How to install Ubuntu 17.10 (Artful Aardvark) Minimal Server - Page 2
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble Numbat)
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
- Ubuntu 17.10 (Artful Aardvark)
- Ubuntu 17.04 (Zesty Zapus)
On this page
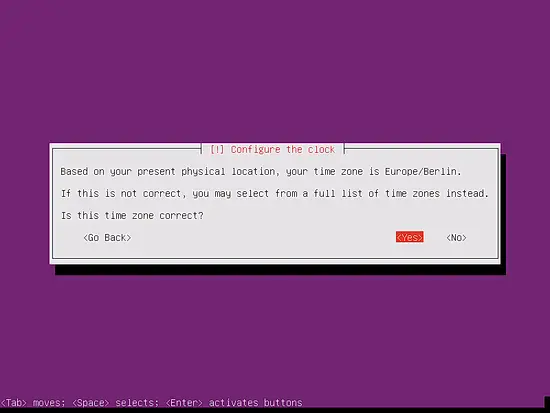
Please check if the installer detected your time zone correctly. If so, select Yes, otherwise No:
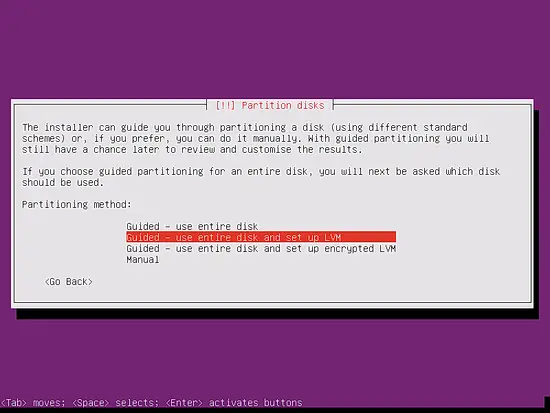
Now you have to partition your hard disk. For simplicity's sake I select Guided - use entire disk and set up LVM - this will create one volume group with two logical volumes, one for the / file system and another one for swap (of course, the partitioning is totally up to you - if you know what you're doing, you can also set up your partitions manually).
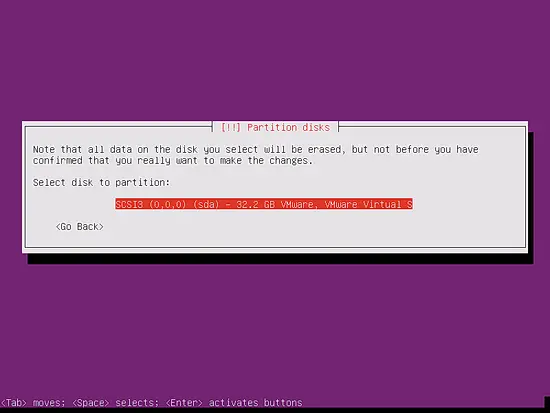
Select the disk that you want to partition:
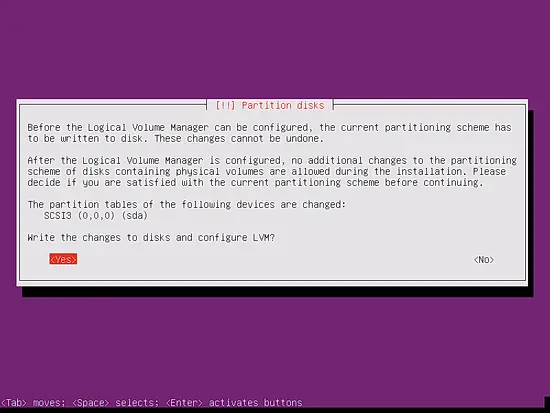
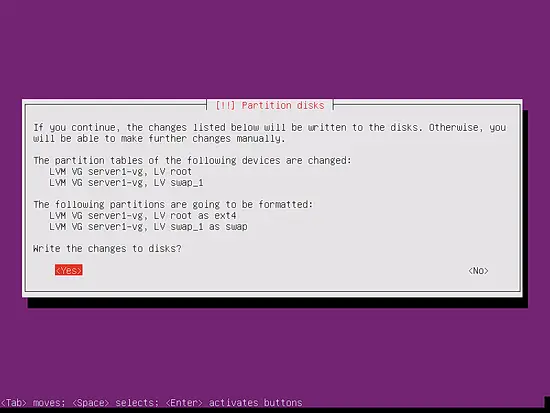
When you're asked Write the changes to disks and configure LVM?, select Yes:
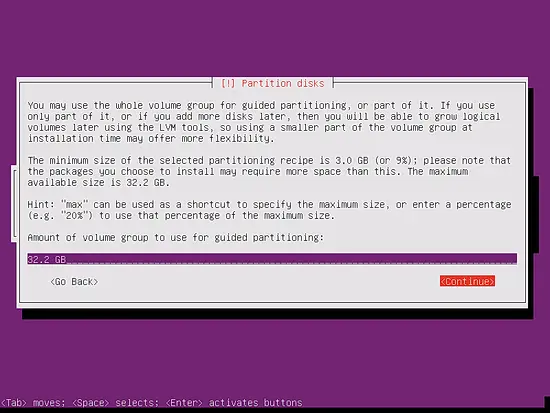
If you have selected Guided - use entire disk and set up LVM, the partitioner will create one big volume group that uses all the disk space. You can now specify how much of that disk space should be used by the logical volumes for / and swap. It makes sense to leave some space unused so that you can later on expand your existing logical volumes or create new ones - this gives you more flexibility.
When you're finished, hit Yes when you're asked to Write the changes to disks?:
Afterward, your new partitions are being created and formatted.
Then the base system is being installed. This will take a few minutes.
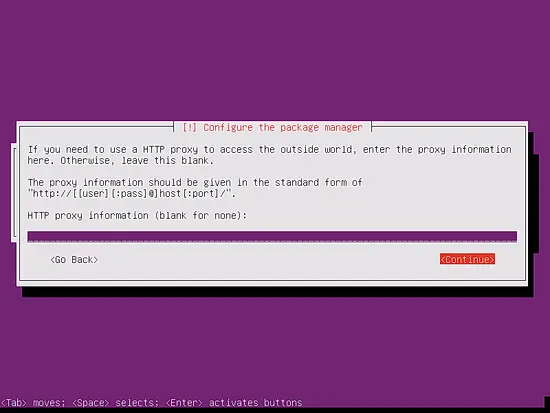
Now the package manager "apt" gets configured. Leave the HTTP proxy line empty unless you're using a proxy server to connect to the Internet:
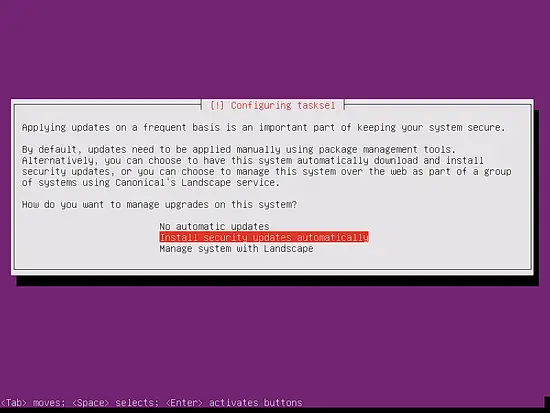
I like to update my servers automatically. Therefore, I select Install Security Updates automatically.
Of course, it's up to you what you select here:
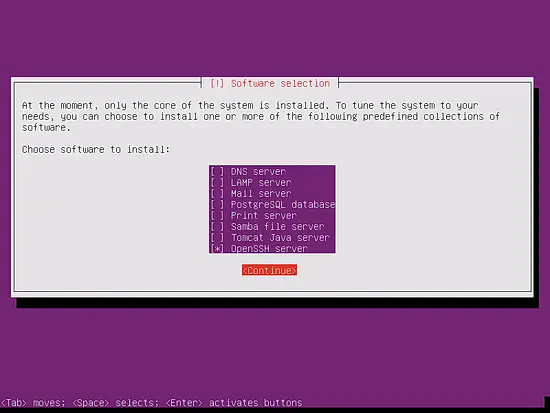
The only items I select here are OpenSSH server so that I can immediately connect to the system with an SSH client such as PuTTY after the installation has finished:
The installation continues:
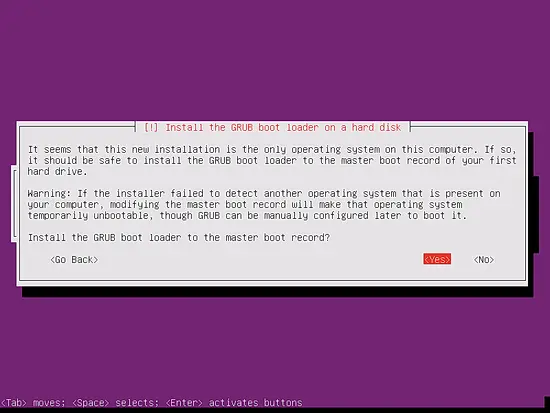
Select Yes when you are asked Install the GRUB boot loader to the master boot record?:
The installer now finished the Ubuntu installation.
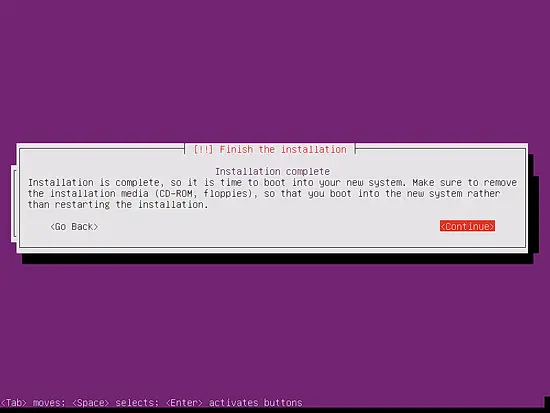
The base system installation is now finished. Remove the installation CD from the CD drive and hit Continue to reboot the system:
The base installation is finished now. In the next chapter, I will explain the configuration of the static network address and install a shell based text editor for editing configuration files.
4. First Login
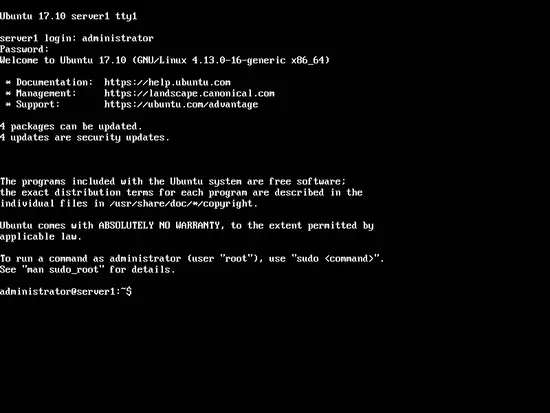
Now Login on the shell (or remotely by SSH) on the server as user "administrator". The username may differ if you have chosen a different name during setup.
5. Get root Privileges
After the reboot, you can log in with your previously created username (e.g. administrator). Because we must run all the steps from this tutorial with root privileges, we can either prepend all commands in this tutorial with the string sudo, or we become root right now by typing:
sudo -s
(You can as well enable the root login by running)
sudo passwd root
And giving root a password. You can then directly log in as root, but this is frowned upon by the Ubuntu developers and community for various reasons. See https://help.ubuntu.com/community/RootSudo.)
6. Install the SSH Server (Optional)
If you did not select to install the OpenSSH server during the system installation above, you could do it now:
apt-get install ssh openssh-server
From now on you can use an SSH client such as PuTTY and connect from your workstation to your Ubuntu 17.10 (Artful Aardvark) server.
7. Install a shell based editor (Optional)
Here we will install two text based editors. The Nano editor is easier to use for newbies while others prefer the traditional vi/vim editor. The default vi program has some strange behavior on Ubuntu and Debian; to fix this, we install vim-nox:
apt-get -y install nano vim-nox
8. Configure the Network
Because the Ubuntu installer has configured our system to get its network settings via DHCP, we have to change that now because a server should have a static IP address. If you want to keep the DHCP-based network configuration, then skip this chapter. Starting with Ubuntu 17.10, the network is configured with Netplan and the configuration file is /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml. The traditional network configuration file /etc/network/interfaces is not used anymore. Edit /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml and adjust it to your needs (in this example setup I will use the IP address 192.168.1.100 and the DNS servers 8.8.4.4, 8.8.8.8 .
Open the network configuration file with nano:
/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
The server is using DHCP right after the install; the interfaces file will look like this:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens33:
dhcp4: yes
To use a static IP address 192.168.1.100, I will change the file so that it looks like this afterward:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens33:
dhcp4: no
dhcp6: no
addresses: [192.168.1.100/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
IMPORTANT: The indentation of the lines matters, add the lines as shown above.
Then restart your network to apply the changes:
sudo netplan generate
sudo netplan apply
Then edit /etc/hosts.
nano /etc/hosts
Make it look like this:
127.0.0.1 localhost
192.168.1.100 server1.example.com server1
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
Now, we will change the hostname of our machine as follows:
echo server1 > /etc/hostname
hostname server1
The first command sets the hostname "server1" in the /etc/hostname file. This file is read by the system at boot time. The second command sets the hostname in the current session so we don't have to restart the server to apply the hostname.
As an alternative to the two commands above you can use the hostnamectl command which is part of the systemd package.
hostnamectl set-hostname server1
Afterward, run:
hostname
hostname -f
The first command returns the short hostname while the second command shows the fully qualified domain name (fqdn):
root@server1:/home/administrator# hostname
server1
root@server1:/home/administrator# hostname -f
server1.example.com
root@server1:/home/administrator#
Congratulations! Now we have a basic Ubuntu 17.10 server setup that provides a solid basis for all kind of Ubuntu Server setups.
9. Virtual Machine image
This tutorial is available as ready to use virtual machine in OVA / OVF format for Howtoforge subscribers. The VM format is compatible with VMWare and Virtualbox and other tools that can import the ova or ovf format. You can find the download link in the right menu on the top. Click on the filename to start the download.
The login details of the VM are:
SSH Login
Username: administrator
Password: howtoforge
The administrator user has sudo permissions.
Please change the passwords after the first boot.
The VM is configured for the static IP 192.168.1.100, the IP can be changed in the file /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml as shown in the tutorial step 8.
10. Links
Ubuntu: http://www.ubuntu.com/