How to Install Magento eCommerce Suite on Debian 12 with Nginx and Elasticsearch
On this page
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 - Configure Firewall
- Step 2 - Install PHP and its extensions
- Step 3 - Install Composer
- Step 4 - Install MariaDB
- Step 5 - Configure MariaDB
- Step 6 - Install Nginx
- Step 7 - Install SSL
- Step 8 - Install Elasticsearch
- Step 9 - Install Redis server
- Step 10 - Download Magento
- Step 11 - Install Magento
- Step 12 - Configure PHP-FPM
- Step 13 - Configure Nginx
- Step 14 - Disable Two factor Authentication
- Step 15 - Access the Administration Portal
- Step 16 - Enable and Configure Two-factor Authentication
- Conclusion
Magento is an open-source e-commerce platform written in PHP. It was acquired by Adobe in 2018. It is also offered as a commercial and cloud-based product. You can use Magento to create high-capacity professional shopping websites. It offers both - a single-store and a multiple-store mode. It comes with lots of modules to extend its functionality.
In this tutorial, we will install the Magento open-source community edition. It offers all the functionality you need to set up a professional online store. We will also install Elasticsearch for searching through the product catalog, Redis for the session and file cache, and serve it using the Nginx server.
Prerequisites
-
A server running Debian 12 with a minimum of 2GB RAM. You may need more RAM depending on your requirements.
-
A non-root user with sudo privileges.
-
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the server,
magento.example.com -
Make sure everything is updated.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt upgrade
-
Few packages that your system needs.
$ sudo apt install wget curl nano ufw software-properties-common dirmngr apt-transport-https gnupg2 ca-certificates lsb-release debian-archive-keyring unzip -y
Some of these packages may already be installed on your system.
Step 1 - Configure Firewall
The first step is to configure the firewall. Debian comes with ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall) by default.
Check if the firewall is running.
$ sudo ufw status
You should see something like the following.
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Allow HTTP and HTTPS ports as well.
$ sudo ufw allow http $ sudo ufw allow https
Check the status of the firewall again.
$ sudo ufw status
You should see a similar output.
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443 ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 2 - Install PHP and its extensions
Debian 12 ships with PHP 8.2 version by default. You can install it and the extensions required by Magento by running the following command.
$ sudo apt install php-fpm php-cli php-mysql php-mbstring php-xml php-gd php-bcmath php-zip php-curl php-tidy php-intl php-soap php-xsl libsodium-dev libsodium23 libssl-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev
To always stay on the latest version of PHP or if you want to install multiple versions of PHP, add Ondrej's PHP repository.
First, import Sury's repo PHP GPG key.
$ sudo curl -sSLo /usr/share/keyrings/deb.sury.org-php.gpg https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg
Add Ondrej Sury's PHP repository.
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/deb.sury.org-php.gpg] https://packages.sury.org/php/ $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list'
Update the system repository list.
$ sudo apt update
Next, install PHP and its extensions required by Magento.
$ sudo apt install php8.2-fpm php8.2-mysql php8.2-bcmath php8.2-xml php8.2-zip php8.2-curl php8.2-mbstring php8.2-gd php8.2-tidy php8.2-intl php8.2-cli php8.2-soap php8.2-xsl libsodium-dev libsodium23 libssl-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev
Verify the installation.
$ php --version
PHP 8.2.8 (cli) (built: Jul 16 2023 11:00:43) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v4.2.8, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.2.8, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
Step 3 - Install Composer
Composer is a dependency management tool for PHP and is required for Magento installation.
Run the following commands to download the Composer binary. Magento requires Composer 2.2 LTS so we have modified the command accordingly.
$ php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
$ php composer-setup.php --2.2
$ php -r "unlink('composer-setup.php');"
Install Composer by moving the binary to the /usr/local/bin directory.
$ sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
Verify the installation by checking its version.
$ composer --version Composer version 2.2.21 2023-02-15 13:07:40
Step 4 - Install MariaDB
Debian 12 does not ship with MySQL by default and they haven't released an official package for it yet. Therefore, we will be using MariaDB for it. MariaDB doesn't have an official package for Debian 12 as well but Debian ships with it. Therefore, install it using the following command.
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server
Check the version of MySQL.
$ mysql --version mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.11.3-MariaDB, for debian-linux-gnu (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper
Now, this version of MariaDB is not supported by Magento and the official MariaDB package for Debian 12 is not available at the moment. So we will continue with the installation and use a workaround later to bypass the restriction.
Run the MariaDB secure install script.
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
You will be asked for the root password. Press Enter because we haven't set any password for it.
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
Next, you will be asked if you want to switch to the Unix socket authentication method. The unix_socket plugin allows you to use your operating system credentials to connect to the MariaDB server. Since you already have a protected root account, enter n to proceed.
OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation. You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] n
Next, you will be asked if you want to change your root password. On Debian 12, the root password is tied closely to automated system maintenance, so it should be left alone. Type n to proceed further.
... skipping. You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Change the root password? [Y/n] n
Next, you will be asked certain questions to improve MariaDB security. Type Y to remove anonymous users, disallow remote root logins, remove the test database, and reload the privilege tables.
... skipping. By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y ... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y ... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB!
You can enter the MariaDB shell by typing sudo mysql or sudo mariadb on the command line.
Step 5 - Configure MariaDB
Log in to the MariaDB shell.
$ sudo mysql
Create a database for Magento.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE magento;
Create an SQL user account.
mysql> CREATE USER 'magentouser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Your_password2';
Grant all privileges on the database to the user.
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON magento.* TO 'magentouser'@'localhost';
Since we are not modifying the root user, you should create another SQL user for performing administrative tasks which employ password authentication. Choose a strong password for this one.
MariaDB> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'navjot'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Yourpassword32!' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Flush user privileges.
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Exit the shell.
mysql> exit
Step 6 - Install Nginx
Debian 12 ships with an older version of Nginx. To install the latest version, you need to download the official Nginx repository.
Import Nginx's signing key.
$ curl https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor \
| sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
Add the repository for Nginx's stable version.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] \
http://nginx.org/packages/debian `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Update the system repositories.
$ sudo apt update
Install Nginx.
$ sudo apt install nginx
Verify the installation. On Debian systems, the following command will only work with sudo.
$ sudo nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.24.0
Start the Nginx server.
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
Check the service status.
? nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-08-02 06:45:52 UTC; 14s ago
Docs: https://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 18326 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 18327 (nginx)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 2315)
Memory: 1.8M
CPU: 11ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??18327 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
??18328 "nginx: worker process"
Step 7 - Install SSL
We need to install Certbot to generate the SSL certificate. You can either install Certbot using Debian's repository or grab the latest version using the Snapd tool. We will be using the Snapd version.
Debian 12 comes doesn't come with Snapd installed. Install Snapd package.
$ sudo apt install snapd
Run the following commands to ensure that your version of Snapd is up to date.
$ sudo snap install core && sudo snap refresh core
Install Certbot.
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
Use the following command to ensure that the Certbot command can be run by creating a symbolic link to the /usr/bin directory.
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
Verify if Certbot is functioning properly.
$ certbot --version certbot 2.6.0
Run the following command to generate an SSL Certificate.
$ sudo certbot certonly --nginx --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d magento.example.com
The above command will download a certificate to the /etc/letsencrypt/live/magento.example.com directory on your server.
Generate a Diffie-Hellman group certificate.
$ sudo openssl dhparam -dsaparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 4096
Check the Certbot renewal scheduler service.
$ sudo systemctl list-timers
You will find snap.certbot.renew.service as one of the services scheduled to run.
NEXT LEFT LAST PASSED UNIT ACTIVATES ..... Wed 2023-08-02 08:09:00 UTC 9h left Wed 2023-08-02 07:39:06 UTC 2h 59min ago snap.certbot.renew.timer snap.certbot.renew.service Thu 2023-08-03 06:41:11 UTC 9h left Wed 2023-08-02 06:24:33 UTC 10h ago apt-daily-upgrade.timer apt-daily-upgrade.service Wed 2023-08-02 14:06:00 UTC 11h left Sun 2021-11-14 02:03:02 UTC 5min ago apt-daily.timer apt-daily.service
Do a dry run of the process to check whether the SSL renewal is working fine.
$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see no errors, you are all set. Your certificate will renew automatically.
Step 8 - Install Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is used by Magento for product searches. We will install Elasticsearch 7.x using its official repository since it is the version that is compatible with Magento.
Import Elasticsearch's GPG key.
$ wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg
Add the Elasticsearch repository.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
Update the system's repository list.
$ sudo apt update
Install Elasticsearch.
$ sudo apt install elasticsearch
Elasticsearch uses a lot of memory. You need to limit its usage depending on your server size. Create the file /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options.d/memory.options file and open it for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options.d/memory.options
Paste the following code in it. Modify the values according to your server size. The first value refers to the initial memory and the second one refers to the maximum available memory. For 1GB and more, use -Xms1g format.
-Xms512m -Xmx784m
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted. This configures Elasticsearch to use 1GB of RAM. You can use any value as necessary.
Start and enable the service.
$ sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch --now
Check if Elasticsearch is working.
$ curl http://localhost:9200
You should see the following output.
{
"name" : "magento",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "LNFRevgvQIOGeWCdtvc7bA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.17.12",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "e3b0c3d3c5c130e1dc6d567d6baef1c73eeb2059",
"build_date" : "2023-07-20T05:33:33.690180787Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.11.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Step 9 - Install Redis server
Magento uses Redis for session and cache storage. It is entirely optional and you can use the database for session storage. But Redis does a better job. The latest version of Magento works with Redis 7.0. Debian ships with Redis 6.0 so we will use the Redis repository for installation.
Import the official Redis GPG key.
$ curl -fsSL https://packages.redis.io/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg
Add the APT repository to your sources list.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.redis.io/deb $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/redis.list
Update the system repository list.
$ sudo apt update
Issue the following command to install the Redis server.
$ sudo apt install redis
Confirm the Redis version.
$ redis-server -v Redis server v=7.0.12 sha=00000000:0 malloc=jemalloc-5.2.1 bits=64 build=d706905cc5f560c1
Let us verify the service connection by using the following command.
$ redis-cli
You will be switched to the Redis shell.
The first step is to set the password for the Redis default user. Replace Your_Redis_Password with a strong password of your choice. Make sure you prefix the password with the > character.
127.0.0.1:6379> acl setuser default >Your_Redis_Password
Test the Redis Authentication.
127.0.0.1:6379> AUTH Your_Redis_Password OK
Ping the service.
127.0.0.1:6379> ping PONG
Exit the service by typing exit.
Step 10 - Download Magento
Create a web root directory for Magento.
$ sudo mkdir /var/www/magento -p
Give the rights to the Magento directory to the current user.
$ sudo chown $USER:$USER /var/www/magento/ -R
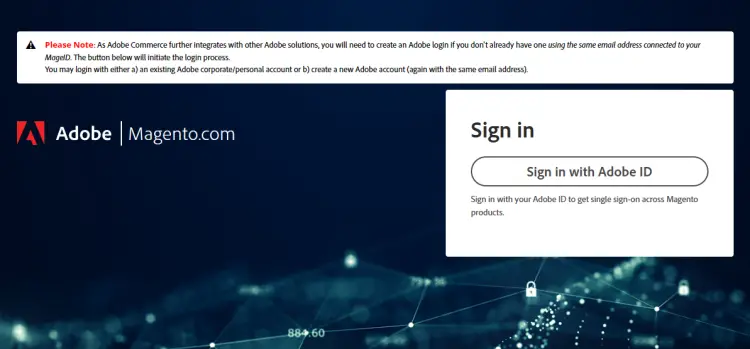
Before we move further, you need to authentication keys required by the Magento repository. Visit the website https://account.magento.com/ and you will get the following page asking you to log in using your Adobe ID.
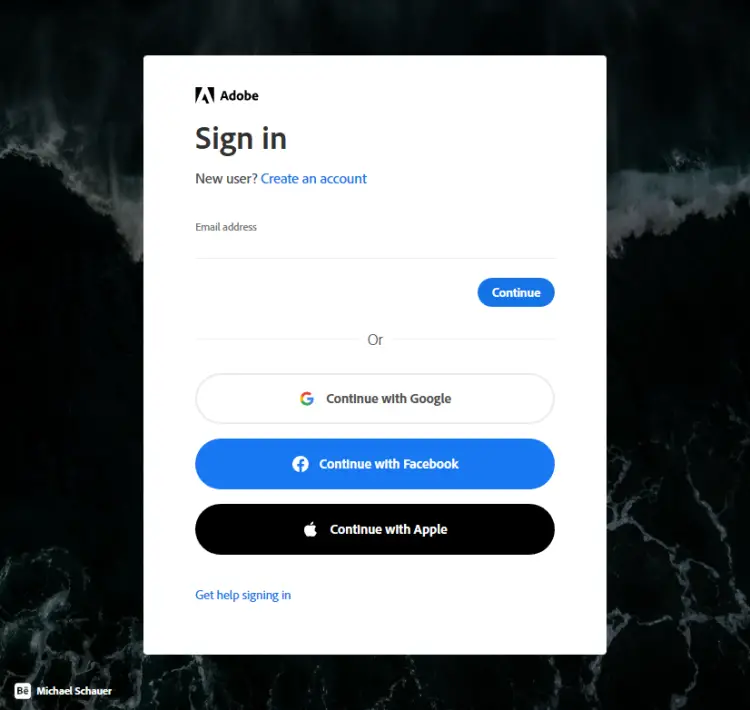
Click the Sign in with Adobe ID button to get to the following page.
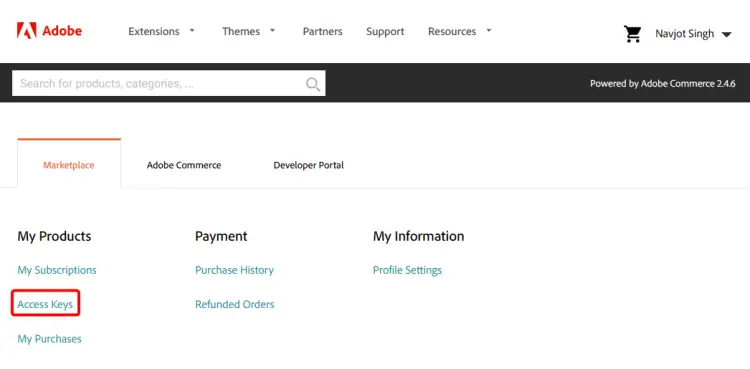
If you have an Adobe ID, enter your credentials to continue or you can create an account here. Once you have created your account and logged in, open the URL https://marketplace.magento.com/customer/accessKeys/. You can also access this page by visiting your profile and clicking the Access Keys link.
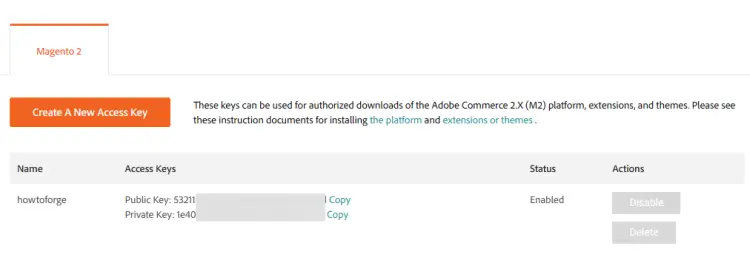
Click the Create A New Access Key button to create your authentication key. Give a name to your key for identification.
Note down both the public and private keys for the next step.
Create the ~/.config/composer/auth.json file and open it for editing.
$ nano ~/.config/composer/auth.json
Paste the following code in it. Use the public key for the username and the private key for the password.
{
"http-basic": {
"repo.magento.com": {
"username": "<public_key>",
"password": "<private_key>"
}
}
}
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Switch to the /var/www/magento directory.
$ cd /var/www/magento
Create the Magento project. Note the period at the end of the command. It refers to the current directory in which the command is being run.
$ composer create-project --repository-url=https://repo.magento.com/ magento/project-community-edition .
You should see a similar output.
Creating a "magento/project-community-edition" project at "./" Installing magento/project-community-edition (2.4.6-p1) - Downloading magento/project-community-edition (2.4.6-p1) - Installing magento/project-community-edition (2.4.6-p1): Extracting archive Created project in /var/www/magento/. Loading composer repositories with package information Info from https://repo.packagist.org: #StandWithUkraine Updating dependencies Lock file operations: 565 installs, 0 updates, 0 removals - Locking 2tvenom/cborencode (1.0.2) - Locking adobe-commerce/adobe-ims-metapackage (2.2.0) - Locking allure-framework/allure-codeception (v2.3.0) - Locking allure-framework/allure-php-commons (v2.3.1) - Locking allure-framework/allure-phpunit (v2.1.0) ...............................................
There is an issue with the sample Nginx configuration file provided by Adobe. Run the following command to fix it.
$ sed -i 's/php-fpm:9000/fastcgi_backend/g' /var/www/magento/nginx.conf.sample
Run the following commands to set the file permissions and make Magento binary executable. Also, set the owner of the Magento directory to the Nginx user so that it can access the website.
$ sudo find var generated vendor pub/static pub/media app/etc -type f -exec chmod g+w {} +
$ sudo find var generated vendor pub/static pub/media app/etc -type d -exec chmod g+ws {} +
$ sudo chown -R :nginx .
$ sudo chmod u+x bin/magento
Step 11 - Install Magento
Before proceeding with the installation, we need to modify the installer so it allows us to use MariaDB 10.11.3 which is not currently supported by Magento. Magento supports MariaDB 10.2-10.6 versions so far.
Open the file /var/www/magento/app/etc/di.xml for editing.
$ sudo nano /var/www/magento/app/etc/di.xml
Search for the following line.
<item name="MariaDB-(10.2-10.6)" xsi:type="string">^10\.[2-6]\.</item>
Replace it with the following code.
<item name="MariaDB-(10.2-10.11)" xsi:type="string">^10\.([2-9]|10|11)\.</item>
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Make sure you are in the Magento directory.
$ cd /var/www/magento
Run the following command to install Magento.
$ bin/magento setup:install \ --base-url=http://magento.example.com \ --use-secure=1 \ --base-url-secure=https://magento.example.com \ --use-secure-admin=1 \ --db-host=localhost \ --db-name=magento \ --db-user=magentouser \ --db-password=Your_password2 \ --admin-firstname=Navjot \ --admin-lastname=Singh \ [email protected] \ --admin-user=navjot \ --admin-password=admin_password \ --language=en_US \ --currency=USD \ --timezone=America/Chicago \ --use-rewrites=1 \ --elasticsearch-host=http://127.0.0.1 \ --elasticsearch-port=9200 \ --session-save=redis \ --session-save-redis-db=0 \ --session-save-redis-password=redis_password \ --cache-backend=redis \ --cache-backend-redis-db=2 \ --cache-backend-redis-password=redis_password \ --page-cache=redis \ --page-cache-redis-db=4 \ --page-cache-redis-password=redis_password
Once the process is complete, you will get a similar output.
....... [SUCCESS]: Magento installation complete. [SUCCESS]: Magento Admin URI: /admin_11xb2x Nothing to import.
Note down the Admin URI which you will need later to access the administration panel.
Create Magento cron jobs.
$ php bin/magento cron:install
Verify the cron job.
$ crontab -l
You should see the following output.
#~ MAGENTO START d1957f62aa710cc367525c9ec68dd7456d4311756b5aa37d2143c4a98b25318c * * * * * /usr/bin/php8.2 /var/www/magento/bin/magento cron:run 2>&1 | grep -v "Ran jobs by schedule" >> /var/www/magento/var/log/magento.cron.log #~ MAGENTO END d1957f62aa710cc367525c9ec68dd7456d4311756b5aa37d2143c4a98b25318c
Step 12 - Configure PHP-FPM
Open the file /etc/php/8.2/fpm/pool.d/www.conf.
$ sudo nano /etc/php/8.2/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
We need to set the Unix user/group of PHP processes to nginx. Find the user=www-data and group=www-data lines in the file and change them to nginx.
... ; Unix user/group of the child processes. This can be used only if the master ; process running user is root. It is set after the child process is created. ; The user and group can be specified either by their name or by their numeric ; IDs. ; Note: If the user is root, the executable needs to be started with ; --allow-to-run-as-root option to work. ; Default Values: The user is set to master process running user by default. ; If the group is not set, the user's group is used. user = nginx group = nginx ...
Find the listen.owner = www-data and listen.group = www-data lines in the file and change them to nginx.
; Set permissions for unix socket, if one is used. In Linux, read/write ; permissions must be set in order to allow connections from a web server. Many ; BSD-derived systems allow connections regardless of permissions. The owner ; and group can be specified either by name or by their numeric IDs. ; Default Values: user and group are set as the running user ; mode is set to 0660 listen.owner = nginx listen.group = nginx
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Increase the execution time for PHP-FPM and PHP-CLI to 180 seconds.
$ sudo sed -i 's/max_execution_time = 30/max_execution_time = 180/' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini $ sudo sed -i 's/max_execution_time = 30/max_execution_time = 180/' /etc/php/8.2/cli/php.ini
Increase the memory limit for PHP-FPM from 128MB to 256MB. You can raise the limit depending on your server size and requirements.
$ sudo sed -i 's/memory_limit = 128M/memory_limit = 256M/' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini
Magento by default sets the file size limit for the media library as 2MB. Run the following commands to increase the file size limit to 25MB.
$ sudo sed -i 's/upload_max_filesize = 2M/upload_max_filesize = 25M/g' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini $ sudo sed -i 's/post_max_size = 8M/post_max_size = 25M/g' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini
Turn on the Zlib Compression.
$ sudo sed -i 's/zlib.output_compression = Off/zlib.output_compression = On/g' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini
Restart the PHP-FPM service.
$ sudo systemctl restart php8.2-fpm
Change the group of the PHP sessions directory to Nginx.
$ sudo chgrp -R nginx /var/lib/php/sessions
Step 13 - Configure Nginx
Open the file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Add the following line before the line include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;.
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Create and open the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/magento.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/magento.conf
Paste the following code in it.
upstream fastcgi_backend {
server unix:/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock;
}
server {
# Redirect any http requests to https
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name magento.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name magento.example.com;
set $MAGE_ROOT /var/www/magento;
include /var/www/magento/nginx.conf.sample;
client_max_body_size 25m;
access_log /var/log/nginx/magento.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/magento.error.log;
# TLS configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/magento.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/magento.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/magento.example.com/chain.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
# OCSP Stapling ---
# fetch OCSP records from URL in ssl_certificate and cache them
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
}
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted once finished.
Magento comes with an Nginx configuration template at /var/www/magento/nginx.conf.sample which we have included in our configuration. The $MAGE_ROOT variable points to the Magento web root directory which we have set in our file and is used in the sample configuration file.
Verify the Nginx configuration file syntax.
$ sudo nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Restart the Nginx service.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
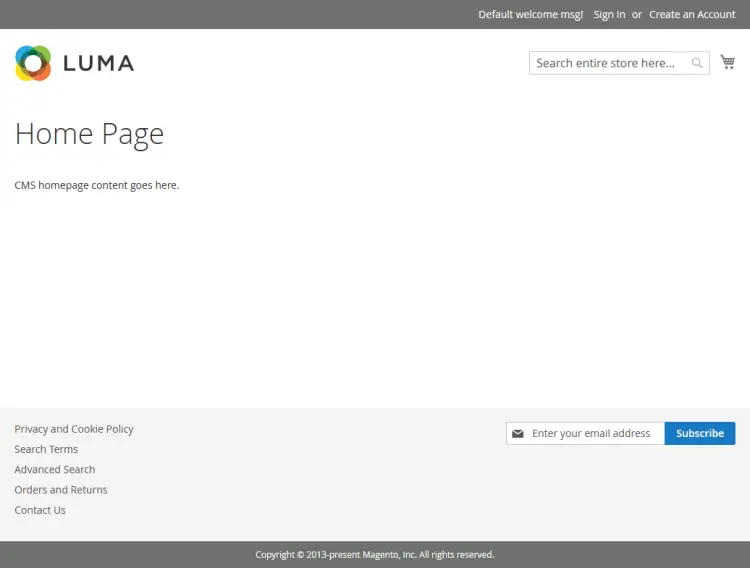
Open the Magento website via the URL https://magento.example.com. You should see the following page.
If the CSS and JS don't load for you, then run the following commands.
$ cd /var/www/magento $ php bin/magento setup:static-content:deploy -f $ php bin/magento indexer:reindex
Step 14 - Disable Two factor Authentication
Before accessing the administration panel, we need to disable the two-factor authentication which is enabled by default. Magento tries to send mail via sendmail for enabling two-factor authentication during installation but since we didn't configure that, the only way to access the dashboard is to disable the feature first.
If you have sendmail configured on your server to send emails, then you can skip this step. To disable two-factor authentication, we need to disable two of Magento's modules using the following commands.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento module:disable Magento_AdminAdobeImsTwoFactorAuth $ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento module:disable Magento_TwoFactorAuth
Run the following command to create the classes.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento setup:di:compile
Clean the cache as well.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento c:c
Step 15 - Access the Administration Portal
You will need to open the administration portal using the URI the Magento install script gave you. If you somehow forgot to note it down or lost it, you can retrieve the URI again using the following command.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento info:adminuri Admin URI: /admin_11xb2x
Open the URL https://magento.example.com/admin_11xb2x in your browser and you will get the following screen.
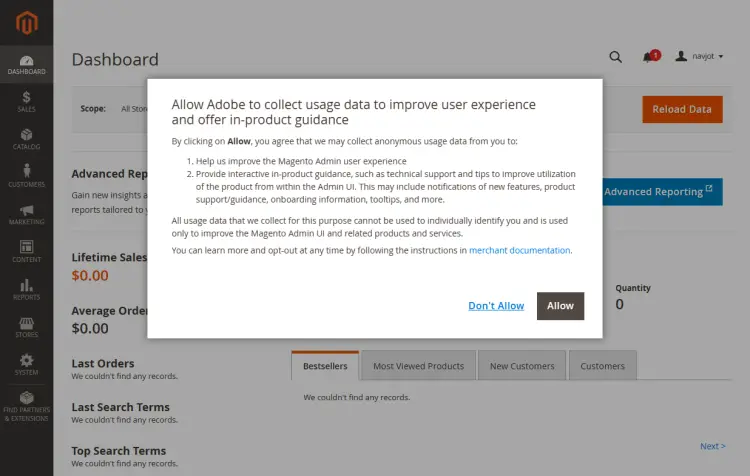
Enter your administrator credentials supplied during the installation and click the Sign in button to proceed. You will be greeted with the following screen.
You will get a popup asking permission for Adobe to collect usage data. Click the Don't Allow button to proceed.
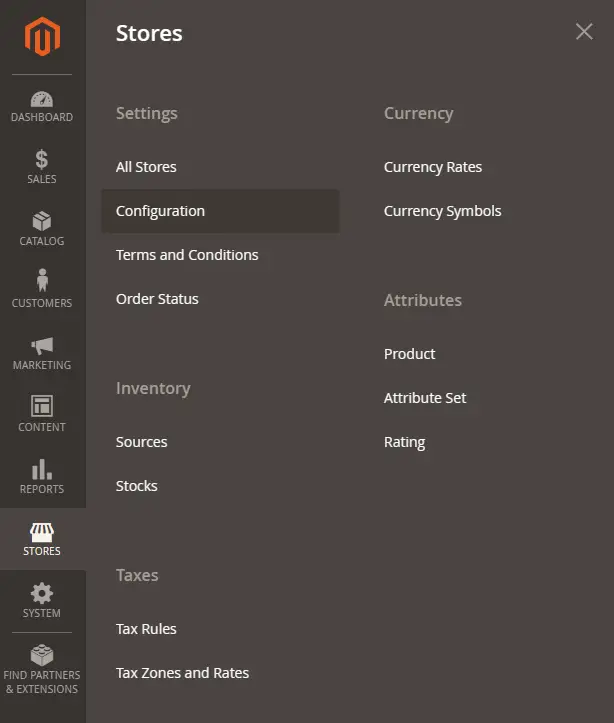
The next step is to configure SMTP for emails so that we can re-enable two-factor authentication. Visit the Stores >> Configuration menu.
Expand the Advanced Menu from the left side and click the Systems option to open the Email settings page.
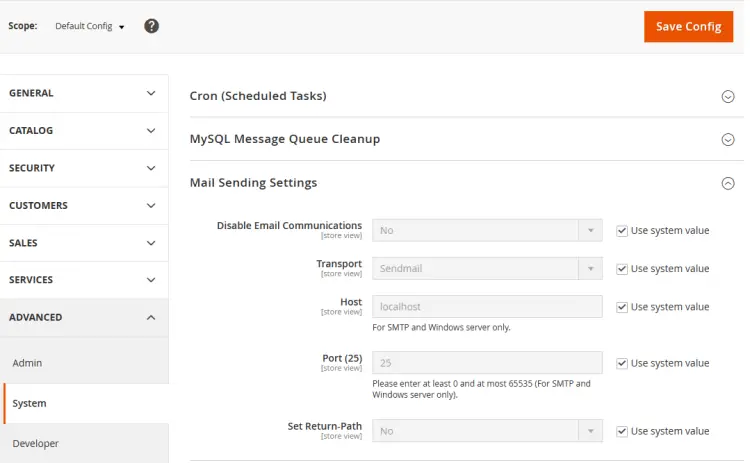
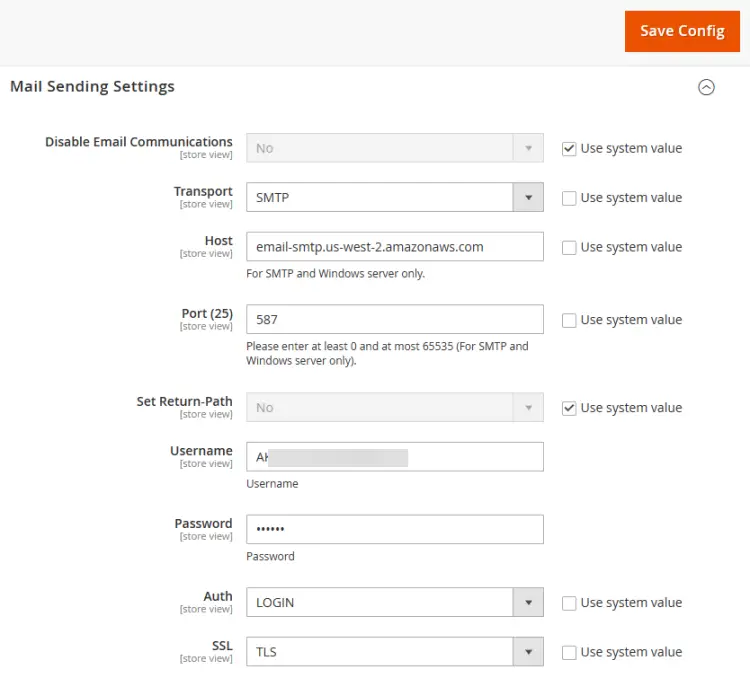
Uncheck the Use system value in front of the Transport, Host, and, Port options. Click the dropdown menu for Transport and select SMTP from it. For our tutorial, we are using Amazon SES as the mailer.
Enter your SMTP host, 587 as the port, username, and password, set Auth to LOGIN and set SSL to TLS in the given fields. Click the Save Config button when you are done. Now that we have configured the email settings, the next step is to configure the store email IDs so that we can test them.
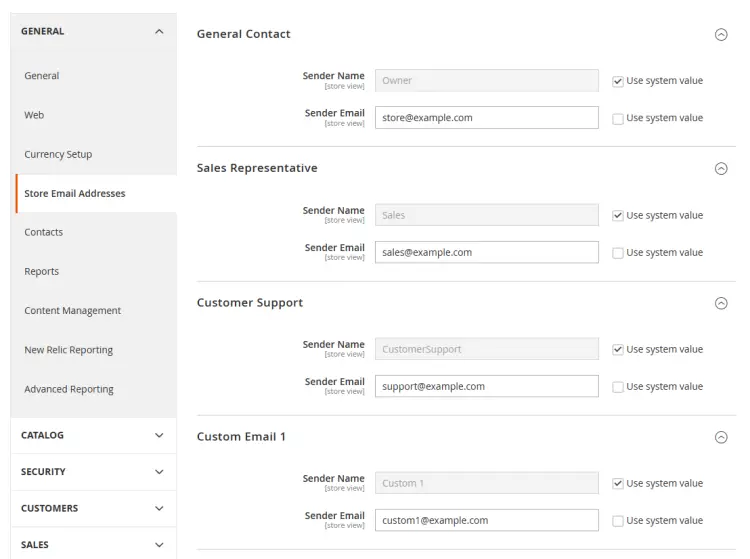
Scroll up and expand the General menu on the same page and select the Store Email Addresses option.
Uncheck the default Sender Email fields and enter your store's email ids. Click the Save Config button when you are done. Similarly, open the Contacts screen and make the same changes and click the Save Config button to finish it.
Changing administrator options can affect the cache and you will get a warning. Run the following command to clear the cache manually.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento c:c
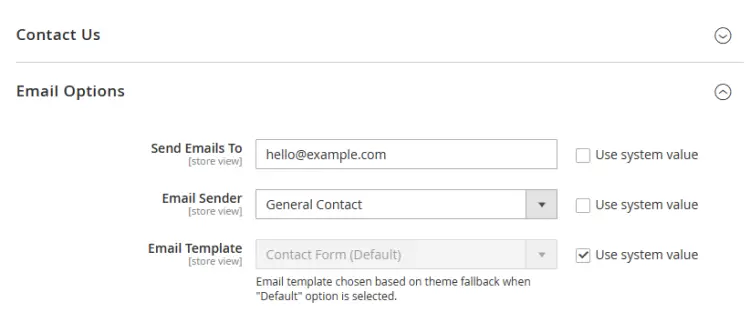
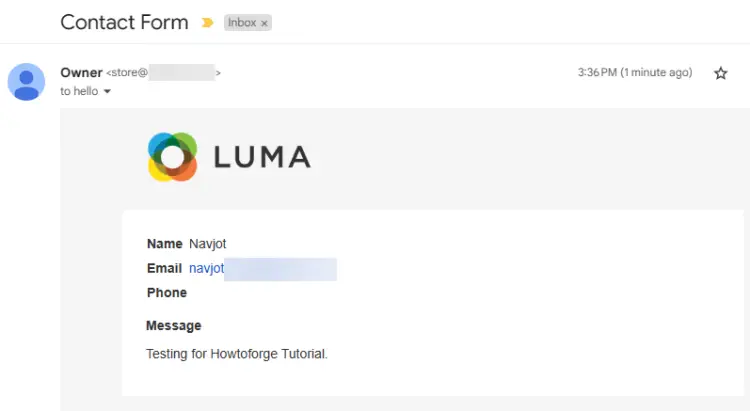
To test the emails, visit the storefront page and open the Contact Us page. You can use the URL https://magento.example.com/contact/ directly to access it. Send a test message and click the Submit button. You should receive a similar mail.
Step 16 - Enable and Configure Two-factor Authentication
Now that we have enabled the SMTP mailer, it is time to re-enable two-factor authentication. Run the following commands to enable two-factor authentication.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento module:enable Magento_AdminAdobeImsTwoFactorAuth $ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento module:enable Magento_TwoFactorAuth
Upgrade the setup for the modules.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento setup:upgrade
Run the following command to create the classes.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento setup:di:compile
Clean the cache as well.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento c:c
If you are not able to access the admin area, run the following commands as well.
Force deploy the static content.
$ php /var/www/magento/bin/magento setup:static-content:Deploy -f
Set the file permissions.
$ cd /var/www/magento
$ sudo find var generated vendor pub/static pub/media app/etc -type f -exec chmod g+w {} +
$ sudo find var generated vendor pub/static pub/media app/etc -type d -exec chmod g+ws {} +
$ sudo chown -R :nginx .
Visit the Admin portal and you will get the following screen.
We will be using the Google Authenticator Method. You can use a hardware key if you have that. Google Authenticator method works with any TOTP app including Authy, 1Password, Bitwarden, Microsoft Authenticator, etc. Click the Apply button to proceed.
On the next page, you will get the QR code to scan with your 2FA app. Enter the details into your app and copy the generated code into the Authenticator code field. Click the Confirm button to proceed to the admin dashboard.
Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on installing Magento eCommerce Site on a Debian 12 server with an Nginx server and Elasticsearch. If you have any questions, post them in the comments below.