Server Monitoring With Icinga On Debian Squeeze - Page 2
On this page
3 Configuring Icinga
server1.example.com:
The main Icinga configuration file is /etc/icinga/icinga.cfg, additional configurations are stored in /etc/icinga/commands.cfg and /etc/icinga/resource.cfg. Usually the default configuration is ok, so you don't have to change these files.
The first thing you should change is the contact details in /etc/icinga/objects/contacts_icinga.cfg so that notifications are sent to the correct email address:
vi /etc/icinga/objects/contacts_icinga.cfg
[...]
define contact{
contact_name root
alias Falko Timme
service_notification_period 24x7
host_notification_period 24x7
service_notification_options w,u,c,r
host_notification_options d,r
service_notification_commands notify-service-by-email
host_notification_commands notify-host-by-email
email [email protected]
}
[...]
|
The service checks for localhost (= server1.example.com) are defined in /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg - take a look at that file:
cat /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg
# A simple configuration file for monitoring the local host
# This can serve as an example for configuring other servers;
# Custom services specific to this host are added here, but services
# defined in icinga-common_services.cfg may also apply.
#
define host{
use generic-host ; Name of host template to use
host_name localhost
alias localhost
address 127.0.0.1
}
# Define a service to check the disk space of the root partition
# on the local machine. Warning if < 20% free, critical if
# < 10% free space on partition.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description Disk Space
check_command check_all_disks!20%!10%
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently logged in
# users on the local machine. Warning if > 20 users, critical
# if > 50 users.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description Current Users
check_command check_users!20!50
}
# Define a service to check the number of currently running procs
# on the local machine. Warning if > 250 processes, critical if
# > 400 processes.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_procs!250!400
}
# Define a service to check the load on the local machine.
define service{
use generic-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description Current Load
check_command check_load!5.0!4.0!3.0!10.0!6.0!4.0
}
|
The check_command commands (like check_all_disks) are defined in the Nagios plugin configuration files in the /etc/nagios-plugins/config directory:
ls -l /etc/nagios-plugins/config
root@server1:~# ls -l /etc/nagios-plugins/config
total 144
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 277 May 23 04:55 apt.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 182 May 23 04:55 breeze.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 458 May 23 04:55 dhcp.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 909 May 23 04:55 disk.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1722 May 23 04:55 disk-smb.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 321 May 23 04:55 dns.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 673 May 23 04:55 dummy.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 146 May 23 04:55 flexlm.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 159 May 23 04:55 fping.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 414 May 23 04:55 ftp.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 320 May 23 04:55 games.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 157 May 23 04:55 hppjd.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3579 May 23 04:55 http.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 818 May 23 04:55 ifstatus.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 748 May 23 04:55 ldap.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 195 May 23 04:55 load.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2062 May 23 04:55 mail.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 708 May 23 04:55 mailq.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 385 May 23 04:55 mrtg.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 567 May 23 04:55 mysql.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2355 May 23 04:55 netware.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 420 May 23 04:55 news.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 491 May 23 04:55 nt.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 466 May 23 04:55 ntp.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 426 May 23 04:55 pgsql.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2026 May 23 04:55 ping.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 511 May 23 04:55 procs.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 240 May 23 04:55 radius.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 397 May 23 04:55 real.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 315 May 23 04:55 rpc-nfs.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5550 May 23 04:55 snmp.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 753 May 23 04:55 ssh.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 784 May 23 04:55 tcp_udp.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 438 May 23 04:55 telnet.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 155 May 23 04:55 users.cfg
root@server1:~#
Let's check out the /etc/nagios-plugins/config/disk.cfg file:
cat /etc/nagios-plugins/config/disk.cfg
# 'check_disk' command definition
define command{
command_name check_disk
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '$ARG1$' -c '$ARG2$' -e -p '$ARG3$'
}
# 'check_all_disks' command definition
define command{
command_name check_all_disks
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '$ARG1$' -c '$ARG2$' -e
}
# 'ssh_disk' command definition
define command{
command_name ssh_disk
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_by_ssh -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -C "/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '$ARG1$' -c '$ARG2$' -e -p '$ARG3$'"
}
####
# use these checks, if you want to test IPv4 connectivity on IPv6 enabled systems
####
# 'ssh_disk_4' command definition
define command{
command_name ssh_disk_4
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_by_ssh -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -C "/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '$ARG1$' -c '$ARG2$' -e -p '$ARG3$'" -4
}
|
As you see, the check_all_disks command is defined as /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '$ARG1$' -c '$ARG2$' -e. If you take a look at the /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg file again, you see that we have the line check_command check_all_disks!20%!10% in it. Icinga allows us to pass command line arguments to service checks by separating them with an exclamation mark (!), so check_command check_all_disks!20%!10% means we pass 20% as the first command line argument and 10% as the second command line argument to the /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '$ARG1$' -c '$ARG2$' -e command so that it finally translates to /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w '20%' -c '10%' -e.
If you want to pass a command line argument that contains an exclamation mark, you must escape the exclamation mark with a backslash: \!
The Nagios plugins (i.e., the tools Icinga uses to run checks) are located in the /usr/lib/nagios/plugins directory:
ls -l /usr/lib/nagios/plugins
root@server1:~# ls -l /usr/lib/nagios/plugins
total 2476
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 106120 May 23 04:55 check_apt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 5369 May 23 04:55 check_bgpstate
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2242 May 23 04:55 check_breeze
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 46192 May 23 04:55 check_by_ssh
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_clamd -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 32072 May 23 04:55 check_cluster
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 44816 May 23 04:55 check_dhcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 41392 May 23 04:55 check_dig
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 119216 May 23 04:55 check_disk
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8726 May 23 04:55 check_disk_smb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 45488 May 23 04:55 check_dns
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 28968 May 23 04:55 check_dummy
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3053 May 23 04:55 check_file_age
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 6315 May 23 04:55 check_flexlm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 44656 May 23 04:55 check_fping
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_ftp -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36584 May 23 04:55 check_game
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Aug 23 12:14 check_host -> check_icmp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 41136 May 23 04:55 check_hpjd
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 164624 May 23 04:55 check_http
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 49264 May 23 04:55 check_icmp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 34536 May 23 04:55 check_ide_smart
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 15134 May 23 04:55 check_ifoperstatus
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 12598 May 23 04:55 check_ifstatus
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_imap -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 6887 May 23 04:55 check_ircd
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_jabber -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 40816 May 23 04:55 check_ldap
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Aug 23 12:14 check_ldaps -> check_ldap
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3407 May 23 04:55 check_linux_raid
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36168 May 23 04:55 check_load
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 6026 May 23 04:55 check_log
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 20284 May 23 04:55 check_mailq
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36264 May 23 04:55 check_mrtg
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 34440 May 23 04:55 check_mrtgtraf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 45936 May 23 04:55 check_mysql
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 44688 May 23 04:55 check_mysql_query
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36616 May 23 04:55 check_nagios
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_nntp -> check_tcp
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_nntps -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 48720 May 23 04:55 check_nt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 46288 May 23 04:55 check_ntp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 44880 May 23 04:55 check_ntp_peer
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 42224 May 23 04:55 check_ntp_time
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 60912 May 23 04:55 check_nwstat
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8326 May 23 04:55 check_oracle
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 40400 May 23 04:55 check_overcr
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 40656 May 23 04:55 check_pgsql
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 48848 May 23 04:55 check_ping
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_pop -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 114640 May 23 04:55 check_procs
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 40624 May 23 04:55 check_radius
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 40464 May 23 04:55 check_real
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 9581 May 23 04:55 check_rpc
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Aug 23 12:14 check_rta_multi -> check_icmp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1137 May 23 04:55 check_sensors
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_simap -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 127216 May 23 04:55 check_smtp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 152008 May 23 04:55 check_snmp
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_spop -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36688 May 23 04:55 check_ssh
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_ssmtp -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 37832 May 23 04:55 check_swap
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 49328 May 23 04:55 check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 38128 May 23 04:55 check_time
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Aug 23 12:14 check_udp -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 44560 May 23 04:55 check_ups
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36168 May 23 04:55 check_users
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2936 May 23 04:55 check_wave
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 38152 May 23 04:55 negate
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 36104 May 23 04:55 urlize
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1938 May 23 04:55 utils.pm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 862 May 23 04:55 utils.sh
root@server1:~#
To find out what command line arguments a plugin can take, call that plugin with the --help switch. For example, to find out how the check_disk plugin can be used, run
/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk --help
With this knowledge you can modify the service checks in /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg to your likings, and you can add/modify plugin configurations in the /etc/nagios-plugins/config directory.
Now let's assume we want to add a service check for MySQL, we first take a look at the appropriate plugin configuration:
cat /etc/nagios-plugins/config/mysql.cfg
# 'check_mysql' command definition
define command{
command_name check_mysql
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_mysql -H '$HOSTADDRESS$'
}
# 'check_mysql_cmdlinecred' command definition
define command{
command_name check_mysql_cmdlinecred
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_mysql -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -u '$ARG1$' -p '$ARG2$'
}
# 'check_mysql_database' command definition
define command{
command_name check_mysql_database
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_mysql -d '$ARG3$' -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -u '$ARG1$' -p '$ARG2$'
}
|
The command I want to use is check_mysql_cmdlinecred - this takes a MySQL username and a password as arguments (besides the host address which is taken from the host_name parameter of the service check definition. I want to use the MySQL user nagios with the password howtoforge here, so I add the following section to /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg:
vi /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg
[...]
define service{
use generic-service
host_name localhost
service_description MySQL
check_command check_mysql_cmdlinecred!nagios!howtoforge
}
|
Before we restart Icinga, we must create the MySQL user nagios with the password howtoforge:
mysql -u root -p
GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO nagios@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'howtoforge';
GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO [email protected] IDENTIFIED BY 'howtoforge';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit;
(The USAGE privilege is a synonym for 'no privileges', i.e., the nagios user can connect to MySQL, but not alter or read any data.)
Now we restart Icinga so that our changes take effect:
/etc/init.d/icinga restart
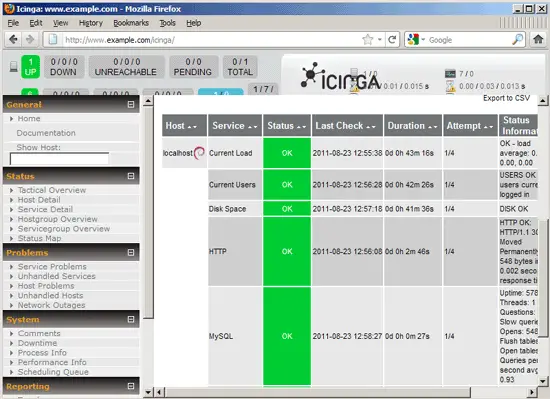
If you check localhost's services in the Icinga web interface now, you should see that a check for MySQL has been added:
Likewise, we can add checks for SMTP, POP3, and IMAP - these are just connection checks, so we don't need any arguments:
vi /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg
[...]
define service{
use generic-service
host_name localhost
service_description SMTP
check_command check_smtp
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name localhost
service_description POP3
check_command check_pop
}
define service{
use generic-service
host_name localhost
service_description IMAP
check_command check_imap
}
|
Restart Icinga...
/etc/init.d/icinga restart
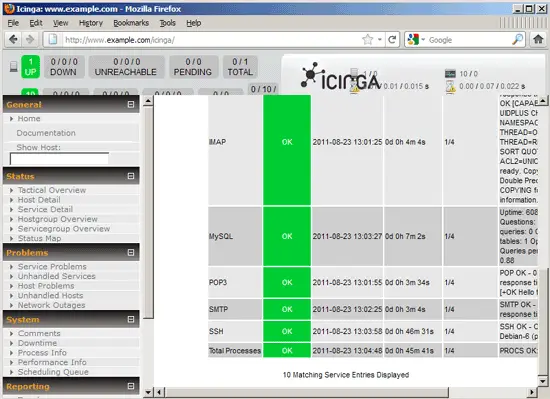
... and a few moments later you should see the new checks in the Icinga web interface:
You might have noticed the SSH and HTTP checks for localhost which are not defined in /etc/icinga/objects/localhost_icinga.cfg. These are defined in hostgroups in the /etc/icinga/objects/hostgroups_icinga.cfg file. A hostgroup allows us to run a service check for multiple servers and define it only once. Take a look at that file:
cat /etc/icinga/objects/hostgroups_icinga.cfg
# Some generic hostgroup definitions
# A simple wildcard hostgroup
define hostgroup {
hostgroup_name all
alias All Servers
members *
}
# A list of your Debian GNU/Linux servers
define hostgroup {
hostgroup_name debian-servers
alias Debian GNU/Linux Servers
members localhost
}
# A list of your web servers
define hostgroup {
hostgroup_name http-servers
alias HTTP servers
members localhost
}
# A list of your ssh-accessible servers
define hostgroup {
hostgroup_name ssh-servers
alias SSH servers
members localhost
}
|
As you see, we have a hostgroup called http-servers and a hostgroup called ssh-servers, and localhost is a member of each of these groups. The service checks for the hostgroups are defined in /etc/icinga/objects/services_icinga.cfg. This file contains service checks and refers to the hostgroups to which these checks should be applied by using the hostgroup_name parameter:
cat /etc/icinga/objects/services_icinga.cfg
# check that web services are running
define service {
hostgroup_name http-servers
service_description HTTP
check_command check_http
use generic-service
notification_interval 0 ; set > 0 if you want to be renotified
}
# check that ssh services are running
define service {
hostgroup_name ssh-servers
service_description SSH
check_command check_ssh
use generic-service
notification_interval 0 ; set > 0 if you want to be renotified
}
|
As you see, the SSH ang HTTP service checks are defined here.