How to Install Zeek Network Security Monitoring Tool on Ubuntu 22.04
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble Numbat)
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
On this page
Zeek is a free, open-source, and worlds leading security monitoring tool used as a network intrusion detection system and network traffic analyzer. Security professionals use it to detect suspicious signatures and track DNS, HTTP, and FTP activity. Zeek works by logging network activity in a separate file. This file contains all important information like, MIME types, server responses, DNS requests, HTTP sessions, requested URIs, SSL certificates, and more.
This tutorial will show you how to install the Zeek network security tool on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04 with a minimum 2 GB RAM.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Getting Started
First, you must update all your system packages to the updated version. You can update all of them by running the following command.
apt update -y
apt upgrade -y
After updating all the system packages, install some required packages using the following command.
apt install curl gnupg2 wget -y
Add Zeek Repository
By default, the Zeek package is not included in the Ubuntu default repository. So you will need to add the Zeek repository to APT.
First, download and add the Zeek GPG key with the following command.
curl -fsSL https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/security:zeek/xUbuntu_22.04/Release.key | gpg --dearmor | tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/security_zeek.gpg
Next, add the Zeek repository with the following command.
echo 'deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/security:/zeek/xUbuntu_22.04/ /' | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/security:zeek.list
Next, update the repository cache using the following command.
apt update -y
Install Zeek
You can now install the Zeek tool by just running the following command.
apt install zeek -y
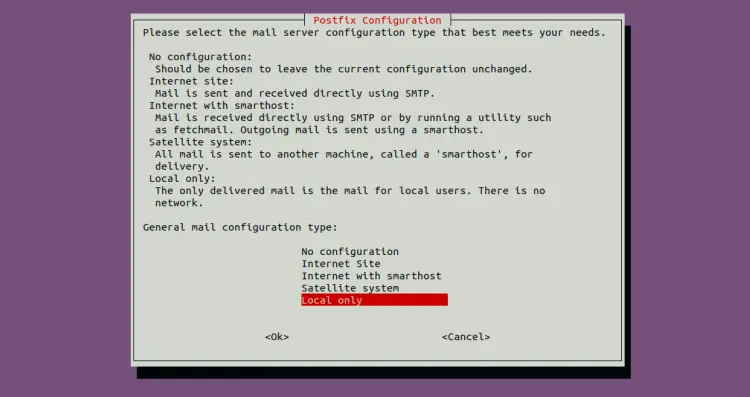
During the installation, you will be asked to select your mail server as shown below:
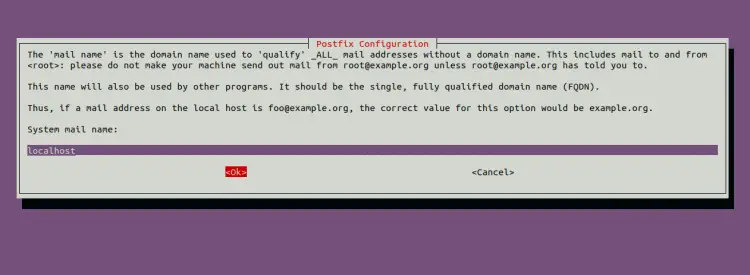
Select local only and press the Enter key. You will be asked to provide your mail server hostname.
Type your hostname and press the Enter key to finish the installation.
Next, you will need to add the Zeek installation path to your system variable. You can add it with the following command.
echo "export PATH=$PATH:/opt/zeek/bin" >> ~/.bashrc
Next, activate the system variable with the following command.
source ~/.bashrc
You can now verify the Zeek version using the following command:
zeek --version
You will get the following output.
zeek version 5.1.1
Configure Zeek Server
First, edit the Zeek network configuration file and define your network.
nano /opt/zeek/etc/networks.cfg
Here is the default networks. You can add more networks at the end of the file.
10.0.0.0/8 Private IP space 172.16.0.0/12 Private IP space 192.168.0.0/16 Private IP space
Save and close the file then edit the Zeek main configuration file.
nano /opt/zeek/etc/node.cfg
Comment on the following lines:
#[zeek] #type=standalone #host=localhost #interface=eth0
Then, add the following configurations at the end of the file.
[zeek-logger] type=logger host=your-server-ip # [zeek-manager] type=manager host=your-server-ip # [zeek-proxy] type=proxy host=your-server-ip # [zeek-worker] type=worker host=your-server-ip interface=eth0 # [zeek-worker-lo] type=worker host=localhost interface=lo
Save the file then verify the Zeek configuration using the following command.
zeekctl check
You will get the following output.
Hint: Run the zeekctl "deploy" command to get started. zeek-logger scripts are ok. zeek-manager scripts are ok. zeek-proxy scripts are ok. zeek-worker scripts are ok. zeek-worker-lo scripts are ok.
You can now deploy the Zeek using the following command.
zeekctl deploy
You will get the following output.
checking configurations ... installing ... creating policy directories ... installing site policies ... generating cluster-layout.zeek ... generating local-networks.zeek ... generating zeekctl-config.zeek ... generating zeekctl-config.sh ... stopping ... stopping workers ... stopping proxy ... stopping manager ... stopping logger ... starting ... starting logger ... starting manager ... starting proxy ... starting workers ...
Test Zeek Status
At this point, Zeek is installed and configured. You can now check the Zeek status with the following command.
zeekctl status
You will get the following output.
Name Type Host Status Pid Started zeek-logger logger 209.23.10.179 running 58935 19 Jan 05:37:02 zeek-manager manager 209.23.10.179 running 58985 19 Jan 05:37:03 zeek-proxy proxy 209.23.10.179 running 59035 19 Jan 05:37:05 zeek-worker worker 209.23.10.179 running 59107 19 Jan 05:37:06 zeek-worker-lo worker localhost running 59104 19 Jan 05:37:06
Zeek stores their logs at /opt/zeek/logs/current/ directory. You can check all log files using the following command.
ls -l /opt/zeek/logs/current/
You will see the following output.
total 72 -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 1735 Jan 19 05:37 broker.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 2166 Jan 19 05:37 cluster.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 187 Jan 19 05:37 packet_filter.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 6158 Jan 19 05:37 conn.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 31212 Jan 19 05:37 loaded_scripts.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 666 Jan 19 05:37 reporter.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 601 Jan 19 05:37 stats.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 0 Jan 19 05:37 stderr.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 204 Jan 19 05:37 stdout.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 266 Jan 19 05:37 telemetry.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 960 Jan 19 05:37 weird.log
To check the Zeek cluster log, run the following command.
tail /opt/zeek/logs/current/cluster.log
You will get the following output.
1674106627.672399 zeek-proxy got hello from zeek-worker-lo (62498247-62ce-5763-b201-a0f0e52b71f9) 1674106627.744144 zeek-proxy got hello from zeek-worker (0c8c7207-f1a1-540d-aee0-2b55cf76e69f) 1674106627.674594 zeek-manager got hello from zeek-worker-lo (62498247-62ce-5763-b201-a0f0e52b71f9) 1674106627.752439 zeek-manager got hello from zeek-worker (0c8c7207-f1a1-540d-aee0-2b55cf76e69f) 1674106627.672635 zeek-worker-lo got hello from zeek-proxy (b0734910-55c0-5aa5-b5fb-abdf7c083d3e) 1674106627.674358 zeek-worker-lo got hello from zeek-manager (b4a3890a-a470-5a1d-b2c7-fc48fd683ff9) 1674106627.666564 zeek-worker-lo got hello from zeek-logger (405e0618-3699-5b85-ac39-0af2743c0aab) 1674106627.708986 zeek-worker got hello from zeek-manager (b4a3890a-a470-5a1d-b2c7-fc48fd683ff9) 1674106627.699878 zeek-worker got hello from zeek-proxy (b0734910-55c0-5aa5-b5fb-abdf7c083d3e) 1674106627.706099 zeek-worker got hello from zeek-logger (405e0618-3699-5b85-ac39-0af2743c0aab)
To check the Zeek connection log, run the following command.
tail /opt/zeek/logs/current/conn.log
You will get the following output.
1674106667.717311 Camkki2oVKl4J9dgpd 209.23.10.179 47762 209.23.10.179 56180 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 CccC 0 0 0 0 - 1674106667.742276 CZ7aKU3nUfkjSSN5x6 209.23.10.179 56182 209.23.10.179 47762 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 CcCc 0 0 0 0 - 1674106667.742332 Cd58V813jeHygHXQS2 209.23.10.179 56176 209.23.10.179 47762 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 CcCc 0 0 0 0 - 1674106668.621860 CZlcm316EidXbp4aMj 209.23.10.179 41430 209.23.10.179 47761 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 Cc 0 0 0 0 -
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed the Zeek security monitoring tool on Ubuntu 22.04 server. I hope this post will help to understand the network's architecture and investigate any malicious activity. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.