How to Install Pydio Cells File Sharing Server on Ubuntu 22.04
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble Numbat)
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
On this page
Pydio Cells also known as a Pydio is an open-source file-sharing and synchronization application written in the Golang language. It is run on a server or cloud and used for sharing files with the client. It is a self-hosted document sharing and collaboration tool that allows you to share and access various documents such as files, images, and videos from anywhere using a mobile app, desktop software, or a web browser. It offers native clients for Linux, Windows, and macOS, and mobile clients for Android and iOS.
This guide will explain how to install the Pydio file-sharing application on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Install and Configure MariaDB
Pydio uses MariaDB to store its data, so you must install the MariaDB database server on your server. You can install it by running the following command:
apt install mariadb-server -y
after installing the MariaDB server, you can secure the MariaDB installation using the following command:
mysql_secure_installation
This script will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow root login remotely and remove the test database as shown below:
Set root password? [Y/n] n Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next, log in to MariaDB as a root user:
mysql -u root -p
Once you are logged in, create a database and user with the following command:
CREATE DATABASE pydiodb;
CREATE USER 'pydiodb'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Next, grant all the privileges to the Pydio with the following command:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON pydiodb.* to 'pydiouser'@'localhost';
Next, flush the privileges and exit from the MariaDB shell with the following command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
Install Pydio Cells on Ubuntu 22.04
By default, the Pydio package is not available in the Ubuntu 22.04 repository. So you will need to download it from their official website.
You can download the latest version of Pydio cells using the following command:
distribId=cells
wget -O /usr/bin/cells https://download.pydio.com/latest/${distribId}/release/{latest}/linux-amd64/${distribId}
Once the download is completed, set proper permission on the downloaded file and bind it to the HTTP port using the following command:
chmod +x /usr/bin/cells
setcap 'cap_net_bind_service=+ep' /usr/bin/cells
Next, verify the Pydio cells version using the following command:
cells version
You will get the following output:
Pydio Cells Home Edition Version: 4.0.5 Built: 01 Dec 22 04:24 +0000 Git commit: 406762a4b5bff7b60189291ad4ee16c69a94ecd7 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Go version: go1.19.3
Configure Pydio Cells
Next, configure the Pydio cells using the following command:
cells configure
You will be asked to select the different installation types.
Welcome to Pydio Cells Home Edition installation Pydio Cells Home Edition (v4.0.5) will be configured to run on this machine. Make sure to prepare access and credentials to a MySQL 5.6+ (or MariaDB equivalent) server. Pick your installation mode when you are ready. ? Browser-based (requires a browser access)
Select the browser-based installation and press the Enter key. Once the Pydio Cells is configured, you will get the following output:
Use the arrow keys to navigate: ↓ ↑ → ←
? Installation mode:
? Browser-based (requires a browser access)
Command line (performed in this terminal)
? Browser-based (requires a browser access)
Installation Server is starting...
Listening to: https://0.0.0.0:8080
2022-12-13T05:43:12.641Z INFO pydio.rest.config starting {"service": "pydio.rest.config", "hook router to": "/a/config"}
2022-12-13T05:43:12.659Z INFO pydio.rest.install starting {"service": "pydio.rest.install", "hook router to": "/a/install"}
Open a browser window to: [https://0.0.0.0:8080]
2022-12-13T05:43:14.741Z INFO pydio.server.caddy ? Created a new local CA at "rootCA.pem" ????
2022-12-13T05:43:14.858Z INFO pydio.server.caddy ? Created a new certificate valid for the following names ????
2022-12-13T05:43:14.858Z INFO pydio.server.caddy - "127.0.0.1"
2022-12-13T05:43:14.858Z INFO pydio.server.caddy - "139.84.138.121"
2022-12-13T05:43:14.859Z INFO pydio.server.caddy - "localhost"
2022-12-13T05:43:14.859Z INFO pydio.server.caddy ? The certificate is at "5b92168f4e3239411477f1f5f42539f4.pem"
and the key at "5b92168f4e3239411477f1f5f42539f4-key.pem"
2022-12-13T05:43:14.859Z INFO pydio.server.caddy
2022-12-13T05:43:14.859Z INFO pydio.server.caddy
2022-12-13T05:43:14.859Z INFO pydio.server.caddy ???? If you are behind a reverse proxy, you can either install the RootCA on the proxy machine trust store, or configure your proxy to `insecure_skip_verify` for pointing to Cells.
2022-12-13T05:43:14.860Z INFO pydio.server.caddy ???? If you are developing locally, you may install the RootCA in your system trust store to see a green light in your browser!
2022-12-13T05:43:14.860Z INFO pydio.server.caddy ???? To easily install the RootCA in your trust store, use https://github.com/FiloSottile/mkcert. Set the $CAROOT environment variable to the rootCA folder then use 'mkcert -install'
2022-12-13T05:43:14.860Z INFO pydio.server.caddy
2022-12-13T05:43:14.862Z WARN pydio.server.caddy admin - admin endpoint disabled
2022-12-13T05:43:14.862Z INFO pydio.server.caddy tls.cache.maintenance - started background certificate maintenance{"cache": "0xc0002bdab0"}
2022-12-13T05:43:14.863Z INFO pydio.rest.install ready
2022-12-13T05:43:14.864Z INFO pydio.web.install ready
2022-12-13T05:43:14.865Z INFO pydio.rest.config ready
2022-12-13T05:43:14.865Z WARN pydio.server.caddy tls - stapling OCSP{"error": "no OCSP stapling for [localhost 127.0.0.1 139.84.138.121]: no OCSP server specified in certificate"}
2022-12-13T05:43:14.865Z WARN pydio.server.caddy http - automatic HTTP->HTTPS redirects are disabled{"server_name": "srv0"}
2022-12-13T05:43:14.866Z INFO pydio.server.caddy autosaved config (load with --resume flag) - {"file": "/root/.config/pydio/cells/caddy/autosave.json"}
2022-12-13T05:43:14.866Z INFO pydio.server.caddy tls - cleaning storage unit{"description": "FileStorage:/root/.config/pydio/cells/caddy"}
2022-12-13T05:43:14.866Z INFO pydio.server.caddy tls - finished cleaning storage units
At this point, Pydio Cells is installed and configured. You can now proceed to the next step.
Access Pydio Cells Web Interface
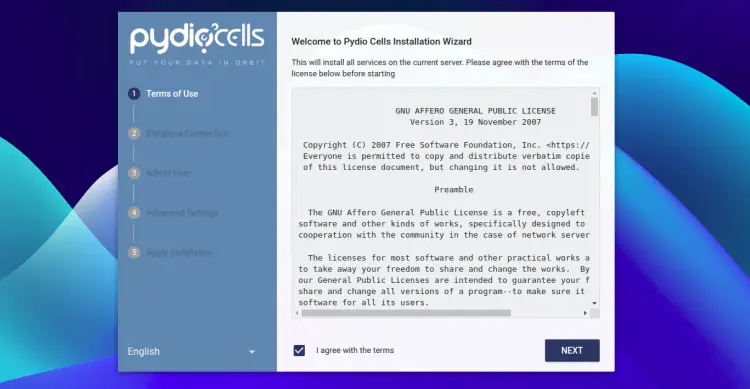
You can now access the Pydio Cells using the URL https://your-server-ip:8080. You should see the Pydio Cells License agreement page:
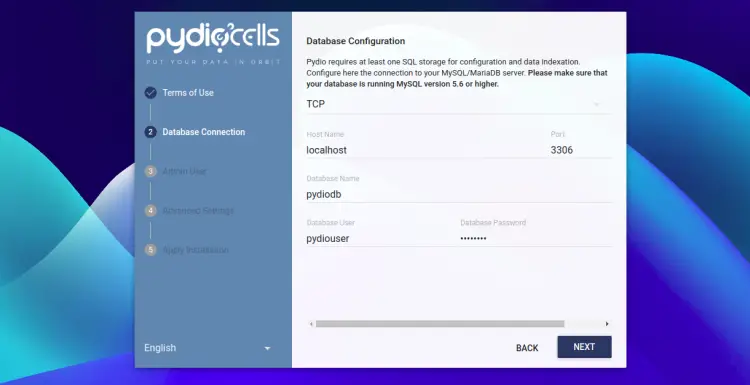
Agree to the License agreement and click on the NEXT button. You should see the database configuration page.
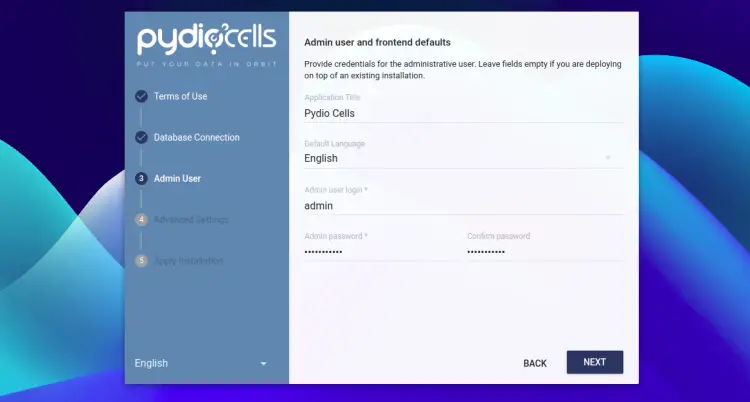
Provide your database configuration and click on the NEXT button. You should see the admin user creation page:
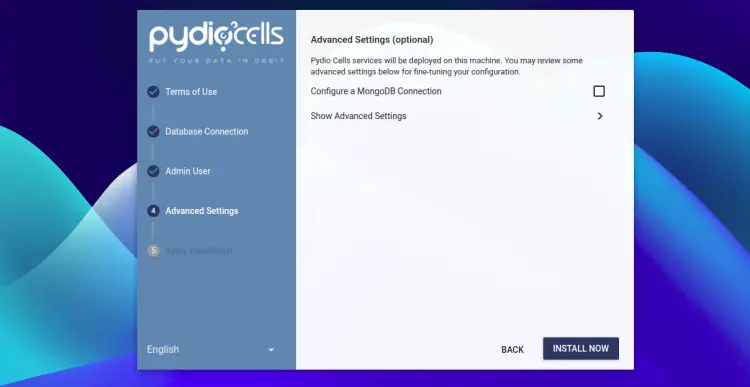
Provide your admin username, password and click on the NEXT button. You should see the following page:
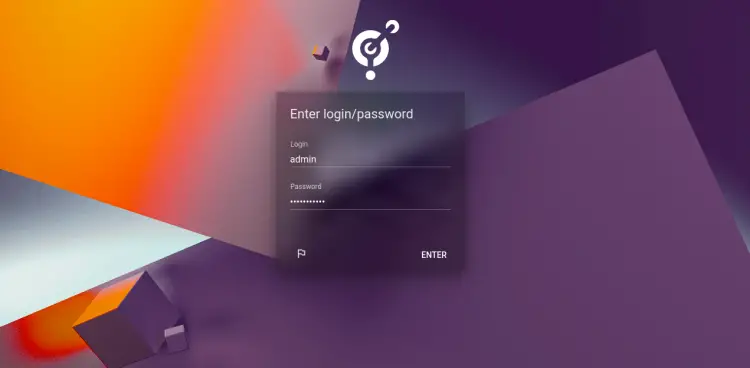
Now, click on the INSTALL NOW button. You should see the Pydio Cells login page:
Provide your admin username, password and click on the ENTER button. You should see the Pydio dashboard on the following page:
Create Systemd Service File for Pydio Cells
Next, you will need to create a systemd service file to manage the Pydio service. First, press the CTRL+C to stop the Pydio service then create a systemd service file with the following command:
nano /etc/systemd/system/cells.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit] Description=Pydio Cells Documentation=https://pydio.com Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target AssertFileIsExecutable=/usr/bin/cells [Service] User=root Group=root PermissionsStartOnly=true AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE ExecStart=/usr/bin/cells start Restart=on-failure StandardOutput=journal StandardError=inherit LimitNOFILE=65536 TimeoutStopSec=5 KillSignal=INT SendSIGKILL=yes SuccessExitStatus=0 WorkingDirectory=/root [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file then reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes:
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start and enable the Pydio service with the following command:
systemctl enable cells
systemctl start cells
You can also check the Pydio status with the following command:
systemctl status cells
You will get the following output:
? cells.service - Pydio Cells
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/cells.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-12-13 11:34:24 UTC; 6s ago
Docs: https://pydio.com
Main PID: 25764 (cells)
Tasks: 119 (limit: 2341)
Memory: 421.6M
CPU: 4.114s
CGroup: /system.slice/cells.service
??25764 /usr/bin/cells start
??25769 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.jobs$
??25775 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.search$
??25781 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.gateway.websocket$
??25783 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.sync.pydiods1$
??25787 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.sync.personal$
??25790 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.sync.cellsdata$
??25802 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.sync.versions$
??25805 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.sync.thumbnail>
??25816 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.tasks$
??25819 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.objects.local1$
??25847 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.index.pydiods1$
??25848 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.index.personal$
??25849 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.index.cellsdat>
??25850 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.index.versions$
??25851 /usr/bin/cells start --fork --config local --registry grpc://:8000 --broker grpc://:8003 ^pydio.grpc.data.index.thumbnai>
Dec 13 12:34:29 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:29.294Z INFO pydio.test.objects Started
Dec 13 12:34:29 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:29.307Z INFO pydio.gateway.grpc Activating self-signed configura>
Dec 13 12:34:29 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:29.308Z INFO pydio.gateway.grpc Started
Dec 13 12:34:30 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:30.191Z INFO pydio.grpc.data.index.pydiods1 Warning: no private >
Dec 13 12:34:30 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:30.194Z INFO pydio.grpc.data.index.personal Warning: no private >
Dec 13 12:34:30 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:30.195Z INFO pydio.grpc.data.index.cellsdata Warning: no private>
Dec 13 12:34:30 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:30.204Z INFO pydio.grpc.data.index.thumbnails Warning: no privat>
Dec 13 12:34:30 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:30.212Z INFO pydio.grpc.data.index.versions Warning: no private >
Dec 13 12:34:30 ubuntu2204 cells[25764]: 2022-12-13T11:34:30.326Z INFO pydio.gateway.proxy Restarting proxy {"caddy>
You can now access the Pydio Cells dashboard using the URL https://your-server-ip:8080
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed and configured Pydio Cells on Ubuntu 22.04. You can now deploy Pydio Cells on your own server, upload your files, documents and images from the Pydio dashboard, and access it from any mobile or web browser. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.