Running Feng Office (Community Edition) On Nginx (LEMP) On Debian Squeeze/Ubuntu 11.10
Version 1.0
Author: Falko Timme  Follow me on Twitter
Follow me on Twitter
This tutorial shows how you can install and run Feng Office (Community Edition) on a Debian Squeeze or Ubuntu 11.10 system that has nginx installed instead of Apache (LEMP = Linux + nginx (pronounced "engine x") + MySQL + PHP). Feng Office is a web-based software that integrates project management, client relationship management, billing, financing, among other features that help you efficiently run your professional services business. nginx is a HTTP server that uses much less resources than Apache and delivers pages a lot of faster, especially static files.
I do not issue any guarantee that this will work for you!
1 Preliminary Note
The Feng Office version I use in this tutorial is 2.0.0beta4. As it is marked as beta, it can still contain some bugs.
I want to install Feng Office in a vhost called www.example.com/example.com here with the document root /var/www/www.example.com/web.
You should have a working LEMP installation, as shown in these tutorials:
- Installing Nginx With PHP5 And MySQL Support On Debian Squeeze
- Installing Nginx With PHP5 (And PHP-FPM) And MySQL Support On Ubuntu 11.10
A note for Ubuntu users:
Because we must run all the steps from this tutorial with root privileges, we can either prepend all commands in this tutorial with the string sudo, or we become root right now by typing
sudo su
2 Configuring PHP
APC is a free and open PHP opcode cacher for caching and optimizing PHP intermediate code. It's similar to other PHP opcode cachers, such as eAccelerator and XCache. It is strongly recommended to have one of these installed to speed up your PHP page.
APC can be installed as follows:
apt-get install php-apc
If you use PHP-FPM as your FastCGI daemon (like in Installing Nginx With PHP5 (And PHP-FPM) And MySQL Support On Ubuntu 11.10), restart it as follows:
/etc/init.d/php5-fpm restart
If you use lighttpd's spawn-fcgi program as your FastCGI daemon (like in Installing Nginx With PHP5 And MySQL Support On Debian Squeeze), we must kill the current spawn-fcgi process (running on port 9000) and create a new one. Run
netstat -tap
to find out the PID of the current spawn-fcgi process:
root@server1:~# netstat -tap
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 *:sunrpc *:* LISTEN 734/portmap
tcp 0 0 *:www *:* LISTEN 2987/nginx
tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN 1531/sshd
tcp 0 0 *:57174 *:* LISTEN 748/rpc.statd
tcp 0 0 localhost.localdom:smtp *:* LISTEN 1507/exim4
tcp 0 0 localhost.localdom:9000 *:* LISTEN 1542/php5-cgi
tcp 0 0 localhost.localdo:mysql *:* LISTEN 1168/mysqld
tcp 0 52 server1.example.com:ssh 192.168.0.198:2462 ESTABLISHED 1557/0
tcp6 0 0 [::]:www [::]:* LISTEN 2987/nginx
tcp6 0 0 [::]:ssh [::]:* LISTEN 1531/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:smtp [::]:* LISTEN 1507/exim4
root@server1:~#
In the above output, the PID is 1542, so we can kill the current process as follows:
kill -9 1542
Afterwards we create a new spawn-fcgi process:
/usr/bin/spawn-fcgi -a 127.0.0.1 -p 9000 -u www-data -g www-data -f /usr/bin/php5-cgi -P /var/run/fastcgi-php.pid
3 Installing Feng Office
The document root of my www.example.com web site is /var/www/www.example.com/web - if it doesn't exist, create it as follows:
mkdir -p /var/www/www.example.com/web
Make sure you have unzip installed:
apt-get install unzip
Next we download Feng Office from http://www.fengoffice.com/web/reference.php?dest=latest_version and place it in our document root:
cd /tmp
wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/opengoo/fengoffice/fengoffice_2.0.0beta4/fengoffice2_0_0beta4.zip
unzip fengoffice2_0_0beta4.zip
cd fengoffice/
mv * /var/www/www.example.com/web/
It is recommended to make the document root and the Feng Office files in it writable by the nginx daemon which is running as user www-data and group www-data:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/www.example.com/web
If you haven't already created a MySQL database for Feng Office (including a MySQL Feng Office user), you can do that as follows (I name the database fengoffice in this example, and the user is called fengoffice_admin, and his password is fengoffice_admin_password):
mysqladmin -u root -p create fengoffice
mysql -u root -p
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON fengoffice.* TO 'fengoffice_admin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'fengoffice_admin_password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON fengoffice.* TO 'fengoffice_admin'@'localhost.localdomain' IDENTIFIED BY 'fengoffice_admin_password';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit;
Next we create an nginx vhost configuration for our www.example.com vhost in the /etc/nginx/sites-available/ directory as follows:
vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/www.example.com.vhost
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.example.com example.com;
root /var/www/www.example.com/web;
if ($http_host != "www.example.com") {
rewrite ^ http://www.example.com$request_uri permanent;
}
index index.php index.html;
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
expires max;
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Deny all attempts to access hidden files such as .htaccess, .htpasswd, .DS_Store (Mac).
location ~ /\. {
deny all;
access_log off;
log_not_found off;
}
client_max_body_size 8M;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_index index.php;
}
}
|
To enable the vhost, we create a symlink to it from the /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ directory:
cd /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/www.example.com.vhost www.example.com.vhost
Reload nginx for the changes to take effect:
/etc/init.d/nginx reload
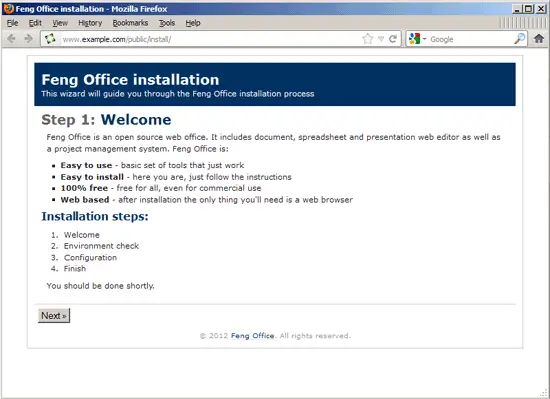
Now we can launch the web-based Feng Office installer by going to http://www.example.com/public/install/ - click on Next:
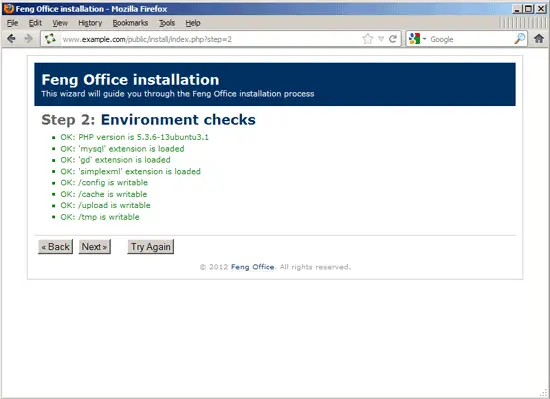
The installer checks if your environment fulfills all requirements. If it does, click on Next:
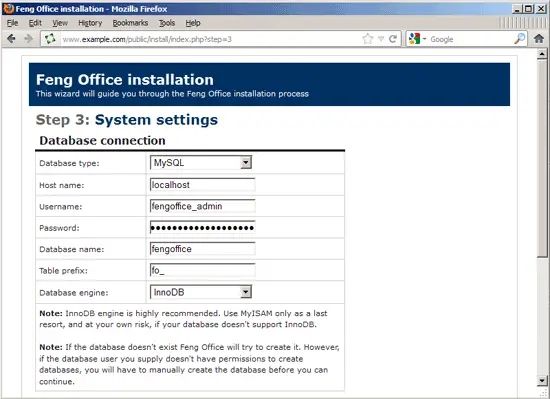
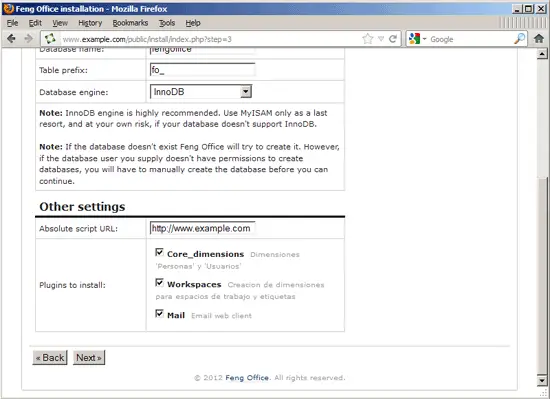
In step 3, fill in your MySQL database details (user: fengoffice_admin; password: fengoffice_admin_password; database: fengoffice). Then scroll down to the bottom of the page...
... and click on Next:
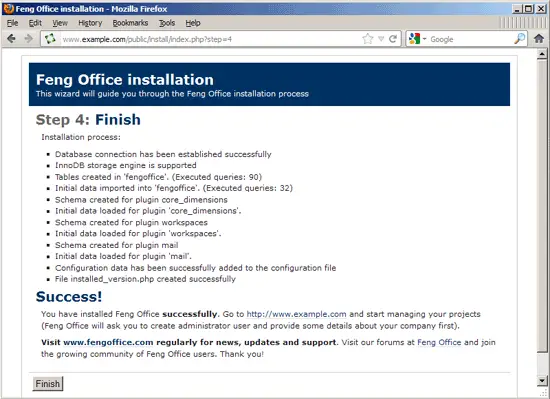
To complete Feng Office installation, click on Finish:
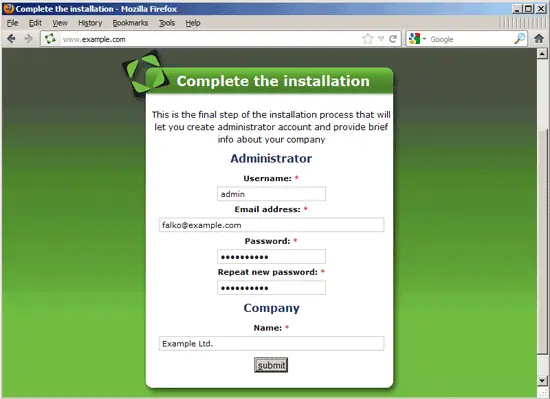
Finally, you have to set up an admin user:
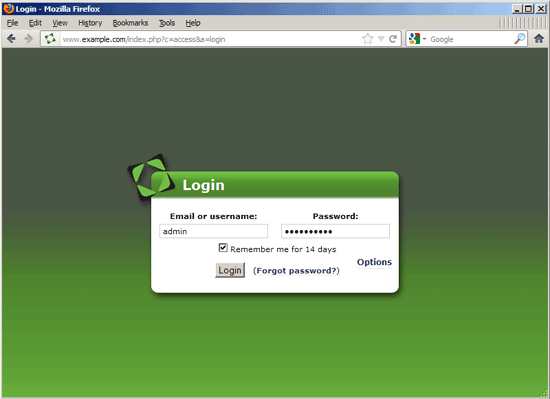
Afterwards, you can log into Feng Office with the admin user details you've just created:
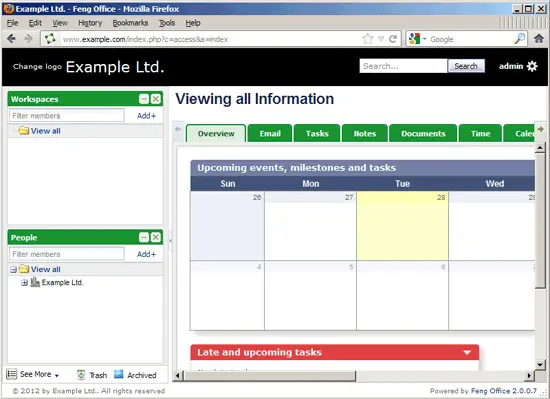
This is how Feng Office looks:
From now on, you can simply use the URL http://www.example.com/ to access Feng Office.
Feng Office uses a cron entry to perform maintenance. Let's add it as follows:
crontab -e
* * * * * /usr/bin/wget -O - -q -t 1 http://www.example.com/cron.php |
That's it, your Feng Office installation is now complete. For further Feng Office setup tweaks, take a look at http://fengoffice.com/web/wiki/doku.php/setup.
4 Links
- Feng Office Community Edition: http://www.fengoffice.com/web/opensource/
- nginx: http://nginx.org/
- nginx Wiki: http://wiki.nginx.org/
- Debian: http://www.debian.org/
- Ubuntu: http://www.ubuntu.com/
About The Author

Falko Timme is the owner of ![]() Timme Hosting (ultra-fast nginx web hosting). He is the lead maintainer of HowtoForge (since 2005) and one of the core developers of ISPConfig (since 2000). He has also contributed to the O'Reilly book "Linux System Administration".
Timme Hosting (ultra-fast nginx web hosting). He is the lead maintainer of HowtoForge (since 2005) and one of the core developers of ISPConfig (since 2000). He has also contributed to the O'Reilly book "Linux System Administration".