How to Install Matomo Web Analytics on CentOS 7
On this page
- Requirements
- Prerequisites
- Initial steps
- Step 1 - Install MariaDB and create a database for Matomo
- Step 2 - Install PHP and necessary PHP extensions
- Step 3 - Install
acme.shclient and obtain Let">) - Step 3 - Install NGINX and configure NGINX for Matomo
- Step 4 - Install Matomo Analytics
- Step 5 - Complete the Matomo Analytics setup
- Links
Matomo (formerly Piwik) is a free and open source web analytics application developed by a team of international developers, that runs on a PHP/MySQL web server. It tracks online visits to one or more websites and displays reports on these visits for analysis. You can think of it as an alternative to Google Analytics. Matomo is open source and its code is publicly available on Github. Some of the features it has are - A/B Testing, Heatmaps, Funnels, Tracking and Reporting API, Google AdWords, Facebook Ads, Bing Ads, Cost Per Click (CPC), etc. This tutorial will show you how to install Matomo on a CentOS 7 system using Nginx as the web server and we will secure the website with a Let's Encrypt SSL certificate.
Requirements
To run Matomo (Piwik) on your CentOS 7 system you will need a couple of things:
- Web server such as Apache, Nginx, IIS.
- PHP version 5.5.9 or higher with pdo and pdo_mysql or mysqli, gd, xml, curl, and mbsting extensions. PHP 7+ is recommended.
- MySQL version 5.5 or higher, or the equivalent MariaDB version. MySQL 5.7+ is recommended.
Prerequisites
- An operating system running CentOS 7.
- A non-root user with sudo privileges.
Initial steps
Check your CentOS version:
cat /etc/centos-release
Set up the timezone:
timedatectl list-timezones
sudo timedatectl set-timezone 'Region/City'Update your operating system packages (software). This is an important first step because it ensures you have the latest updates and security fixes for your operating system's default software packages:
sudo yum update -yInstall some essential packages that are necessary for basic administration of the CentOS operating system:
sudo yum install -y curl wget vim git unzip socat epel-releaseStep 1 - Install MariaDB and create a database for Matomo
Matomo supports MySQL and MariaDB databases. In this tutorial, we will use MariaDB as the database server.
Create MariaDB 10.2 YUM repository for CentOS:
sudo vim /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repoCopy and paste the following text into it:
# MariaDB 10.2 CentOS repository list - created 2017-12-11 23:19 UTC
# http://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/
[mariadb]
name=MariaDB
baseurl=https://yum.mariadb.org/10.2/centos7-amd64
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1After the file is in place, install MariaDB by running:
sudo yum install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-clientCheck the MariaDB version:
mysql --version
# mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.2.21-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using readline 5.1Start and enable MariaDB service:
sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.serviceRun mysql_secure installation script to improve MariaDB security and set the password for MariaDB root user:
sudo mysql_secure_installationAnswer each of the questions:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Press Enter
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password: your_secure_password
Re-enter new password: your_secure_password
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] YConnect to MariaDB shell as the root user:
sudo mysql -u root -p
# Enter password
Create an empty MariaDB database and user for Matomo and remember the credentials:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE dbname;
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON dbname.* TO 'username' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Exit from MariaDB:
MariaDB [(none)]> exitReplace dbname, username and password with your own names.
Step 2 - Install PHP and necessary PHP extensions
Setup the Webtatic YUM repo:
sudo rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpmInstall PHP, as well as the necessary PHP extensions:
sudo yum install -y php72w php72w-cli php72w-fpm php72w-common php72w-curl php72w-gd php72w-xml php72w-mbstring php72w-mysqlnd php72w-jsonTo show PHP compiled in modules, you can run:
php -m
ctype
curl
exif
fileinfo
. . .
. . .Check the PHP version:
php --version
# PHP 7.2.14 (cli) (built: Jan 8 2019 09:59:17) ( NTS )
# Copyright (c) 1997-2018 The PHP Group
# Zend Engine v3.2.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2018 Zend Technologies
Start and enable PHP-FPM service:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm.service
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm.serviceWe can move on to the next step, which is obtaining free SSL certs from Let's Encrypt CA.
Step 3 - Install acme.sh client and obtain Let's Encrypt certificate (optional)
Securing your website with HTTPS is not necessary, but it is a good practice to secure your site traffic. In order to obtain a TLS certificate from Let's Encrypt we will use Acme.sh client. Acme.sh is a pure UNIX shell software for obtaining TLS certificates from Let's Encrypt with zero dependencies.
Download and install Acme.sh:
sudo mkdir /etc/letsencrypt
git clone https://github.com/Neilpang/acme.sh.git
cd acme.sh
sudo ./acme.sh --install --home /etc/letsencrypt --accountemail [email protected]
cd ~Check Acme.sh version:
/etc/letsencrypt/acme.sh --version
# v2.8.0Obtain RSA and ECC/ECDSA certificates for your domain/hostname:
# RSA 2048
sudo /etc/letsencrypt/acme.sh --issue --standalone --home /etc/letsencrypt -d example.com --keylength 2048
# ECDSA
sudo /etc/letsencrypt/acme.sh --issue --standalone --home /etc/letsencrypt -d example.com --keylength ec-256After running the above commands, your certificates and keys will be in:
- For RSA:
/etc/letsencrypt/example.comdirectory. - For ECC/ECDSA:
/etc/letsencrypt/example.com_eccdirectory.
Step 3 - Install NGINX and configure NGINX for Matomo
Matomo can work fine with many popular web server software. In this tutorial, we selected Nginx.
Download and install Nginx from the CentOS repository:
sudo yum install -y nginxCheck the Nginx version:
sudo nginx -v
Start and enable Nginx service:
sudo systemctl start nginx.service
sudo systemctl enable nginx.serviceConfigure Nginx for Matomo by running:
sudo vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/matomo.conf
And populate the file with the following configuration:
server {
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:80;
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/matomo/;
index index.php;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/fullchain.cer;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/example.com.key;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/fullchain.cer;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/example.com.key;
location ~ ^/(index|matomo|piwik|js/index).php {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
try_files $fastcgi_script_name =404;
set $path_info $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param HTTP_PROXY "";
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}
location = /plugins/HeatmapSessionRecording/configs.php {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
try_files $fastcgi_script_name =404;
set $path_info $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param HTTP_PROXY "";
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
}
location ~* ^.+\.php$ {
deny all;
return 403;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ /(config|tmp|core|lang) {
deny all;
return 403;
}
location ~ \.(gif|ico|jpg|png|svg|js|css|htm|html|mp3|mp4|wav|ogg|avi|ttf|eot|woff|woff2|json)$ {
allow all;
}
location ~ /(libs|vendor|plugins|misc/user) {
deny all;
return 403;
}
}NOTE: For complete and production ready Nginx config for Matomo visit https://github.com/matomo-org/matomo-nginx.
Check Nginx configuration for syntax errors:
sudo nginx -tReload Nginx service:
sudo systemctl reload nginx.serviceStep 4 - Install Matomo Analytics
Create /var/www directory:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/Navigate to /var/www directory:
cd /var/www/Download the latest release Matomo via wget and unzip it:
sudo wget https://builds.matomo.org/matomo.zip && sudo unzip matomo.zip
Remove downloaded matomo.zip file:
sudo rm matomo.zipChange ownership of the /var/www/matomo directory to nginx user:
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/matomoRun sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf and set user and group to nginx. Initially, it will be set to user and group apache.
sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
# user = nginx
# group = nginxRestart PHP-FPM service.
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm.serviceStep 5 - Complete the Matomo Analytics setup
Open your site in a web browser and follow the Matomo web installation wizard.
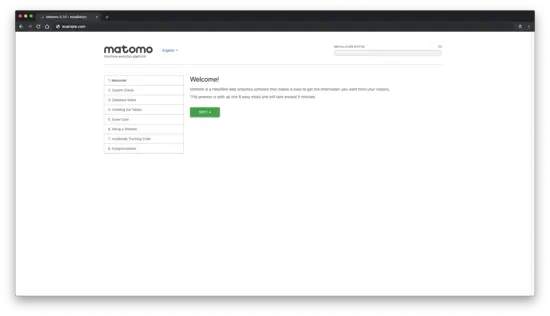
First, Matomo welcome message should appear. Click on the "Next" button:
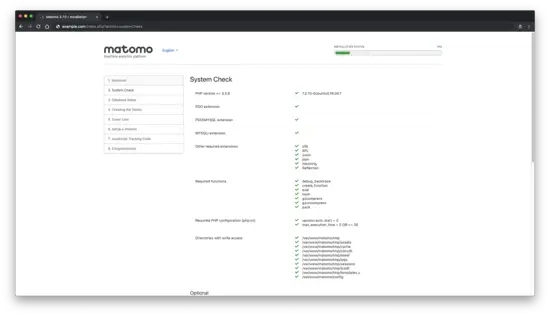
After, you will see a "System Check" page. If something is missing, you will see a warning. If everything is marked with green checkmark click on the "Next" button to procceed to the next step:
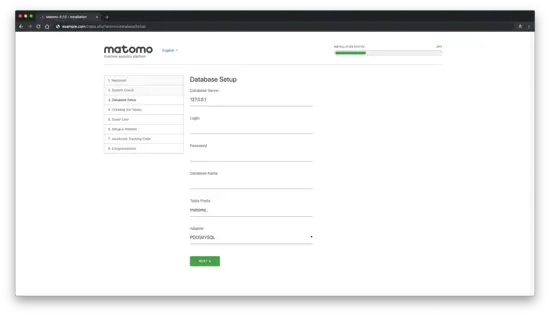
Next, fill in database details and click on the "Next" button:
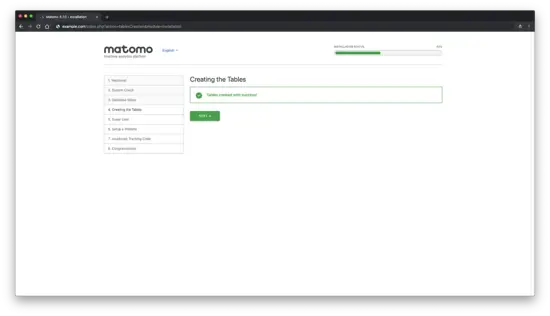
If everything went well with database setup you should see "Tables created with success!" message:
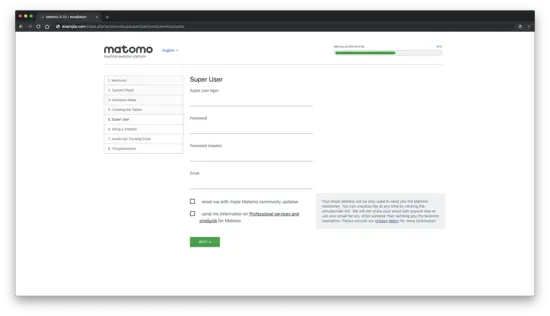
Create Matomo superuser account and click on the "Next" button:
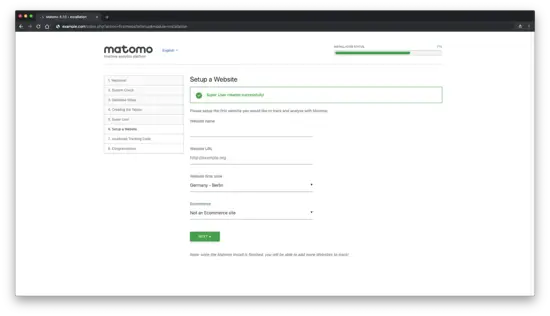
Next, set up the first website you would like to track and analyze with Matomo. Later on, you can add more sites to track with Matomo:
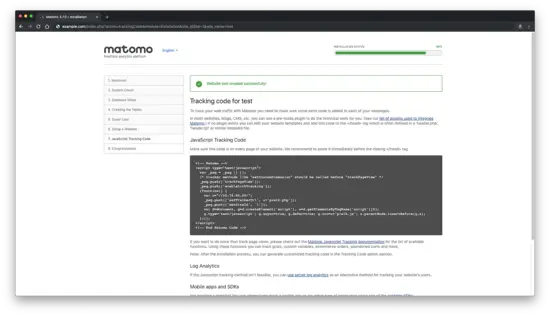
Next, you will be provided with the JavaScript tracking code for your site that you need to add to start tracking.
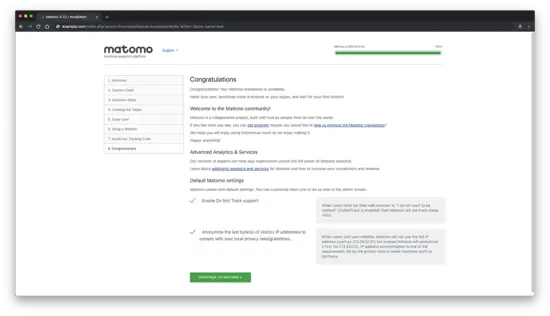
Next, you should see that Matomo installation is completed.
Congratulations! Your Matomo installation is complete.