How to Install Nginx with PHP and MySQL (LEMP Stack) on Ubuntu 18.04
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble Numbat)
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
- Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus)
On this page
Nginx (pronounced "engine x") is a free, open-source, high-performance HTTP server. Nginx is known for its stability, rich feature set, simple configuration, and low resource consumption. This tutorial shows how you can install Nginx on an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server with PHP 7.2 support (through PHP-FPM) and MySQL support (LEMP = Linux + nginx (pronounced "engine x") + MySQL + PHP).
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server
- Root privileges
What we will do?
- Install Nginx
- Install MySQL
- Install PHP-FPM
- Configure Nginx and PHP-FPM
- Install PhpMyAdmin
- Configure PhpMyAdmin
- Testing
Step 1 - Install Nginx
Nginx or engine x is a high-performance HTTP and proxy server with low memory consumption. Most large-scale websites like Netflix, Pinterest, CloudFlare, GitHub are using Nginx.
In this step, we will install Nginx web server from the Ubuntu repository.
Run the command below.
sudo apt install nginx -y
After the installation is complete, start the Nginx service and enable it to launch every time at system boot.
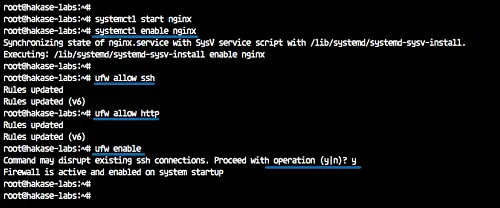
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
The Nginx installation is complete.
Configure the Firewall
It's recommended to turn on the firewall on the server.
Add the SSH and HTTP service port to the firewall configuration.
Run the UFW command below.
ufw allow ssh
ufw allow http
Now start the UFW firewall and enable it to launch everytime at system boot.
ufw enable
The Nginx web server is up and running under the UFW firewall.
Step 2 - Install MySQL
MySQL is the most popular open source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) created by Oracle Corporation. It's a central component of the LEMP Stack, and we will install the latest MySQL version from the Ubuntu repository.
Install MySQL using the apt command below.
sudo apt install mysql-server mysql-client -y
After the MySQL installation is complete, start the MySQL service and enable it to launch everytime at system boot.
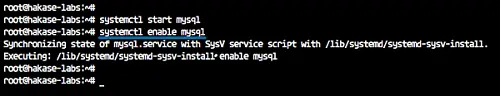
systemctl start mysql
systemctl enable mysql
And we've installed MySQL 5.7 on Ubuntu 18.04 server.
Step 3 - Install PHP-FPM
PHP-FPM or FastCGI Process Manager is an alternative for the older PHP FastCGI which provides additional features and speed improvements. It suits well for small to large sites based on the PHP programming language.
In this step, we will install PHP7.2-FPM with some additional extensions required by phpmyadmin.
Install PHP-FPM using the command below.
sudo apt install php7.2 php7.2-fpm php7.2-cli php7.2-curl php7.2-mysql php7.2-curl php7.2-gd php7.2-mbstring php-pear -y
Now start the PHP-FPM service and enable it to launch every time at system boot after all installation is complete.
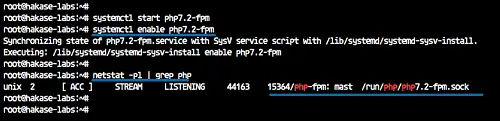
systemctl start php7.2-fpm
systemctl enable php7.2-fpm
PHP7.2-FPM is up and running on Ubuntu 18.04 under the sock file, check it using the netstat command.
netstat -pl | grep php
Step 4 - Configure Nginx and PHP-FPM
In this step, we will configure the Nginx web server and PHP-FPM.
Configure Nginx
Go to the '/etc/nginx' configuration directory, and edit the 'nginx.conf' file using vim or nano.
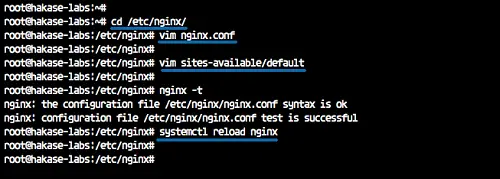
cd /etc/nginx/
vim nginx.conf
Uncomment the following lines.
keepalive_timeout 2; server_tokens off;
Save the configuration file and exit the editor.
Now edit the default Nginx virtual host file.
vim sites-available/default
Uncomment the PHP line shown below and change the sock file line.
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
#
# # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets):
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
# # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets):
# fastcgi_pass 127.2.0.1:9000;
}
Save and exit.
Test Nginx configuration and make sure there is no error, then restart the service.
nginx -t
systemctl reload nginx
Configure PHP-FPM
Go to the '/etc/php/7.2' directory and edit the 'php.ini' file.
cd /etc/php/7.2/
vim fpm/php.ini
Uncomment the 'cgi.fix_patinfo' line and change the value to '0'.
cgi.fix_pathinfo=0
Save and exit.
Reload the PHP-FPM service.
systemctl reload php7.2-fpm
And we've completed configuration of Nginx web server and PHP-FPM.
Step 5 - Install PhpMyAdmin
PhpMyAdmin is a PHP based application to manage MySQL or MariaDB databases from a web browser.
In this step, we will install and configure phpmyadmin under the LEMP (Linux, Nginx, MySQL, and PHP-FPM) stack.
Install PHPMyAdmin using the apt command below.
sudo apt install phpmyadmin -y
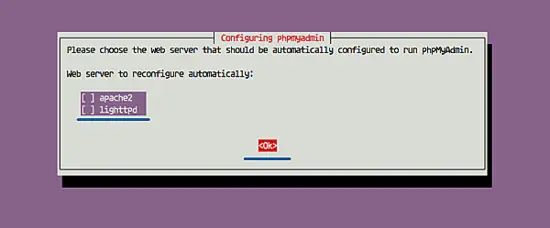
During the installation, it will ask you about the web server configuration for phpmyadmin.
Choose none option and move the cursor to 'OK'.
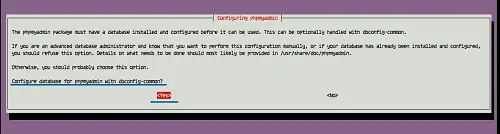
For the phpmyadmin database configuration, choose 'Yes'.
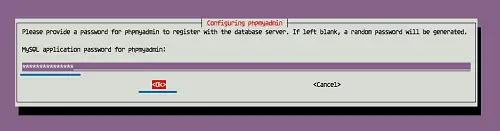
And type new 'STRONG' phpmyadmin admin such as 'Hakaselabs001@#'.
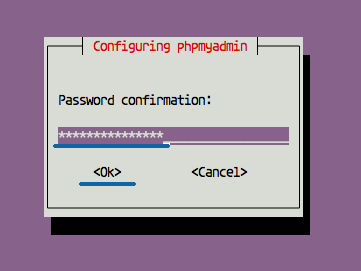
Repeat the 'Hakaselabs001@#' password.
And the phpmyadmin installation is complete.
Step 6 - Configure PhpMyAdmin
After the phpmyadmin installation, we need to configure phpmyadmin to run under the Nginx web server and configure the MySQL user phpmyadmin access.
Configure PhpMyAdmin with Nginx
In order to run phpmyadmin under the Nginx web server, we need to add the configuration to the virtual host configuration file.
Go to the '/etc/nginx' configuration directory, and edit the default virtual host file.
cd /etc/nginx/
vim sites-available/default
Paste the following Nginx configuration for phpmyadmin inside the 'server {...}' bracket.
location /phpmyadmin {
root /usr/share/;
index index.php;
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
location ~ ^/phpmyadmin/(doc|sql|setup)/ {
deny all;
}
location ~ /phpmyadmin/(.+\.php)$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
}
}
Save and exit.
Test the nginx configuration and restart the nginx service.
nginx -t
systemctl reload nginx
And we've added the Nginx configuration for phpmyadmin.
Configure MySQL User for PhpMyAdmin
In this tutorial, we will be using non-root MySQL user for phpmyadmin. We will create a new user and grant all privileges of database inside the server to the user.
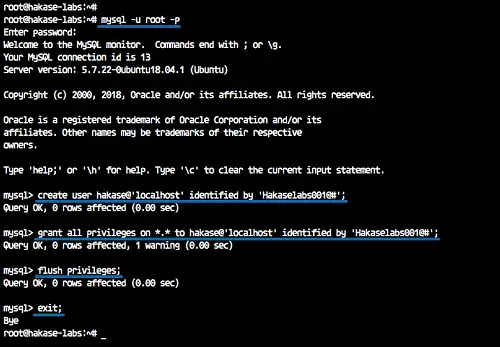
Login to the MySQL shell.
mysql -u root -p
Now create a new user using the MySQL queries below.
create user hakase@'localhost' identified by 'Hakaselabs001@#';
grant all privileges on *.* to hakase@'localhost' identified by 'Hakaselabs001@#';
flush privileges;
exit;
And we've created a new user for phpmyadmin access.
Step 7 - Testing
Test PHP Files
Go to the web-root directory '/var/www/html' and create a new phpinfo file.
cd /var/www/html/
vim info.php
Paste the phpinfo script below.
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and exit.
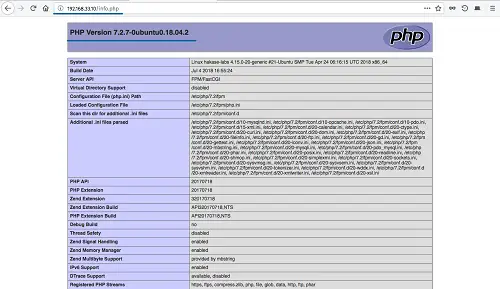
Now open the web browser and type the server IP address as shown below. Replace the IP with your server ip.
http://192.168.33.10/info.php
And below is all information about PHP server configuration.
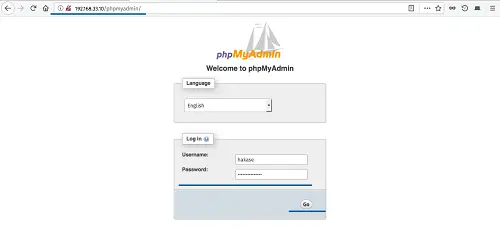
Test Login PhpMyAdmin
On the web browser, type the following phpmyadmin URL (replace the IP with your server IP).
http://192.168.33.10/phpmyadmin/
On the phpmyadmin login page, type the user 'hakase' with password 'Hakaselabs001@#' and click the 'Go' button.
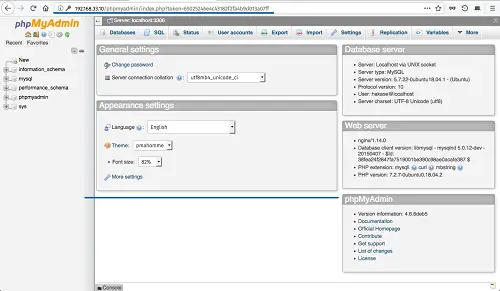
Now we will see the phpmyadmin dashboard as below.
The LEMP Stack and PhpMyAdmin are successfully installed on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.