The Perfect Server - Ubuntu 12.10 (nginx, BIND, Dovecot, ISPConfig 3) - Page 4
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
- Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus)
- Ubuntu 15.10 (Wily Werewolf)
- Ubuntu 15.04 (Vivid Vervet)
- Ubuntu 14.10 (Utopic Unicorn)
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr)
On this page
12 Install Postfix, Dovecot, MySQL, phpMyAdmin, rkhunter, binutils
We can install Postfix, Dovecot, MySQL, rkhunter, and binutils with a single command:
apt-get install postfix postfix-mysql postfix-doc mysql-client mysql-server openssl getmail4 rkhunter binutils dovecot-imapd dovecot-pop3d dovecot-mysql dovecot-sieve sudo
You will be asked the following questions:
New password for the MySQL "root" user: <-- yourrootsqlpassword
Repeat password for the MySQL "root" user: <-- yourrootsqlpassword
General type of mail configuration: <-- Internet Site
System mail name: <-- server1.example.com
Next open the TLS/SSL and submission ports in Postfix:
vi /etc/postfix/master.cf
Uncomment the submission and smtps sections (leave -o milter_macro_daemon_name=ORIGINATING as we don't need it):
[...] submission inet n - - - - smtpd -o syslog_name=postfix/submission -o smtpd_tls_security_level=encrypt -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes -o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject # -o milter_macro_daemon_name=ORIGINATING smtps inet n - - - - smtpd -o syslog_name=postfix/smtps -o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=yes -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes -o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject # -o milter_macro_daemon_name=ORIGINATING [...] |
Restart Postfix afterwards:
/etc/init.d/postfix restart
We want MySQL to listen on all interfaces, not just localhost, therefore we edit /etc/mysql/my.cnf and comment out the line bind-address = 127.0.0.1:
vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
[...] # Instead of skip-networking the default is now to listen only on # localhost which is more compatible and is not less secure. #bind-address = 127.0.0.1 [...] |
Then we restart MySQL:
/etc/init.d/mysql restart
Now check that networking is enabled. Run
netstat -tap | grep mysql
The output should look like this:
root@server1:~# netstat -tap | grep mysql
tcp 0 0 *:mysql *:* LISTEN 21298/mysqld
root@server1:~#
13 Install Amavisd-new, SpamAssassin, And Clamav
To install amavisd-new, SpamAssassin, and ClamAV, we run
apt-get install amavisd-new spamassassin clamav clamav-daemon zoo unzip bzip2 arj nomarch lzop cabextract apt-listchanges libnet-ldap-perl libauthen-sasl-perl clamav-docs daemon libio-string-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl libnet-ident-perl zip libnet-dns-perl
The ISPConfig 3 setup uses amavisd which loads the SpamAssassin filter library internally, so we can stop SpamAssassin to free up some RAM:
/etc/init.d/spamassassin stop
update-rc.d -f spamassassin remove
14 Install Nginx, PHP5 (PHP-FPM), And Fcgiwrap
Nginx is available as a package for Ubuntu which we can install as follows:
apt-get install nginx
If Apache2 is already installed on the system, stop it now...
/etc/init.d/apache2 stop
... and remove Apache's system startup links:
update-rc.d -f apache2 remove
Start nginx afterwards:
/etc/init.d/nginx start
(If both Apache2 and nginx are installed, the ISPConfig 3 installer will ask you which one you want to use - answer nginx in this case. If only one of these both is installed, ISPConfig will do the necessary configuration automatically.)
We can make PHP5 work in nginx through PHP-FPM (PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is an alternative PHP FastCGI implementation with some additional features useful for sites of any size, especially busier sites) which we install as follows:
apt-get install php5-fpm
PHP-FPM is a daemon process (with the init script /etc/init.d/php5-fpm) that runs a FastCGI server on the socket /var/run/php5-fpm.sock.
To get MySQL support in PHP, we can install the php5-mysql package. It's a good idea to install some other PHP5 modules as well as you might need them for your applications. You can search for available PHP5 modules like this:
apt-cache search php5
Pick the ones you need and install them like this:
apt-get install php5-mysql php5-curl php5-gd php5-intl php-pear php5-imagick php5-imap php5-mcrypt php5-memcache php5-ming php5-ps php5-pspell php5-recode php5-snmp php5-sqlite php5-tidy php5-xmlrpc php5-xsl
Xcache is a free and open PHP opcode cacher for caching and optimizing PHP intermediate code. It's similar to other PHP opcode cachers, such as eAccelerator and APC. It is strongly recommended to have one of these installed to speed up your PHP page.
Xcache can be installed as follows:
apt-get install php5-xcache
Now reload PHP-FPM:
/etc/init.d/php5-fpm reload
To get CGI support in nginx, we install Fcgiwrap.
Fcgiwrap is a CGI wrapper that should work also for complex CGI scripts and can be used for shared hosting environments because it allows each vhost to use its own cgi-bin directory.
Install the fcgiwrap package:
apt-get install fcgiwrap
After the installation, the fcgiwrap daemon should already be started; its socket is /var/run/fcgiwrap.socket. If it is not running, you can use the /etc/init.d/fcgiwrap script to start it.
That's it! Now when you create an nginx vhost, ISPConfig will take care of the correct vhost configuration.
14.1 Additional PHP Versions
Starting with the upcoming ISPConfig 3.0.5, it will be possible to have multiple PHP versions on one server (selectable through ISPConfig) which can be run through FastCGI and PHP-FPM. The PHP version coming with Ubuntu 12.10 is 5.4.6, so I will show now how to build PHP 5.3.18 so that it can be used on the same server while Ubuntu's default PHP is installed. I will install PHP 5.3.18 in the /opt/php-5.3.18 directory.
Download and extract PHP 5.3.18:
mkdir /opt/php-5.3.18
mkdir /usr/local/src/php5-build
cd /usr/local/src/php5-build
wget http://de.php.net/get/php-5.3.18.tar.bz2/from/this/mirror -O php-5.3.18.tar.bz2
tar jxf php-5.3.18.tar.bz2
cd php-5.3.18/
Install the prerequisites for building PHP5:
apt-get build-dep php5
apt-get install libfcgi-dev libfcgi0ldbl libjpeg62-dbg libmcrypt-dev libssl-dev
Configure an build PHP 5.3.18 as follows (you can adjust the ./configure command to your needs, take a look at
./configure --help
to see all available options; if you use a different ./configure command, it is possible that additional libraries are required, or the build process will fail):
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/php-5.3.18 \
--with-pdo-pgsql \
--with-zlib-dir \
--with-freetype-dir \
--enable-fpm \
--enable-mbstring \
--with-libxml-dir=/usr \
--enable-soap \
--enable-calendar \
--with-curl --with-mcrypt \
--with-zlib \
--with-gd \
--with-pgsql \
--disable-rpath \
--enable-inline-optimization \
--with-bz2 \
--with-zlib \
--enable-sockets \
--enable-sysvsem \
--enable-sysvshm \
--enable-pcntl \
--enable-mbregex \
--with-mhash \
--enable-zip \
--with-pcre-regex \
--with-mysql \
--with-pdo-mysql \
--with-mysqli \
--with-jpeg-dir=/usr \
--with-png-dir=/usr \
--enable-gd-native-ttf \
--with-openssl \
--with-fpm-user=www-data \
--with-fpm-group=www-data \
--with-libdir=/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
make
make install
Copy php.ini and php-fpm.conf to the correct locations:
cp /usr/local/src/php5-build/php-5.3.18/php.ini-production /opt/php-5.3.18/lib/php.ini
cp /opt/php-5.3.18/etc/php-fpm.conf.default /opt/php-5.3.18/etc/php-fpm.conf
Open /opt/php-5.3.18/etc/php-fpm.conf and adjust the following settings - in the listen line you must use an unused port (e.g. 8999; port 9000 might be in use by Ubuntu's default PHP-FPM already), and you must add the line include=/opt/php-5.3.18/etc/pool.d/*.conf at the end:
vi /opt/php-5.3.18/etc/php-fpm.conf
[...] pid = run/php-fpm.pid [...] user = www-data group = www-data [...] listen = 127.0.0.1:8999 [...] include=/opt/php-5.3.18/etc/pool.d/*.conf |
Create the pool directory for PHP-FPM:
mkdir /opt/php-5.3.18/etc/pool.d
Next create an init script for PHP-FPM:
vi /etc/init.d/php-5.3.18-fpm
#! /bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: php-5.3.18-fpm
# Required-Start: $all
# Required-Stop: $all
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: starts php-5.3.18-fpm
# Description: starts the PHP FastCGI Process Manager daemon
### END INIT INFO
php_fpm_BIN=/opt/php-5.3.18/sbin/php-fpm
php_fpm_CONF=/opt/php-5.3.18/etc/php-fpm.conf
php_fpm_PID=/opt/php-5.3.18/var/run/php-fpm.pid
php_opts="--fpm-config $php_fpm_CONF"
wait_for_pid () {
try=0
while test $try -lt 35 ; do
case "$1" in
'created')
if [ -f "$2" ] ; then
try=''
break
fi
;;
'removed')
if [ ! -f "$2" ] ; then
try=''
break
fi
;;
esac
echo -n .
try=`expr $try + 1`
sleep 1
done
}
case "$1" in
start)
echo -n "Starting php-fpm "
$php_fpm_BIN $php_opts
if [ "$?" != 0 ] ; then
echo " failed"
exit 1
fi
wait_for_pid created $php_fpm_PID
if [ -n "$try" ] ; then
echo " failed"
exit 1
else
echo " done"
fi
;;
stop)
echo -n "Gracefully shutting down php-fpm "
if [ ! -r $php_fpm_PID ] ; then
echo "warning, no pid file found - php-fpm is not running ?"
exit 1
fi
kill -QUIT `cat $php_fpm_PID`
wait_for_pid removed $php_fpm_PID
if [ -n "$try" ] ; then
echo " failed. Use force-exit"
exit 1
else
echo " done"
echo " done"
fi
;;
force-quit)
echo -n "Terminating php-fpm "
if [ ! -r $php_fpm_PID ] ; then
echo "warning, no pid file found - php-fpm is not running ?"
exit 1
fi
kill -TERM `cat $php_fpm_PID`
wait_for_pid removed $php_fpm_PID
if [ -n "$try" ] ; then
echo " failed"
exit 1
else
echo " done"
fi
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
echo -n "Reload service php-fpm "
if [ ! -r $php_fpm_PID ] ; then
echo "warning, no pid file found - php-fpm is not running ?"
exit 1
fi
kill -USR2 `cat $php_fpm_PID`
echo " done"
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|force-quit|restart|reload}"
exit 1
;;
esac
|
Make the init script executable and create the system startup links:
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/php-5.3.18-fpm
insserv php-5.3.18-fpm
Finally start PHP-FPM:
/etc/init.d/php-5.3.18-fpm start
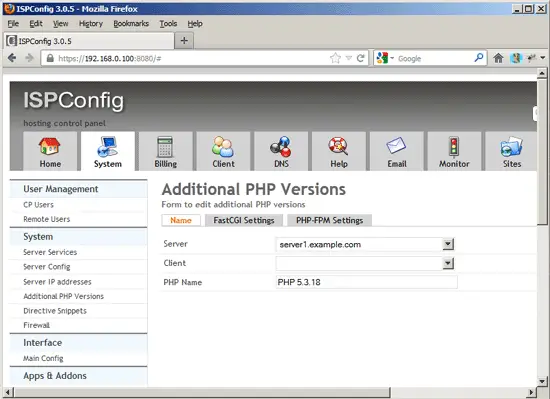
In ISPConfig 3.0.5, you can configure the new PHP version under System > Additional PHP Versions. On the Name tab, you just fill in a name for the PHP version (e.g. PHP 5.3.18) - this PHP version will be listed under this name in the website settings in ISPConfig:
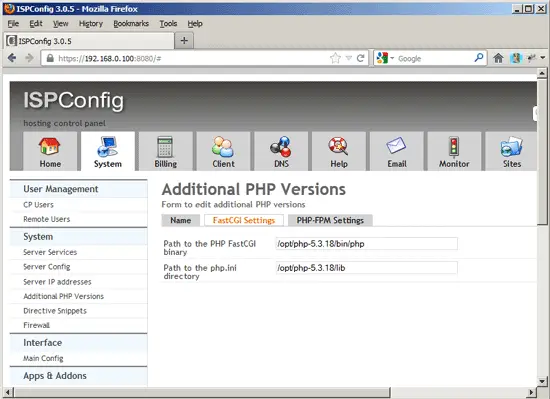
If you want to use this PHP version with FastCGI, go to the FastCGI Settings tab (thePHP-FPM Settings tab can be left empty) and fill out the fields as follows:
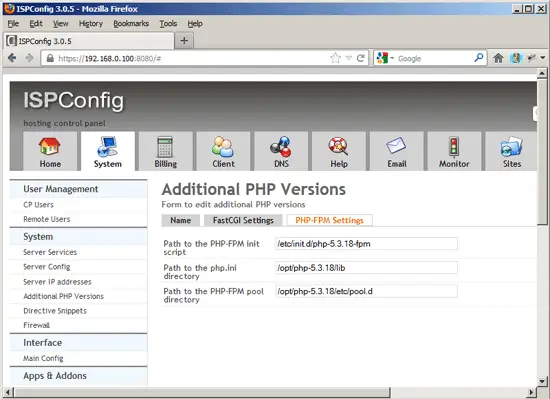
If you want to use this PHP version with PHP-FPM, go to the PHP-FPM Settings tab (the FastCGI Settings tab can be left empty) and fill out the fields as follows:
14.2 Install phpMyAdmin
Install phpMyAdmin as follows:
apt-get install phpmyadmin
You will see the following questions:
Web server to reconfigure automatically: <-- select none (because only apache2 and lighttpd are available as options)
Configure database for phpmyadmin with dbconfig-common? <-- No
You can now find phpMyAdmin in the /usr/share/phpmyadmin/ directory.
After you have installed ISPConfig 3, you can access phpMyAdmin as follows:
The ISPConfig apps vhost on port 8081 for nginx comes with a phpMyAdmin configuration, so you can use http://server1.example.com:8081/phpmyadmin or http://server1.example.com:8081/phpMyAdmin to access phpMyAdmin.
If you want to use a /phpmyadmin or /phpMyAdmin alias that you can use from your web sites, this is a bit more complicated than for Apache because nginx does not have global aliases (i.e., aliases that can be defined for all vhosts). Therefore you have to define these aliases for each vhost from which you want to access phpMyAdmin.
To do this, paste the following into the nginx Directives field on the Options tab of the web site in ISPConfig:
location /phpmyadmin {
root /usr/share/;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location ~ ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.php)$ {
try_files $uri =404;
root /usr/share/;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $request_filename;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_buffer_size 128k;
fastcgi_buffers 256 4k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}
location ~* ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.(jpg|jpeg|gif|css|png|js|ico|html|xml|txt))$ {
root /usr/share/;
}
}
location /phpMyAdmin {
rewrite ^/* /phpmyadmin last;
}
|
If you use https instead of http for your vhost, you should add the line fastcgi_param HTTPS on; to your phpMyAdmin configuration like this:
location /phpmyadmin {
root /usr/share/;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location ~ ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.php)$ {
try_files $uri =404;
root /usr/share/;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param HTTPS on; # <-- add this line
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $request_filename;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_buffer_size 128k;
fastcgi_buffers 256 4k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}
location ~* ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.(jpg|jpeg|gif|css|png|js|ico|html|xml|txt))$ {
root /usr/share/;
}
}
location /phpMyAdmin {
rewrite ^/* /phpmyadmin last;
}
|
If you use both http and https for your vhost, you need to add the following section to the http {} section in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (before any include lines) which determines if the visitor uses http or https and sets the $fastcgi_https variable (which we will use in our phpMyAdmin configuration) accordingly:
vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
[...]
http {
[...]
## Detect when HTTPS is used
map $scheme $fastcgi_https {
default off;
https on;
}
[...]
}
[...]
|
Don't forget to reload nginx afterwards:
/etc/init.d/nginx reload
Then go to the nginx Directives field again, and instead of fastcgi_param HTTPS on; you add the line fastcgi_param HTTPS $fastcgi_https; so that you can use phpMyAdmin for both http and https requests:
location /phpmyadmin {
root /usr/share/;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location ~ ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.php)$ {
try_files $uri =404;
root /usr/share/;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param HTTPS $fastcgi_https; # <-- add this line
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $request_filename;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_buffer_size 128k;
fastcgi_buffers 256 4k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
}
location ~* ^/phpmyadmin/(.+\.(jpg|jpeg|gif|css|png|js|ico|html|xml|txt))$ {
root /usr/share/;
}
}
location /phpMyAdmin {
rewrite ^/* /phpmyadmin last;
}
|