How to Install Arkime Moloch Packet Capture Tool on Ubuntu 22.04
Arkime is a free, open-source, large-scale indexed packet capture and search tool that stores and indexes network traffic in PCAP format. It is also known as Moloch, which is designed to be deployed across multiple clustered systems, providing the ability to scale to handle multiple gigabits per second of traffic. Arkime has a built-in admin interface that helps you browse, search, and export PCAP. You can use other PCAP ingesting tools to analyze your workflow.
This tutorial will show you how to install the Arkime Packet Capture tool on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Getting Started
Before starting, you will need to update your system packages to the latest version. You can update them with the following command:
apt-get update -y
Once all the packages are updated, install the required dependencies using the following command:
apt-get install gnupg2 curl wget -y
Next, you will also need to install Libssl and Libffi libraries to your system. You can download and install both by running the following command:
wget http://es.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/libf/libffi/libffi7_3.3-4_amd64.deb
wget http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/o/openssl/libssl1.1_1.1.1f-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
dpkg -i libffi7_3.3-4_amd64.deb
dpkg -i libssl1.1_1.1.1f-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libssl.so.1.1 /usr/local/lib/
ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libffi.so.7 /usr/local/lib/
Once all the packages are installed, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Elasticsearch
Arkime uses Elasticsearch for indexing and searching. So Elasticsearch must be installed in your system. By default, the latest version of Elasticsearch is not included in the Ubuntu default repository. So you will need to add the Elasticsearch repository to your system.
First, add the GPG key with the following command:
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch --no-check-certificate | apt-key add -
Next, add the Elasticsearch repository to the APT with the following command:
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
Next, update the repository and install the Elasticsearch package with the following command:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install elasticsearch -y
Once the Elasticsearch is installed edit the Elasticsearch configuration file and set the Java memory:
nano /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options
Change the following lines:
-Xms500m -Xmx500m
Save and close the file, then enable the Elasticsearch service to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl enable --now elasticsearch
By default, Elasticsearch listens on port 9200. You can check it with the following command:
ss -antpl | grep 9200
You should get the following output:
LISTEN 0 4096 [::ffff:127.0.0.1]:9200 *:* users:(("java",pid=30581,fd=291))
LISTEN 0 4096 [::1]:9200 [::]:* users:(("java",pid=30581,fd=290))
You can also check Elasticsearch with the following command:
curl http://localhost:9200
You should get the following output:
{
"name" : "ubuntu2204",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "6QiUfVa4Q9G8lxHjuVLjUQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.17.5",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "8d61b4f7ddf931f219e3745f295ed2bbc50c8e84",
"build_date" : "2022-06-23T21:57:28.736740635Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.11.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
At this point, Elasticsearch is installed and running. You can now proceed to the next step.
Install and Configure Arkime
First, download the latest version of Arkime with the following command:
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/files.molo.ch/builds/ubuntu-20.04/arkime_3.4.2-1_amd64.deb
Once the package is downloaded, install the downloaded package with the following command:
apt install ./arkime_3.4.2-1_amd64.deb
Once the Arkime is installed, run the following command to configure it:
/opt/arkime/bin/Configure
You will be asked to specify the network interface as shown below:
Found interfaces: lo;eth0;eth1 Semicolon ';' seperated list of interfaces to monitor [eth1] eth0
Type your network interface name and hit Enter to continue. Once the configuration is finished, you should get the following output:
Install Elasticsearch server locally for demo, must have at least 3G of memory, NOT recommended for production use (yes or no) [no] no
Elasticsearch server URL [http://localhost:9200]
Password to encrypt S2S and other things, don't use spaces [no-default] password
Arkime - Creating configuration files
Installing systemd start files, use systemctl
Arkime - Installing /etc/logrotate.d/arkime to rotate files after 7 days
Arkime - Installing /etc/security/limits.d/99-arkime.conf to make core and memlock unlimited
Download GEO files? You'll need a MaxMind account https://arkime.com/faq#maxmind (yes or no) [yes] no
Arkime - NOT downloading GEO files
Arkime - Configured - Now continue with step 4 in /opt/arkime/README.txt
4) The Configure script can install elasticsearch for you or you can install yourself
systemctl start elasticsearch.service
5) Initialize/Upgrade Elasticsearch Arkime configuration
a) If this is the first install, or want to delete all data
/opt/arkime/db/db.pl http://ESHOST:9200 init
b) If this is an update to a moloch/arkime package
/opt/arkime/db/db.pl http://ESHOST:9200 upgrade
6) Add an admin user if a new install or after an init
/opt/arkime/bin/arkime_add_user.sh admin "Admin User" THEPASSWORD --admin
7) Start everything
systemctl start arkimecapture.service
systemctl start arkimeviewer.service
8) Look at log files for errors
/opt/arkime/logs/viewer.log
/opt/arkime/logs/capture.log
9) Visit http://arkimeHOST:8005 with your favorite browser.
user: admin
password: THEPASSWORD from step #6
If you want IP -> Geo/ASN to work, you need to setup a maxmind account and the geoipupdate program.
See https://arkime.com/faq#maxmind
Any configuration changes can be made to /opt/arkime/etc/config.ini
See https://arkime.com/faq#moloch-is-not-working for issues
Additional information can be found at:
* https://arkime.com/faq
* https://arkime.com/settings
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Initialize Elasticsearch Arkime configuration
Next, you will need to initialize the Elasticsearch Arkime configuration. You can do it with the following command:
/opt/arkime/db/db.pl http://localhost:9200 init
Next, create an admin user account for Arkime with the following command:
/opt/arkime/bin/arkime_add_user.sh admin "Moloch SuperAdmin" password --admin
Next, update the Geo database using the following command:
/opt/arkime/bin/arkime_update_geo.sh
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Start and Manage Arkime Services
Arkime is made from three components, capture, viewer and elasticsearch. So you will need to start the service for each component.
You can start the Arkimecapture and Arkimeviewer service and enable them to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl enable --now arkimecapture
systemctl enable --now arkimeviewer
You can now check the status of both services with the following command:
systemctl status arkimecapture arkimeviewer
You should get the following output:
? arkimecapture.service - Arkime Capture
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/arkimecapture.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-08-15 03:55:10 UTC; 1min 0s ago
Process: 33704 ExecStartPre=/opt/arkime/bin/arkime_config_interfaces.sh -c /opt/arkime/etc/config.ini -n default (code=exited, status=0/S>
Main PID: 33724 (sh)
Tasks: 7 (limit: 2242)
Memory: 213.2M
CPU: 806ms
CGroup: /system.slice/arkimecapture.service
??33724 /bin/sh -c "/opt/arkime/bin/capture -c /opt/arkime/etc/config.ini >> /opt/arkime/logs/capture.log 2>&1"
??33725 /opt/arkime/bin/capture -c /opt/arkime/etc/config.ini
Aug 15 03:55:09 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Starting Arkime Capture...
Aug 15 03:55:10 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Started Arkime Capture.
? arkimeviewer.service - Arkime Viewer
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/arkimeviewer.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-08-15 03:08:39 UTC; 47min ago
Main PID: 31759 (sh)
Tasks: 12 (limit: 2242)
Memory: 56.7M
CPU: 2.127s
CGroup: /system.slice/arkimeviewer.service
??31759 /bin/sh -c "/opt/arkime/bin/node viewer.js -c /opt/arkime/etc/config.ini >> /opt/arkime/logs/viewer.log 2>&1"
??31760 /opt/arkime/bin/node viewer.js -c /opt/arkime/etc/config.ini
Aug 15 03:08:39 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Started Arkime Viewer.
You can check the viewer log with the following command:
tail -f /opt/arkime/logs/viewer.log
You can now check the capture log with the following command:
tail -f /opt/arkime/logs/capture.log
You should see the following output:
Aug 15 03:57:20 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 2/3 ASYNC 201 http://localhost:9200/arkime_dstats/_doc/ubuntu2204-1408-5 804/159 0ms 20ms Aug 15 03:57:20 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 1/3 ASYNC 200 http://localhost:9200/arkime_stats/_doc/ubuntu2204?version_type=external&version=66 798/157 0ms 24ms Aug 15 03:57:22 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 1/3 ASYNC 200 http://localhost:9200/_bulk 715/221 0ms 10ms Aug 15 03:57:22 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 1/3 ASYNC 200 http://localhost:9200/arkime_stats/_doc/ubuntu2204?version_type=external&version=67 805/158 0ms 12ms Aug 15 03:57:24 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 1/3 ASYNC 200 http://localhost:9200/_bulk 1471/253 0ms 24ms Aug 15 03:57:24 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 1/3 ASYNC 200 http://localhost:9200/arkime_stats/_doc/ubuntu2204?version_type=external&version=68 806/157 0ms 18ms Aug 15 03:57:25 http.c:389 moloch_http_curlm_check_multi_info(): 1/3 ASYNC 201 http://localhost:9200/arkime_dstats/_doc/ubuntu2204-1409-5 808/159 0ms 10ms
Access Arkime Web Interface
At this point, Arkime is started and listening on port 8005. You can check it with the following command:
ss -antpl | grep 8005
You should get the following output:
LISTEN 0 511 *:8005 *:* users:(("node",pid=11362,fd=20))
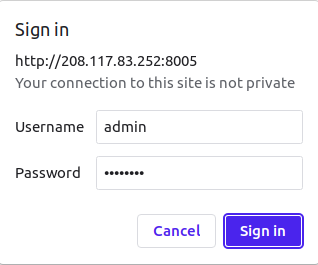
Now, open your web browser and access the Arkime web interface using the URL http://your-server-ip:8005. You will be asked to provide your admin username and password as shown below:
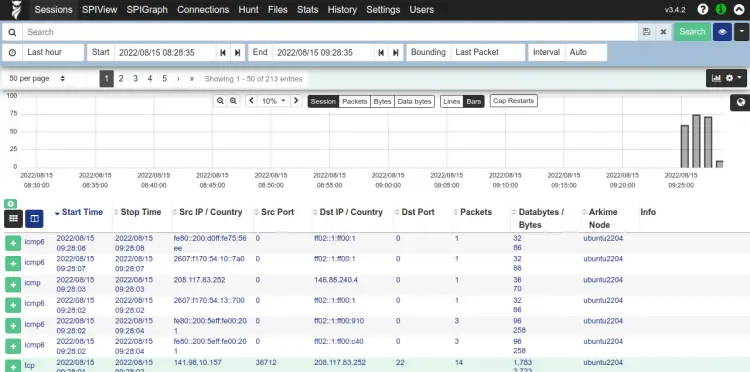
Provide your admin username, password and click on the Sign In button. You should see the Arkime dashboard in the following page:
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed and configured the Arkime packet capture tool on Ubuntu 22.04 server. You can now explore the Arkime for more functionality and start capturing packets. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.