The Perfect Server - CentOS 4.7 Server - Page 3
2 Adjust /etc/hosts
Next we edit /etc/hosts. Make it look like this:
vi /etc/hosts
# Do not remove the following line, or various programs # that require network functionality will fail. 127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost 192.168.0.100 server1.example.com server1 |
3 Configure Additional IP Addresses
(This section is totally optional. It just shows how to add additional IP addresses to your network interface eth0 if you need more than one IP address. If you're fine with one IP address, you can skip this section.)
Let's assume our network interface is eth0. Then there is a file /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 which looks like this:
cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0 BOOTPROTO=static BROADCAST=192.168.0.255 HWADDR=00:0C:29:DC:03:5B IPADDR=192.168.0.100 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 NETWORK=192.168.0.0 ONBOOT=yes TYPE=Ethernet |
Now we want to create the virtual interface eth0:0 with the IP address 192.168.0.101. All we have to do is to create the file /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:0 which looks like this (we can leave out the HWADDR line as it is the same physical network card):
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:0
DEVICE=eth0:0 BOOTPROTO=static BROADCAST=192.168.0.255 IPADDR=192.168.0.101 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 NETWORK=192.168.0.0 ONBOOT=yes TYPE=Ethernet |
Afterwards we have to restart the network:
/etc/init.d/network restart
You might also want to adjust /etc/hosts after you have added new IP addresses, although this is not necessary.
Now run
ifconfig
You should now see your new IP address in the output:
[root@server1 ~]# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:DC:03:5B
inet addr:192.168.0.100 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fedc:35b/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:347 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:401 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:29234 (28.5 KiB) TX bytes:64323 (62.8 KiB)
Interrupt:177 Base address:0x1400
eth0:0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:DC:03:5B
inet addr:192.168.0.101 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
Interrupt:177 Base address:0x1400
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:560 (560.0 b) TX bytes:560 (560.0 b)
[root@server1 ~]#
4 Configure The Firewall
(You can skip this chapter if you have already disabled the firewall during the basic system installation.)
I want to install ISPConfig at the end of this tutorial which comes with its own firewall. That's why I disable the default CentOS firewall now. Of course, you are free to leave it on and configure it to your needs (but then you shouldn't use any other firewall later on as it will most probably interfere with the CentOS firewall).
Run
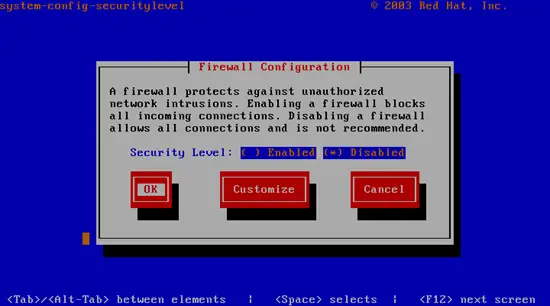
system-config-securitylevel
Select Disabled and press OK.
To check that the firewall has really been disabled, you can run
iptables -L
afterwards. The output should look like this:
[root@server1 ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
[root@server1 ~]#
5 Disable SELinux
(You can skip this chapter if you have already disabled SELinux during the basic system installation.)
SELinux is a security extension of CentOS that should provide extended security. In my opinion you don't need it to configure a secure system, and it usually causes more problems than advantages (think of it after you have done a week of trouble-shooting because some service wasn't working as expected, and then you find out that everything was ok, only SELinux was causing the problem). Therefore I disable it (this is a must if you want to install ISPConfig later on).
Edit /etc/selinux/config and set SELINUX=disabled:
vi /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - SELinux is fully disabled. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= type of policy in use. Possible values are: # targeted - Only targeted network daemons are protected. # strict - Full SELinux protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted |
Afterwards we must reboot the system:
reboot
6 Install Some Software
First we import the GPG keys for software packages:
rpm --import /usr/share/rhn/RPM-GPG-KEY*
Then we update our existing packages on the system:
yum update
Now we install some software packages that are needed later on:
yum install fetchmail wget bzip2 unzip zip nmap openssl lynx fileutils gcc gcc-c++