Install Odoo on CentOS with Nginx
Odoo is an open-source ERP and CRM system used to manage the company's basic needs including materials and warehouse management, human resources, finance, accounting, sales, inventory and many other enterprise features. It is built using Python and uses PostgreSQL as its database. The latest Odoo 14 version has handy features, including a new website builder, new business intelligence tools, new and improved inventory and MRP menus, and more.
This tutorial will show you how to install Odoo 14 with Nginx on CentOS 8.
Prerequisites
- A server running CentOS 8.
- A valid domain name pointed with your server IP.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Getting Started
Before starting, you will need to install Python, wkhtmltopdf and other required dependencies to your system. Run the following command to install all of them:
dnf install python3 redhat-rpm-config libxslt-devel bzip2-devel openldap-devel python3-devel git gcc libjpeg-devel freetype-devel curl unzip -y
dnf install https://github.com/wkhtmltopdf/wkhtmltopdf/releases/download/0.12.5/wkhtmltox-0.12.5-1.centos8.x86_64.rpm
Once all the dependencies are installed, you can proceed to the next step.
Install and Configure PostgreSQL
Odoo uses PostgreSQL as a database backend. So you will need to install it to your system. Run the following command to install the PostgreSQL:
dnf install postgresql postgresql-server postgresql-contrib -y
Once the PostgreSQL is installed, initialized the database with the following command:
postgresql-setup initdb
You should see the following output:
WARNING: using obsoleted argument syntax, try --help WARNING: arguments transformed to: postgresql-setup --initdb --unit postgresql * Initializing database in '/var/lib/pgsql/data' * Initialized, logs are in /var/lib/pgsql/initdb_postgresql.log
Next, start the PostgreSQL service and enable it to start at system reboot:
systemctl start postgresql
systemctl enable postgresql
Next, create a new user for odoo with the following command:
su - postgres -c "createuser -s odoo14"
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Odoo 14
It is recommended to install and run Odoo as a standalone user. You can create a new user for Odoo with the following command:
useradd -m -U -r -d /opt/odoo14 -s /bin/bash odoo14
Note: Odoo user and PostgreSQL user must be same.
Next, switch the user to Odoo 14 and download the latest version of Odoo 14 with the following command:
su - odoo14
git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 14.0 /opt/odoo14/odoo14
Once the download is completed, change the directory to odoo14 and create a new python virtual environment with the following command:
cd /opt/odoo14
python3 -m venv odooenv
Next, activate the virtual environment with the following command:
source odooenv/bin/activate
Next, install other Python dependencies with the following command:
(odooenv) [odoo14@centos8 ~]$ pip3 install wheel
(odooenv) [odoo14@centos8 ~]$ pip3 install -r odoo14/requirements.txt
Next, deactivate from the virtual environment and exit from the Odoo user with the following command:
(odooenv) [odoo14@centos8 ~]$ deactivate
exit
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Configure Odoo 14
Next, you will need to create a directory to store Odoo 14 addons. You can create it with the following command:
mkdir /opt/odoo14/odoo14-custom-addons
Next, set proper ownership to the addons directory:
chown -R odoo14:odoo14 /opt/odoo14/odoo14-custom-addons
Next, create a log directory and file for Odoo 14 and set proper ownership:
mkdir /var/log/odoo14
touch /var/log/odoo14/odoo14.log
chown -R odoo14: /var/log/odoo14/
Next, create a Odoo 14 configuration file:
nano /etc/odoo14.conf
Add the following lines:
[options] ; This is the password that allows database operations: admin_passwd = your_master_password db_host = False db_port = False db_user = odoo14 db_password = False xmlrpc_port = 8069 ; longpolling_port = 8072 logfile = /var/log/odoo14/odoo14.log logrotate = True addons_path = /opt/odoo14/odoo14/addons,/opt/odoo14/odoo14-custom-addons
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Create a Systemd Unit File for Odoo 14
Next, you will need to create a systemd service file to manage the Odoo 14 service. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo14.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit] Description=Odoo14 Requires=postgresql.service After=network.target postgresql.service [Service] Type=simple SyslogIdentifier=odoo14 PermissionsStartOnly=true User=odoo14 Group=odoo14 ExecStart=/opt/odoo14/odooenv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo14/odoo14/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo14.conf StandardOutput=journal+console [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file then reload the systemd daemon with the following command:
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start the Odoo 14 service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start odoo14
systemctl enable odoo14
You can now check the status of the Odoo 14 service with the following command:
systemctl status odoo14
You should get the following output:
? odoo14.service - Odoo14
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/odoo14.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2021-05-01 06:29:56 EDT; 5s ago
Main PID: 26505 (python3)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 25014)
Memory: 91.8M
CGroup: /system.slice/odoo14.service
??26505 /opt/odoo14/odooenv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo14/odoo14/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo14.conf
May 01 06:29:56 centos8 systemd[1]: Started Odoo14.
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Install and Configure Nginx for Odoo 14
At this point, Odoo 14 is installed and running. Now, it is recommended to configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for odoo.
First, install the Nginx package with the following command:
dnf install nginx -y
Once the Nginx is installed, create a new Nginx virtual host configuration file with the following command:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/odoo14.conf
Add the following lines:
upstream odoo {
server 127.0.0.1:8069;
}
upstream odoochat {
server 127.0.0.1:8072;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name odoo.example.com;
proxy_read_timeout 720s;
proxy_connect_timeout 720s;
proxy_send_timeout 720s;
# Proxy headers
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# log files
access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.error.log;
# Handle longpoll requests
location /longpolling {
proxy_pass http://odoochat;
}
# Handle / requests
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_pass http://odoo;
}
# Cache static files
location ~* /web/static/ {
proxy_cache_valid 200 90m;
proxy_buffering on;
expires 864000;
proxy_pass http://odoo;
}
# Gzip
gzip_types text/css text/less text/plain text/xml application/xml application/json application/javascript;
gzip on;
}
Save and close the file then verify the Nginx for any syntax error with the following command:
nginx -t
You should get the following output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Next, start the Nginx service and enable it to start at system reboot:
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
You can also verify the Nginx with the following command:
systemctl status nginx
You should get the following output:
? nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2021-05-01 06:31:19 EDT; 3s ago
Process: 26627 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 26625 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 26623 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 26628 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 25014)
Memory: 5.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??26628 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
??26629 nginx: worker process
??26630 nginx: worker process
May 01 06:31:19 centos8 systemd[1]: Starting The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server...
May 01 06:31:19 centos8 nginx[26625]: nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
May 01 06:31:19 centos8 nginx[26625]: nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
May 01 06:31:19 centos8 systemd[1]: Started The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server.
Next, edit the Odoo 14 configuration file and enable the proxy mode:
nano /etc/odoo14.conf
Add the following line:
proxy_mode = True
Save and close the file then restart the Odoo 14 service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart odoo14
Configure Firewall
Next, you will need to allow port 80 through firewall. You can allow it with the following command:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
Next, reload the firewall to apply the changes:
firewall-cmd --reload
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Access Odoo 14 Dashboard
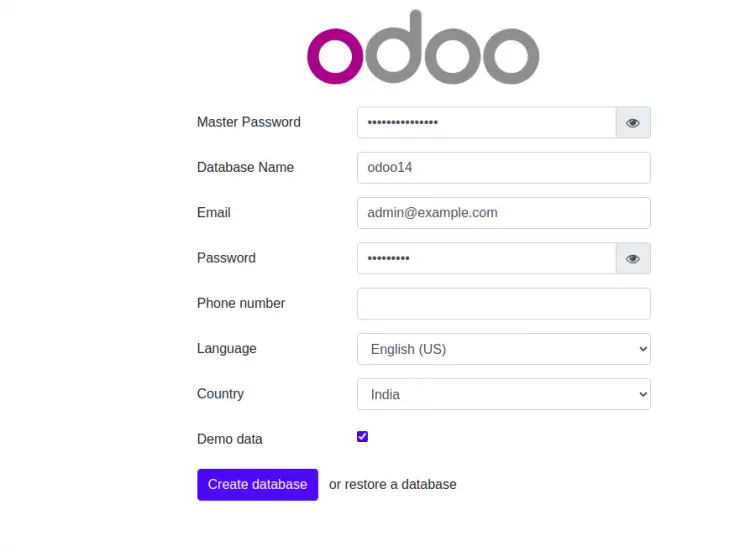
Now, open your web browser and access the Odoo 14 web interface using the URL http://odoo.example.com. You will be redirected to the following page:
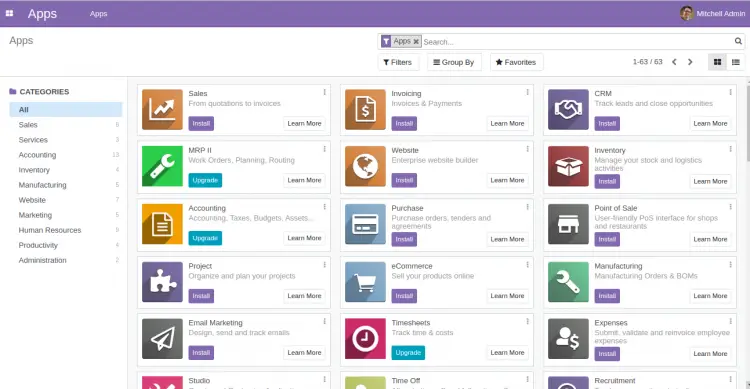
Provide your Odoo master password, database and click on the Create database button. You should see the Odoo 14 dashboard in the following page:
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed Odoo 14 ERP with Nginx on CentOS 8. You can now implement Odoo in your production environment and increase the productivity.