How to Install Sentry with Docker on Ubuntu 22.04
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
On this page
Sentry is a free and open-source error-tracking platform that monitors and fixes crashes in real-time. It allows software developers to see what matters, solve quicker, and learn continuously about their applications. This platform provides real-time insight into production deployments with info to reproduce and fix crashes. Sentry supports all major languages and frameworks and integrates with your favorite apps and services.
This tutorial will show you how to install Sentry Error Tracking System with Docker on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A valid domain name is pointed to your server IP.
- A root password is configured on your server.
Install Required Dependencies
Before starting, updating your packages to the latest version is recommended. You can update them with the following command:
apt update -y
apt upgrade -y
Once your system is updated, install all required packages with the following command:
apt-get install curl git build-essential apt-transport-https ca-certificates software-properties-common -y
After installing all the dependencies, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Docker and Docker Compose
By default, the latest version of Docker and Docker Compose package is not available in the Ubuntu 22.04 default repository. So you will need to add Docker official repository to APT.
First, download and add the Docker GPG key with the following command.
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
Next, add the Docker repository with the following command.
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Once the repository is added, update the repository cache with the following command.
apt update -y
Next, install both Docker and Docker Compose with the following command.
apt install docker docker-compose -y
Once both packages are installed, start the Docker service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start docker
systemctl enable docker
You can now verify the status of Docker with the following command:
systemctl status docker
You should get the following output:
? docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2023-01-10 04:37:27 UTC; 5s ago
TriggeredBy: ? docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 45847 (dockerd)
Tasks: 8
Memory: 29.1M
CPU: 220ms
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
??45847 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Jan 10 04:37:26 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:26.903435377Z" level=info msg="scheme \"unix\" not registered, fallback to defau>
Jan 10 04:37:26 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:26.903453803Z" level=info msg="ccResolverWrapper: sending update to cc: {[{unix:>
Jan 10 04:37:26 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:26.903464761Z" level=info msg="ClientConn switching balancer to \"pick_first\"" >
Jan 10 04:37:26 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:26.916581613Z" level=info msg="Loading containers: start."
Jan 10 04:37:26 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:26.997807510Z" level=info msg="Default bridge (docker0) is assigned with an IP a>
Jan 10 04:37:27 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:27.060381720Z" level=info msg="Loading containers: done."
Jan 10 04:37:27 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:27.074467014Z" level=info msg="Docker daemon" commit=20.10.12-0ubuntu4 graphdriv>
Jan 10 04:37:27 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:27.074649813Z" level=info msg="Daemon has completed initialization"
Jan 10 04:37:27 vultr systemd[1]: Started Docker Application Container Engine.
Jan 10 04:37:27 vultr dockerd[45847]: time="2023-01-10T04:37:27.092699576Z" level=info msg="API listen on /run/docker.sock"
To check the Docker version, run the following command:
docker --version
You should see the following output:
Docker version 20.10.12, build 20.10.12-0ubuntu4
You can also check the Docker compose version using the following command:
docker-compose --version
You should see the following output:
docker-compose version 1.29.2, build unknown
Install Sentry
First, download the latest version of Sentry from the Git repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/getsentry/onpremise
Once the download is complete, change the directory to the downloaded directory and run the Sentry installation script to start the installation.
cd onpremise
bash install.sh
During the installation, you will be asked to create an admin account as shown below:
Here's the info we may collect: - OS username - IP address - install log - runtime errors - performance data Thirty (30) day retention. No marketing. Privacy policy at sentry.io/privacy. Would you like to create a user account now? [Y/n]: y Email: Email: [email protected] Password: Repeat for confirmation: Added to organization: sentry User created: [email protected] Creating missing DSNs Correcting Group.num_comments counter ----------------------------------------------------------------- You're all done! Run the following command to get Sentry running: docker-compose up -d -----------------------------------------------------------------
Next, verify all the downloaded images using the following command.
docker images
You should see the following output.
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE sentry-cleanup-self-hosted-local latest 04fa0fce18f0 4 minutes ago 908MB symbolicator-cleanup-self-hosted-local latest 6837f5f48e6c 5 minutes ago 180MB snuba-cleanup-self-hosted-local latest 242b7b248e1c 5 minutes ago 486MB sentry-self-hosted-local latest 101b00356aa6 5 minutes ago 907MB sentry-self-hosted-jq-local latest 83c66fd3f78f 6 minutes ago 82.5MB getsentry/sentry nightly cf0f404d102e About an hour ago 907MB getsentry/snuba nightly fc6c2d286bf8 8 hours ago 484MB getsentry/relay nightly 43cd2ba5497c 5 days ago 242MB busybox latest 66ba00ad3de8 6 days ago 4.87MB tianon/exim4 latest 12842ac621c1 2 weeks ago 158MB debian bullseye-slim dd94cb611937 2 weeks ago 80.5MB getsentry/sentry-cli latest a585383ff864 2 weeks ago 26.3MB getsentry/symbolicator nightly 80d9b41cd195 3 weeks ago 178MB nginx 1.22.0-alpine 5685937b6bc1 3 months ago 23.5MB postgres 9.6 027ccf656dc1 11 months ago 200MB confluentinc/cp-kafka 5.5.0 efc480c1c89c 15 months ago 598MB confluentinc/cp-zookeeper 5.5.0 ddeb961d8e80 15 months ago 598MB redis 6.2.4-alpine 500703a12fa4 18 months ago 32.3MB memcached 1.6.9-alpine a0132b3398e4 18 months ago 8.09MB curlimages/curl 7.77.0 e062233fb4a9 19 months ago 8.26MB maxmindinc/geoipupdate v4.7.1 8ec32cc727c7 21 months ago 10.6MB clickhouse-self-hosted-local latest abe55fc6544d 2 years ago 497MB yandex/clickhouse-server 20.3.9.70 abe55fc6544d 2 years ago 497MB
Launch Sentry Container
At this point, Sentry is installed. You can now start the Sentry container using the following command:
docker-compose up -d
This will start all the containers for Sentry as shown below:
Starting sentry_onpremise_memcached_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_redis_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_symbolicator_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_symbolicator-cleanup_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_zookeeper_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_clickhouse_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_smtp_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_postgres_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_kafka_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_snuba-consumer_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_snuba-outcomes-consumer_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_snuba-api_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_snuba-sessions-consumer_1 ... done Starting sentry_onpremise_snuba-replacer_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_snuba-cleanup_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_relay_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_web_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_post-process-forwarder_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_cron_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_sentry-cleanup_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_worker_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_ingest-consumer_1 ... done Creating sentry_onpremise_nginx_1 ... done
You can verify the status of all containers using the following command.
docker-compose ps
You should see the following output.
Name Command State Ports ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- sentry-self-hosted_clickhouse_1 /entrypoint.sh Up (healthy) 8123/tcp, 9000/tcp, 9009/tcp sentry-self-hosted_cron_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_geoipupdate_1 /usr/bin/geoipupdate -d /s ... Exit 1 sentry-self-hosted_ingest-consumer_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_kafka_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up (healthy) 9092/tcp sentry-self-hosted_memcached_1 docker-entrypoint.sh memcached Up (healthy) 11211/tcp sentry-self-hosted_nginx_1 /docker-entrypoint.sh ngin ... Up 0.0.0.0:9000->80/tcp,:::9000->80/tcp sentry-self-hosted_post-process-forwarder-errors_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_post-process-forwarder- /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp transactions_1 sentry-self-hosted_postgres_1 /opt/sentry/postgres-entry ... Up (healthy) 5432/tcp sentry-self-hosted_redis_1 docker-entrypoint.sh redis ... Up (healthy) 6379/tcp sentry-self-hosted_relay_1 /bin/bash /docker-entrypoi ... Up 3000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_sentry-cleanup_1 /entrypoint.sh 0 0 * * * g ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_smtp_1 docker-entrypoint.sh exim ... Up 25/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-api_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh api Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-cleanup_1 /entrypoint.sh */5 * * * * ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-consumer_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh con ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-outcomes-consumer_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh con ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-replacer_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh rep ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-sessions-consumer_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh con ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-subscription-consumer-events_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh sub ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-subscription-consumer- ./docker_entrypoint.sh sub ... Up 1218/tcp transactions_1 sentry-self-hosted_snuba-transactions-cleanup_1 /entrypoint.sh */5 * * * * ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_snuba-transactions-consumer_1 ./docker_entrypoint.sh con ... Up 1218/tcp sentry-self-hosted_subscription-consumer-events_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_subscription-consumer-transactions_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_symbolicator-cleanup_1 /entrypoint.sh 55 23 * * * ... Up 3021/tcp sentry-self-hosted_symbolicator_1 /bin/bash /docker-entrypoi ... Up 3021/tcp sentry-self-hosted_web_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up (healthy) 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_worker_1 /etc/sentry/entrypoint.sh ... Up 9000/tcp sentry-self-hosted_zookeeper_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up (healthy) 2181/tcp, 2888/tcp, 3888/tcp
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Access Sentry Web UI
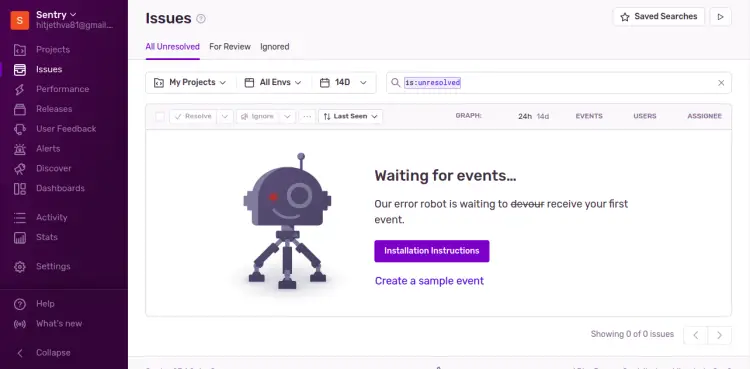
At this point, Sentry is started and listening on port 9000. Now, open your web browser and type the URL http://your-server-ip:9000 to access the Sentry dashboard. You will be redirected to the Sentry login page as shown below:
Provide your admin username, password and click on the Login button. You should see the following page:
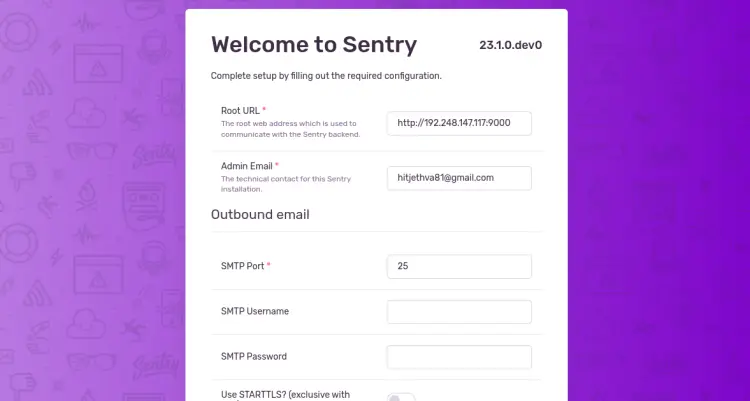
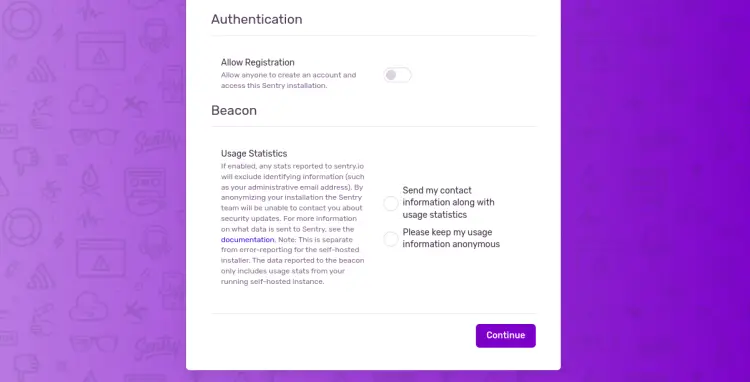
Provide your Sentry URL, email address, and SMTP details, and click on the Continue button. You should see the Sentry default dashboard on the following page:
Conclusion
In this guide, we explained how to install Sentry on Ubuntu 22.04. Now, you can implement Sentry in your organization to track your application across the entire stack in real-time. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.