How to Install Django on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
- Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus)
- Ubuntu 15.04 (Vivid Vervet)
On this page
Django is a web application framework written in python that follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture, it is available for free and released under an open source license. It is fast and designed to help developers get their application online as quickly as possible. Django helps developers to avoid many common security mistakes like SQL Injection, XSS, CSRF and clickjacking.
Django is maintained by the Django Software Foundation and used by many big technology companies, government, and other organizations. Some large websites like Pinterest, Mozilla, Instagram, Discuss, The Washington Post etc. are developed with Django.
In this tutorial, we will install Django 2.0.5 stable version on an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) server. Django can be installed on a server in many ways, in this tutorial, I will show you 3 different ways to install Django:
- Django installation with pip.
- Install Django with virtualenv.
- Install Django from it's github repository.
When the Django installation is done, I will show you the first steps to start a new project with the Django web framework.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 18.04 - 64bit.
- Root privileges.
Step 1 - Setup Python 3 on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
We will configure python 3 before we start with the Django installation.
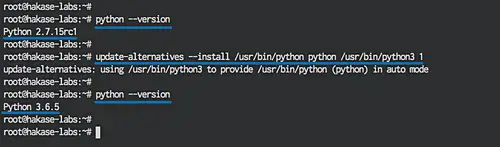
On my Ubuntu machine, there are two versions of python available, python2.7 as default python version and python3.
In this step, we will change the default python version to python 3.
Check the python version:
python --version
So the default python is 2.7 at the moment.
Next, change the default python to python version 3 with the 'update-alternatives' command:
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3 1
Now check again the python version:
python --version
And you will get python 3.6 as a default python on the system.
Note:
By default, ubuntu 18.04 has no 'python' command, because it brings the 'python3' command as default python.
See the BionicBeaver ReleaseNotes.
Step 2 - Install Django
In this step, I will show you 3 ways to install Django. Please follow either chapter 2.1, 2.2 or 2.3 to install Django but not all 3 options at the same time :).
2.1. Install Django with Pip
Pip is a package management system for python. Python has a central package repository from which we can download the python package. It's called Python Package Index (PyPI).
In order to install Django with pip, we need to install 'python3-pip' package to the ubuntu 18.04 system.
Run command below to install pip for python 3.
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
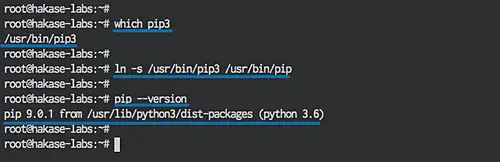
The installation will add a new binary file called 'pip3'. To make it easier to use pip, I will create a symlink for pip3 to pip:
which pip3
ln -s /usr/bin/pip3 /usr/bin/pip
Now check the version :
pip --version
The pip installation is done. Now we can use the pip command to install python packages.
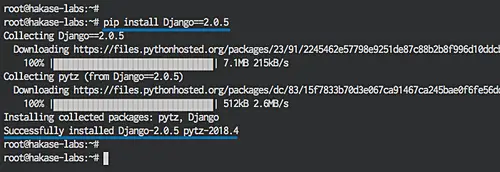
Let's install Django 2.0.5 stable version to the server with pip command below:
pip install Django==2.0.5
Note:
We set the Django==2.0.5 to get a specific version. If you want a different version, just change the number e.g. to django==1.10 etc.
If you get an error about locale settings, run the following command to reconfigure the locale settings:
export LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8
export LANG=en_US.UTF-8
export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
locale-gen en_US.UTF-8
dpkg-reconfigure locales
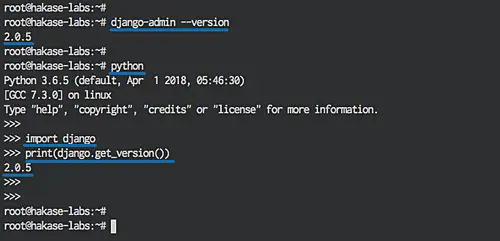
After the installation is complete, check the Django version with the command below:
django-admin --version
Alternatively, we can use the following command:
python
import django
print(django.get_version())
You will see that Django 2.0.5 stable has been installed on the system.
Django 2.0.5 has been installed on the system with pip. Proceed with chapter 3.
2.2. Install Django with Virtualenv
Virtualenv is a python environment builder. It is used to create isolated python environments. We can choose the version of python that will be installed in the virtualenv environment. This is very useful for developers, they can run and develop an application with different python versions and different environments on one OS.
Virtualenv is available on PyPI repository - we can install it with the pip command:
pip install virtualenv
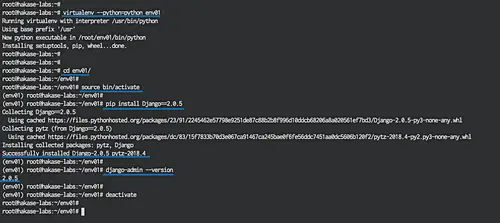
Now we can use the virtualenv command to create a new environment with python3 as default python version. So let's create a new environment "env01" with python3 as the python version and pip3 for the django installation.
virtualenv --python=python3 env01
The command will create a new directory called 'env01' which contains the directories bin, include and lib for pyhton.
The virtualenv has been created, now let's log into the new environment with the following command:
cd env01/
source bin/activate
Next, install Django in the the virtual environment that we've created:
pip install django==2.0.5
When the installation finished, check the Django installation:
django-admin --version
Django 2.0.5 has been successfully installed in our virtual environment. Proceed with chapter 3.
2.3. Install Django from Git Repository
In order to install Django from the Git Repository, we need to install git to the system.
Install git using apt command below.
sudo apt install git -y
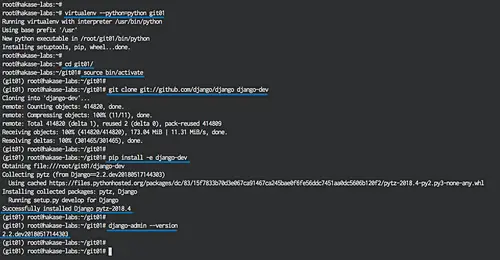
Next, create new virtual environment named 'git01' using the virtualenv command.
virtualenv --python=python git01
Activate the 'git01' virtual environment.
cd git01/
source bin/activate
Next, clone the django source code from github using git.
git clone git://github.com/django/django django-dev
Install django development version using pip command as shown below.
pip install -e django-dev
Note:
-e = Install a package in editable mode or a local package. In this chapter, we install Django from the local code on the 'django-dev' that we've cloned.
When the installation process is done, let's check the Django version on the server:
django-admin --version
You will get the django development version installed from the Github Repository.
Step 3 - Create you First Project with Django
In this step, we will install Django inside a virtual environment and then start our first project with Django. Make sure the 'virtualenv' packages is installed on the system.
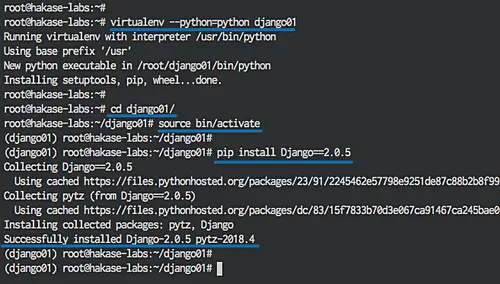
Create new virtual environment named 'django01'.
virtualenv --python=python django01
Go to the 'django01' directory and activate the virtual environment.
cd django01/
source bin/activate
Now install Django 2.0.5 stable version using pip.
pip install Django==2.0.5
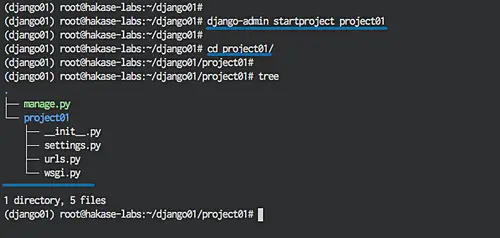
When the installation is complete, create a new project called 'project01' with the django-admin command:
django-admin startproject project01
The command will create a new directory 'project01' that contains Django files:
cd project01/
tree
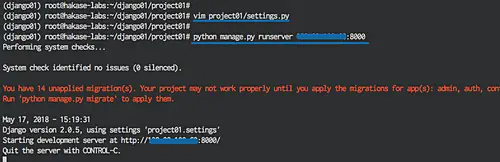
Now edit the 'settings.py' under the 'project01' directory using vim command.
vim project01/settings.py
Type the server IP address inside the 'ALLOWED_HOSTS' line as shown below.
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['192.168.10.100']
Save and exit.
Now run the python django runserver command.
python manage.py runserver 192.168.10.100:8000
The command will run python django on the IP address '192.168.10.100', on port '8000'.
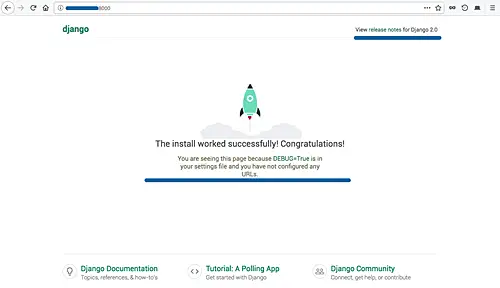
Open your web browser and type the server IP address with port 8000.
And you will get the beautiful default django page as below.
Note:
Press 'Ctrl+c' to exit from the django runserver.
Next, we will configure the Django admin. Django will automatically generate the database for a superuser. Before we create the superuser, run the command below:
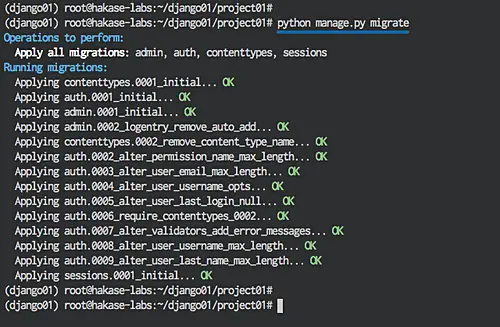
python manage.py migrate
migrate: make adds the models (adding fields, deleting etc.) into the database scheme, the default database is sqlite3.
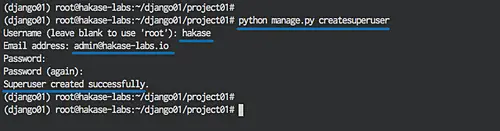
Now create the admin/superuser:
python manage.py createsuperuser
Type your django admin user, email, and password.
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): hakase Email address: [email protected] Password: Password (again): Superuser created successfully.
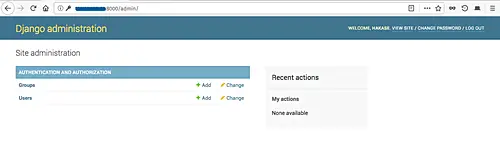
The Django superuser has been created, now you can execute the runserver command, then go to the browser and visit the django admin page:
python manage.py runserver 192.168.10.100:8000
Visit Django admin page: http://192.168.10.100:8000/admin/
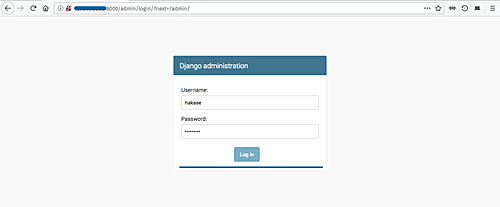
Login with username hakase and your password, you will see the admin page:
Django has been successfully installed inside a virtual environment and we've created a sample Django project named 'project01' inside the 'django01' directory.
Conclusion
Django is a web framework based on the Python programming language, it is released as free software under an open source license and maintained by the Django Software Foundation. Django is very fast and allows it to build web applications rapidly. Django is a web framework that uses the MVC (Model-View-Controller) paradigm. We can install Django on a server with the pip command, in a virtual environment with virtualenv, and directly from the Django git repository.