Low Cost SAN
Version No.: 1
Date: 25/04/2009
Revision History
|
Version No. |
Date |
Prepared by |
Significant Changes
|
|
1. |
25/04/2009 |
Krishna Kumar |
|
1 Objective
The objective of this document is to provide making of Low Cost SAN using FOSS tools. We have tried to set up a SAN which has following features:
• Low cost and easily affordable
• Ensured Scalability
• High Reliability
• Easily Manageable
• High Performance
• Ensured Security
• High availability
2 Definitions, Acronyms and Abbreviations
This section provides a list of all definitions, acronyms and terms required to properly interpret this document as well as to understand SAN terms and terminology.
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
AoE |
ATA over Ethernet, a open storage protocol |
|
ATA |
Advance Technology Attachment |
|
Targets |
End Point of communication ( normally refers to server side ) |
|
Initiators |
A host that requests access to storage device ( client end ) |
|
RHCS |
Red Hat Clustering Suite |
|
Heartbeat |
A signal periodically sent out by a hardware component in order to inform another component that it is working normally |
|
ISCSI |
Internet Small Computer System Interface |
|
SATA |
Serial ATA, a newer version of ATA interface |
|
GFS |
Global File System, a cluster aware filesystem for Linux |
|
SAN |
Storage Area Networking |
|
LVM |
Logical Volume Manager |
|
RAID |
Redundant Array of Inexpensive disks |
|
DRBD |
Distributed Replicated Block Device |
|
NBD |
Network Block Device |
|
ENBD |
Enhanced Network Block Device |
|
GNBD |
Global Network Block Device |
|
HA |
High Availability, a clustering solution for Linux which provides reliability, availability and serviceability |
|
FOSS |
Free Open Source Software |
|
DFS |
Distributed File System for Windows |
|
LVS |
Linux Virtual Server |
3 References
This section tells all the references and urls used to prepare this document.
|
SN |
URLS |
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
7 |
http://www.redhat.com/docs/manuals/enterprise/RHEL-5-manual/Cluster Administration/ |
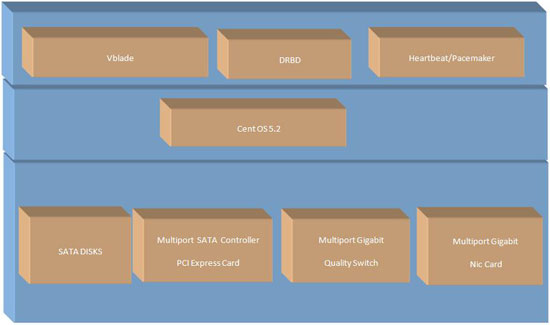
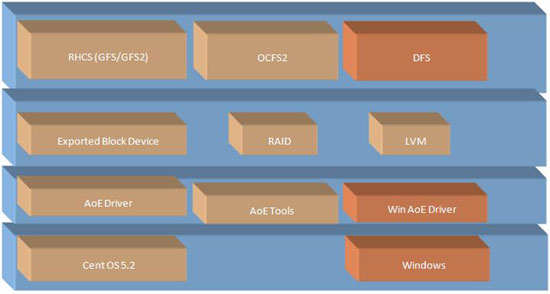
4 Layered Architecture of SAN
4.1 Brief Description and Layered Architecture
This is the investigation document which touches each aspect of Low Cost SAN making right from hardware, OS and Softwares. The layered architecture of our SAN is shown in following diagrams.
Server Architecture:
In this diagram, three boxes in red color depicts the solution for windows and DFS is Microsoft distributed file system for windows server.
4.2 SAN Features and available options
Having above architecture in mind we have tried to achieve all the features of low cost SAN in terms of speed, reliability, security, scalability and availability. Following table gives us an overview against the features and corresponding available options. All the softwares which we have used to achieve SAN features are available on FOSS:
|
SAN Features |
Available Options On FOSS |
|
Low Cost & Simplicity |
AoE Protocol and corresponding softwares are available on FOSS. |
|
Security |
No routability provides inherent security |
|
Speed of ATA disk |
1) Typical 7200-rpm SATA disk drive: 105 MB/s (sustained throughput) 2) Typical 7200-rpm PATA disk drive: 72 MB/s (sustained throughput) |
|
Speed of Ethernet |
1) Gigabit Ethernet (1000baseT): 125 MB/s 2)10-Gigabit Ethernet: 1,250 MB/s |
|
Data Packets |
AoE simply delivers 48 bytes and data ( only extra 48 bytes ) |
|
Full Virtualization Support |
Fully Compatible with hypervisors such as Xen, VMware, Microsoft Virtual PC to virtualize computers that are used as servers |
|
Virtualized disk |
We can combine multiple 22 TB disk into a single RAID disk. |
|
Device access through Internet |
Remote access to an AoE device through the Internet can be achieved through tunneling, we can use software to convert local packets into routable packets at both ends of a link. |
|
Easy management of AoE Servers and nodes |
AoE Tools like CEC provides a terminal interface for AoE device. All the clusters and nodes can also be managed by RHCS cluster manager |
|
Connecting Multiple Disks |
24 port SATA controller PCI express card having capacity >=2TB per disk |
|
Theoretical limits of AoE devices |
AoE has a limitation of 65535 major x 255 minor addresses, so you're |
|
Diskless booting Support |
Diskless booting (PXE booting) is available in AoE for windows as well as for Linux |
|
Fencing |
RHCS fencing daemon provide fencing against corresponding failover domains |
|
Network Load balancing |
RHCS lvs and piranha provides network load balancing |
|
Proper Synchronization among all the nodes |
RHCS GFS/GFS2 uses DLM to provide this feature |
|
Block Level Redundancy |
DRBD is a tool available on Foss to provide high availability in SAN in terms of block level. If DRBD is used with heartbeat and rhcs, it's a very good solution for HA in storage networking. |
|
Directory level Redundancy |
NFS fail over and auto mounting is easily handled by RHCS. |
|
Resource Management and ensured communication among other nodes |
CMAN of RHCS and Heartbeat are good solutions against this. |
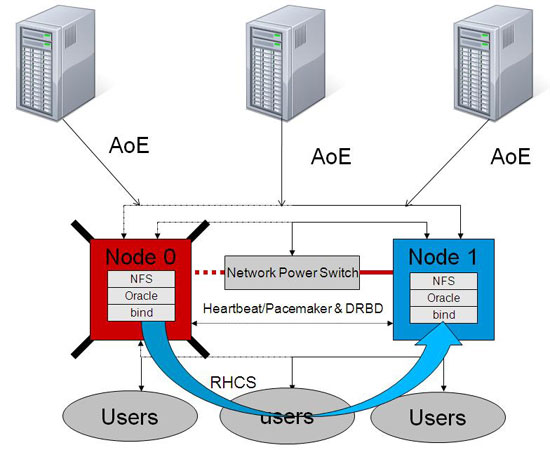
4.3 Overview of SAN with HA/Failover
The main challenge of a reliable SAN is high availability and zero down time. Thanks to the tools like LVS, RHCS, HEARTBEAT and DRBD by which we can easily restart our applications and can do migration of services. Following diagram shows the failover a node and relocation of services, so that users get their applications running even if corresponding node crashed.