Virtual Hosting With PureFTPd And MySQL (Incl. Quota And Bandwidth Management) On OpenSUSE 11.3 - Page 2
6 Populate The Database And Test
To populate the database you can use the MySQL shell:
mysql -u root -p
USE pureftpd;
Now we create the user exampleuser with the status 1 (which means his ftp account is active), the password secret (which will be stored encrypted using MySQL's MD5 function), the UID and GID 2001 (use the userid and groupid of the user/group you created at the end of step two!), the home directory /home/www.example.com, an upload and download bandwidth of 100 KB/sec. (kilobytes per second), and a quota of 50 MB:
INSERT INTO `ftpd` (`User`, `status`, `Password`, `Uid`, `Gid`, `Dir`, `ULBandwidth`, `DLBandwidth`, `comment`, `ipaccess`, `QuotaSize`, `QuotaFiles`) VALUES ('exampleuser', '1', MD5('secret'), '2001', '2001', '/home/www.example.com', '100', '100', '', '*', '50', '0');
quit;
Now open your FTP client program on your work station (something like WS_FTP or SmartFTP if you are on a Windows system or gFTP on a Linux desktop) and try to connect. As hostname you use server1.example.com (or the IP address of the system), the username is exampleuser, and the password is secret.
If you are able to connect - congratulations! If not, something went wrong.
Now, if you run
ls -l /home
you should see that the directory /home/www.example.com (exampleuser's home directory) has been created automatically, and it is owned by ftpuser and ftpgroup (the user/group we created at the end of step two):
server1:~ # ls -l /home
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 6 administrator users 4096 Jul 19 17:26 administrator
drwx------ 2 ftpuser ftpgroup 4096 Sep 13 20:57 www.example.com
server1:~ #
7 Database Administration
For most people it is easier if they have a graphical front-end to MySQL; therefore you can also use phpMyAdmin (in this example under http://server1.example.com/phpMyAdmin/ or http://192.168.0.100/phpMyAdmin/) to administrate the pureftpd database.
Whenever you want to create a new user, you have to create an entry in the table ftpd so I will explain the columns of this table here:
ftpd Table:
- User: The name of the virtual PureFTPd user (e.g. exampleuser).
- status: 0 or 1. 0 means the account is disabled, the user cannot login.
- Password: The password of the virtual user. Make sure you use MySQL's MD5 function to save the password encrypted as an MD5 string:
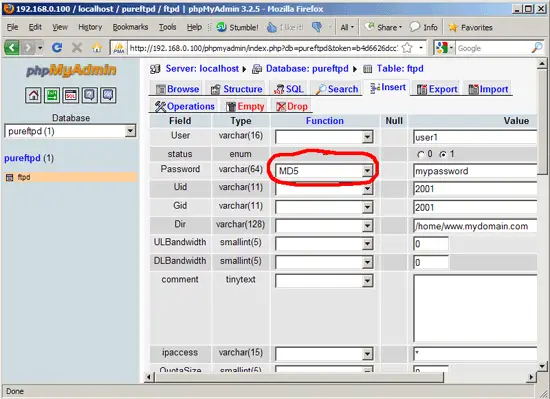
- UID: The userid of the ftp user you created at the end of step two (e.g. 2001).
- GID: The groupid of the ftp group you created at the end of step two (e.g. 2001).
- Dir: The home directory of the virtual PureFTPd user (e.g. /home/www.example.com). If it does not exist, it will be created when the new user logs in the first time via FTP. The virtual user will be jailed into this home directory, i.e., he cannot access other directories outside his home directory.
- ULBandwidth: Upload bandwidth of the virtual user in KB/sec. (kilobytes per second). 0 means unlimited.
- DLBandwidth: Download bandwidth of the virtual user in KB/sec. (kilobytes per second). 0 means unlimited.
- comment: You can enter any comment here (e.g. for your internal administration) here. Normally you leave this field empty.
- ipaccess: Enter IP addresses here that are allowed to connect to this FTP account. * means any IP address is allowed to connect.
- QuotaSize: Storage space in MB (not KB, as in ULBandwidth and DLBandwidth!) the virtual user is allowed to use on the FTP server. 0 means unlimited.
- QuotaFiles: amount of files the virtual user is allowed to save on the FTP server. 0 means unlimited.
8 Anonymous FTP
If you want to create an anonymous ftp account (an ftp account that everybody can login to without a password), you need a user and a group called ftp. Both have been created automatically when you installed the pure-ftpd package, so you don't need to create them manually. However, ftp's homedir is /srv/ftp by default, but I'd like to create the anonymous ftp directory in /home/ftp (the normal users' ftp directories are in /home as well, e.g. /home/www.example.com). But of course, you can use the /srv/ftp directory for anonymous ftp, if you prefer it.
If you want to use /home/ftp, open /etc/passwd and change the ftp user's homedir from /srv/ftp to /home/ftp (don't do this if you want to use /srv/ftp):
vi /etc/passwd
[...] #ftp:x:40:49:FTP account:/srv/ftp:/bin/bash |
Then move /srv/ftp to /home (don't do this if you want to use /srv/ftp):
mv /srv/ftp /home
Then we create the directory /home/ftp/incoming which will allow anonymous users to upload files. We will give the /home/ftp/incoming directory permissions of 311 so that users can upload, but not see or download any files in that directory. The /home/ftp directory will have permissions of 555 which allows seeing and downloading of files:
chown ftp:nobody /home/ftp
cd /home/ftp
mkdir incoming
chown ftp:nobody incoming/
chmod 311 incoming/
cd ../
chmod 555 ftp/
(If you want to use /srv/ftp instead, replace /home/ftp with /srv/ftp in the above commands.)
Anonymous users will be able to log in, and they will be allowed to download files from /home/ftp, but uploads will be limited to /home/ftp/incoming (and once a file is uploaded into /home/ftp/incoming, it cannot be read nor downloaded from there; the server admin has to move it into /home/ftp first to make it available to others).
Now we have to configure PureFTPd for anonymous ftp. Open /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.conf and make sure that you have the following settings in it:
vi /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.conf
[...] NoAnonymous no [...] AntiWarez no [...] AnonymousBandwidth 8 [...] AnonymousCantUpload no [...] |
(The AnonymousBandwidth setting is optional - it allows you to limit upload and download bandwidths for anonymous users. 8 means 8 KB/sec. Use any value you like, or comment out the line if you don't want to limit bandwidths.)
Finally, we restart PureFTPd:
/etc/init.d/pure-ftpd restart
9 Links
- PureFTPd: http://www.pureftpd.org/
- MySQL: http://www.mysql.com/
- phpMyAdmin: http://www.phpmyadmin.net/
- OpenSUSE: http://www.opensuse.org/