Install and Use Docker Compose on CentOS 8
Docker Compose is a tool that can be used to define and run multiple containers as a single service. With Docker Compose, you can link multiple containers and deploy an application from a single command. It is mainly used in the development, testing and staging environment. Docker Compose uses a YAML file to define a complex stack in a file and running it with a single command.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and use Docker Compose in CentOS 8.
Requirements
- A server running CentOS 8.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Install Docker
Before starting, make sure you have Docker installed on your server. If not installed, you will need to add Docker-CE repository to your system. You can add it with the following command:
dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Once the repository is added, install the latest version of docker using the following command:
dnf install docker-ce --nobest -y
systemctl start docker
systemctl enable docker
You can verify the docker version with the following command:
docker --version
You should see the following output:
Docker version 19.03.5, build 633a0ea
Install Docker Compose
By default, Docker Compose is not available in the CentOS 8 default repository. So you will need to download it from the Git repository.
First, install the curl command with the following command:
dnf install curl -y
Next, download the latest version of Docker Compose from the Git reposiotry using curl as shown below:
curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.25.0/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Once the download is completed, make the downloaded binary file executable with the following command:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Next, you can verify the Compose version using the following command:
docker-compose --version
You should see the following output:
docker-compose version 1.25.0, build 0a186604
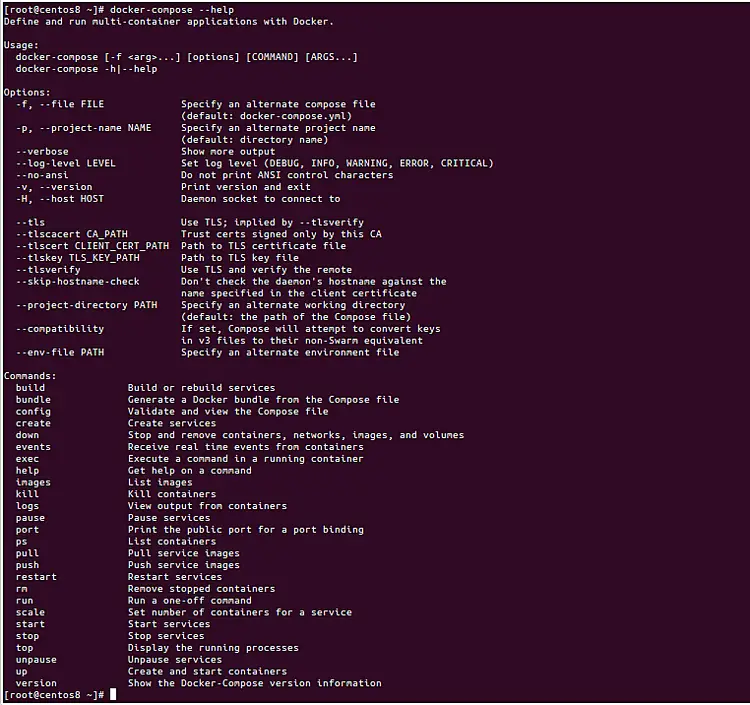
You can see all the options available with docker-compose using the following command:
docker-compose --help
You should see the following page:
Deploy Drupal with Docker Compose
In this section, we will show you how to install Drupal using Docker Compose.
First, create a directory for your drupal with the following command:
mkdir drupal
Next, create a drupal.yaml file inside the drupal directory:
nano drupal/docker-compose.yaml
Add the following contents:
version: '3.3'
services:
drupal:
image: drupal:latest
ports:
- 80:80
volumes:
- drupal_modules:/var/www/html/modules
- drupal_profiles:/var/www/html/profiles
- drupal_themes:/var/www/html/themes
- drupal_sites:/var/www/html/sites
restart: always
postgres:
image: postgres:10
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: your_postgres_password
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
restart: always
volumes:
drupal_modules:
drupal_profiles:
drupal_themes:
drupal_sites:
db_data:
Save and close the file when you are finished. Next, change the directory to drupal and start your Docker container with the following command:
cd drupal
docker-compose up -d
The above command will download and run the drupal and postgresql containers.
You can check your running containers with the following command:
docker-compose ps
You should see the following output:
Name Command State Ports ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- drupal_drupal_1 docker-php-entrypoint apac ... Up 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp drupal_postgres_1 docker-entrypoint.sh postgres Up 5432/tcp
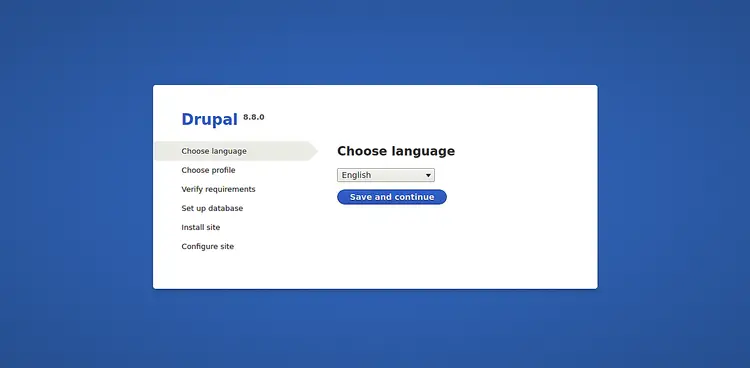
Now, you can visit the URL http://your-server-ip to access the Drupal web installation wizard as shown below:
Working with Docker Compose
In this section, we will show you how to use docker-compose command.
To stop the Docker Compose services run the following command inside the drupal directory:
docker-compose stop
You should see the following output:
Stopping drupal_drupal_1 ... done Stopping drupal_postgres_1 ... done
To start the Docker Compose services run the following command inside the drupal directory:
docker-compose start
To view the log of containers run the following command:
docker-compose logs
To view the logs of a specific container run the following command:
docker-compose logs drupal
You can view your configuration file using the following command:
docker-compose config
To pause and unpause the containers run the following command:
docker-compose pause
Output:
Pausing drupal_postgres_1 ... done Pausing drupal_drupal_1 ... done
docker-compose unpause
Output:
Unpausing drupal_drupal_1 ... done Unpausing drupal_postgres_1 ... done
To remove all the containers run the following command:
docker-compose down
You should see the following output:
Stopping drupal_drupal_1 ... done Stopping drupal_postgres_1 ... done Removing drupal_drupal_1 ... done Removing drupal_postgres_1 ... done Removing network drupal_default
You can also remove the data volumes using the following command:
docker-compose down --volumes
You should see the following output:
Removing network drupal_default WARNING: Network drupal_default not found. Removing volume drupal_drupal_modules Removing volume drupal_drupal_profiles Removing volume drupal_drupal_themes Removing volume drupal_drupal_sites Removing volume drupal_db_data
Conclusion
In the above tutorial, we learned how to install and use Docker Compose in CentOS 8. I hope you have enough knowledge on how to use Docker Compose command to manage the Docker containers.