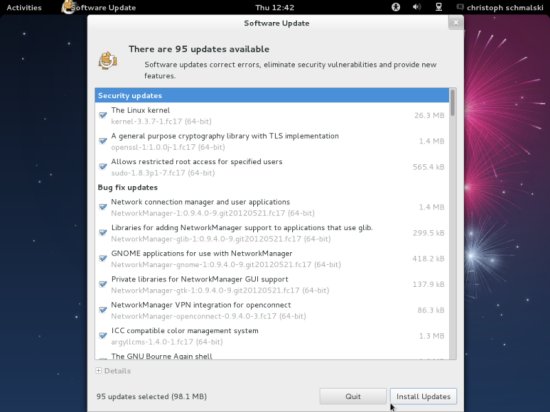
The Software Update wizard comes up and checks for the latest updates. Click on Install Updates to install them:
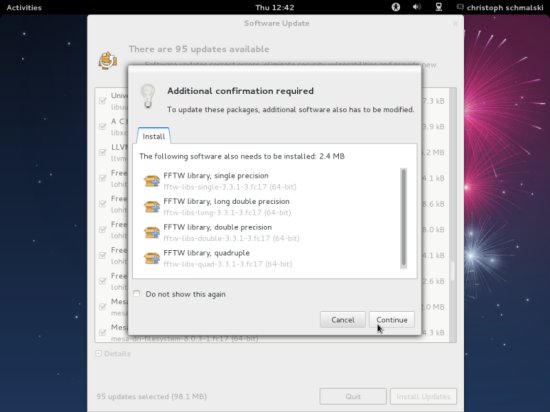
Some of the updates might need to install packages they depend on. Click Continue to go on:
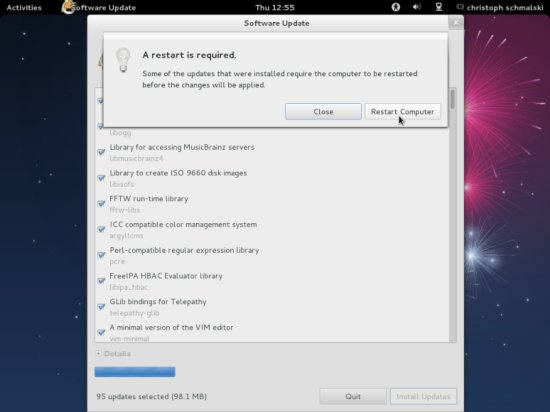
In some cases a restart is required after updating the system. Do so by clicking on Restart Computer:
The system is now up-to-date.
4 Disable SELinux
SELinux is a security extension of Fedora that should provide extended security. In my opinion you don't need it to configure a secure system, and it usually causes more problems than advantages (think of it after you have done a week of trouble-shooting because some service wasn't working as expected, and then you find out that everything was ok, only SELinux was causing the problem). Therefore I choose disable it, although you might prefer to go with it. I haven't tested this setup with SELinux enabled - it might well be that it works without problems, but if it does not, you can try to turn SELinux off and see if the problem is gone.
To disable SELinux, open a terminal (Activities > Applications > Terminal).
Open /etc/sysconfig/selinux as root:
sudo gedit /etc/sysconfig/selinux
... and set SELINUX to disabled:
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. |
To make the change effective, we must reboot the system:
reboot
5 Inventory Of What We Have So Far
Now let's browse all menus to see which of our needed applications are already installed:
You should find the following situation ([x] marks an application that is already installed, whereas [ ] is an application that is missing):
Graphics:
[ ] The GIMP
[x] Shotwell Photo Manager
[ ] Pinta
Internet:
[x] Firefox
[ ] FileZilla
[ ] Thunderbird
[ ] Deluge
[ ] Skype
[ ] Marble
[ ] Pidgin
[ ] Dropbox
[ ] Gwibber Social Client
Office:
[ ] LibreOffice Writer
[ ] LibreOffice Calc
[ ] Adobe Reader
[ ] GnuCash
[ ] Scribus
Sound & Video:
[ ] Audacity
[ ] Banshee
[ ] dvd::rip
[ ] VLC Media Player
[ ] K3B
[ ] Multimedia-Codecs
[ ] Winff
Programming:
[ ] KompoZer
[ ] Eclipse
Other:
[ ] VirtualBox
[ ] TrueType fonts
[ ] Java
[x] Read/Write support for NTFS partitions
[x] gedit
So some applications are already on the system. NTFS read-/write support is enabled by default on Fedora 17.