How to Install Elgg Social Network on Ubuntu 20.04
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
On this page
Elgg is a free and open-source social networking platform used for building an online social environment. It is simple, easy to use, customizable, and provides a powerful web UI to manage the content over the internet. It allows schools, colleges, and universities to create their own social environment in campus.
This post will show you how to install Elgg with Nginx and Let's Encrypt SSL on Ubuntu 20.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 20.04.
- A valid domain name pointed with your server IP.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Getting Started
First, update the system packages to the updated version by running the following command:
apt-get update -y
Once all the packages are updated, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Nginx, PHP, and MariaDB
Before starting, make sure Nginx, MariaDB, PHP, and other PHP extensions are installed in your system. If not installed you can install them with the following command:
apt-get install nginx mariadb-server php php-cli php-fpm php-json php-pdo php-mysql php-zip php-gd php-mbstring php-curl php-xml php-pear php-bcmath unzip curl -y
After installing all the packages, edit the php.ini file and tweak some settings:
nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini
Change the following values as per your requirements:
memory_limit = 256M post_max_size = 64M upload_max_filesize = 32M date.timezone = UTC
Save and close the file then restart the PHP-FPM service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Create a Database for Elgg
Next, you will need to create a database and user for Elgg. First, log in to MySQL with the following command:
mysql
Once you are connected, create a database and user with the following command:
CREATE DATABASE elgg_db;
CREATE USER elgg_user@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'securepassword';
Next, grant all the privileges to the Elgg database with the following command:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON elgg_db.* TO elgg_user@localhost;
Next, flush the privileges and exit from the MySQL with the following command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
At this point, the MariaDB database and user are created for Elgg. You can now proceed to the next step.
Download Elgg
Next, you will need to download the latest version of Elgg from the Github website. You can download it with the following command:
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/Elgg/Elgg/releases/latest |grep browser_download_url | cut -d '"' -f 4 | wget -i -
Once the download is completed, unzip the downloaded file with the following command:
unzip elgg-*.zip
Next, move the extracted directory to the Nginx web root directory with the following command:
mv elgg-*/ /var/www/html/elgg
Next, create a data directory for Elgg and set proper ownership to the data directory and elgg directory:
mkdir /var/www/html/data
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/elgg/
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/data
chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/elgg
At this point, Elgg is downloaded to the Nginx web root directory. You can now proceed to the next step.
Configure Nginx for Elgg
Next, you will need to create an Nginx virtual host configuration file to host Elgg on the internet. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/elgg.conf
Add the following lines:
server {
listen 80;
server_name elgg.domain.com;
root /var/www/html/elgg;
index index.php;
access_log /var/log/nginx/elgg_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/elgg_error.log;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(.*)$;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
}
Save and close the file then verify the Nginx for any syntax error:
nginx -t
You should see the following output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Next, restart the Nginx service using the following command:
systemctl restart nginx
You can check the status of the Nginx service with the following command:
systemctl status nginx
You should see the following output:
? nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2021-07-30 15:43:55 UTC; 5s ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Process: 18432 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 18443 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 18445 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4691)
Memory: 3.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??18445 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
??18446 nginx: worker process
??18447 nginx: worker process
Jul 30 15:43:55 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Starting A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server...
Jul 30 15:43:55 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Started A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server.
Access Elgg Web UI
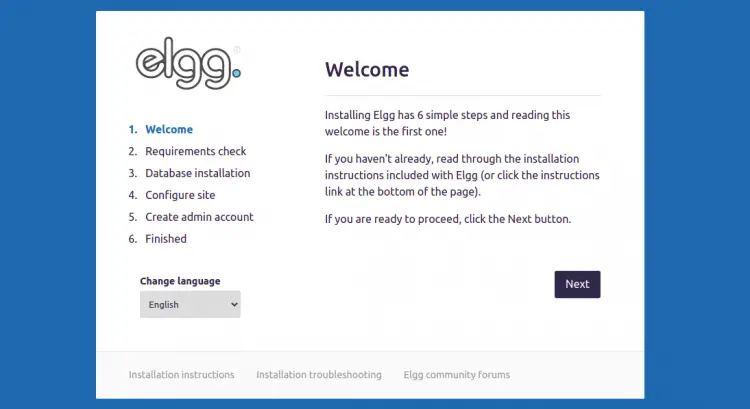
Now, open your web browser and access the Elgg web interface using the URL http://elgg.domain.com. You will be redirected to the Elgg welcome page:
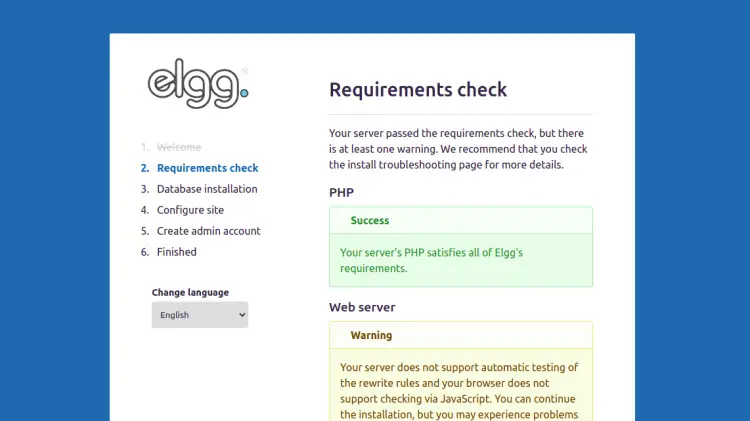
Click on the Next button. You should see the PHP requirements check page:
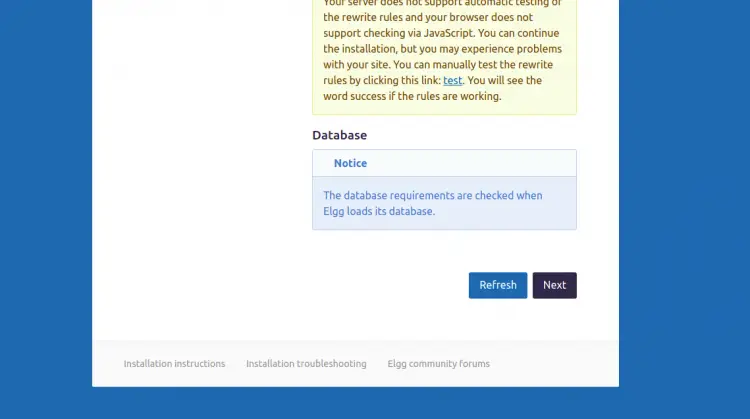
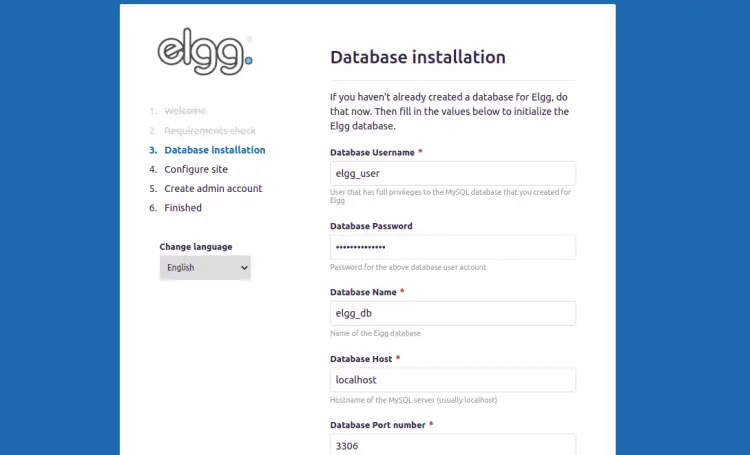
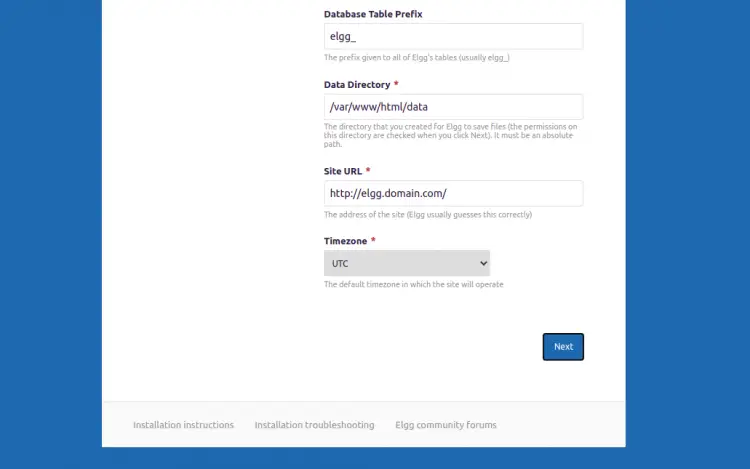
Make sure all the requirements are installed then click on the Next button. You should see the database configuration page:
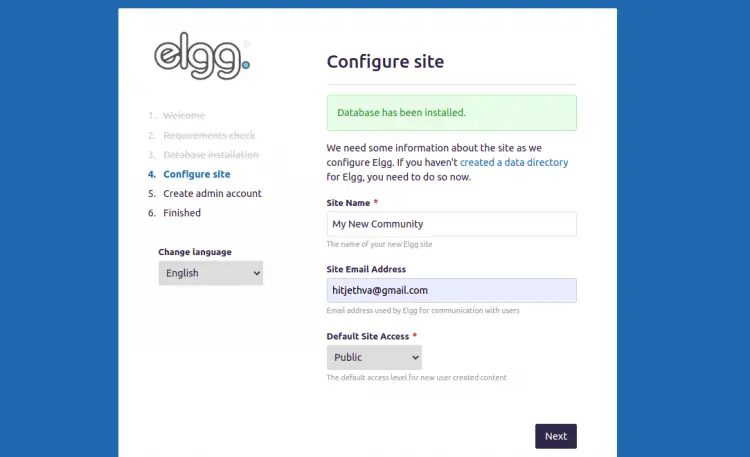
Provide your database information, data directory, site URL, and click on the Next button. You should see the site configuration page:
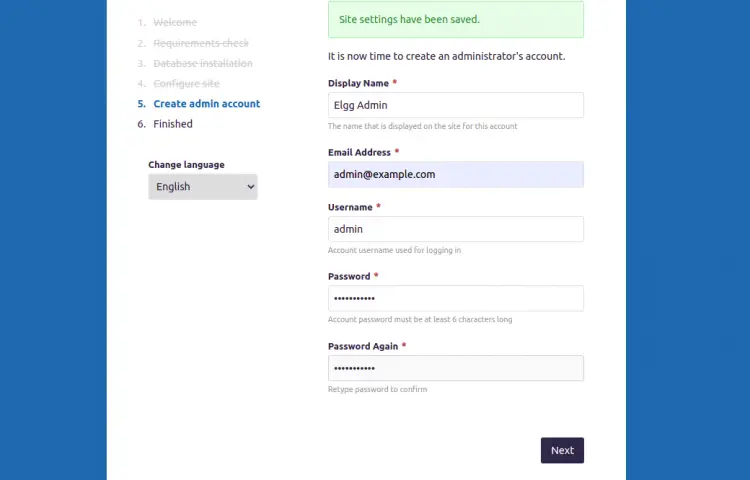
Provide your site information and click on the Next button. You should see the Elgg admin user creation page:
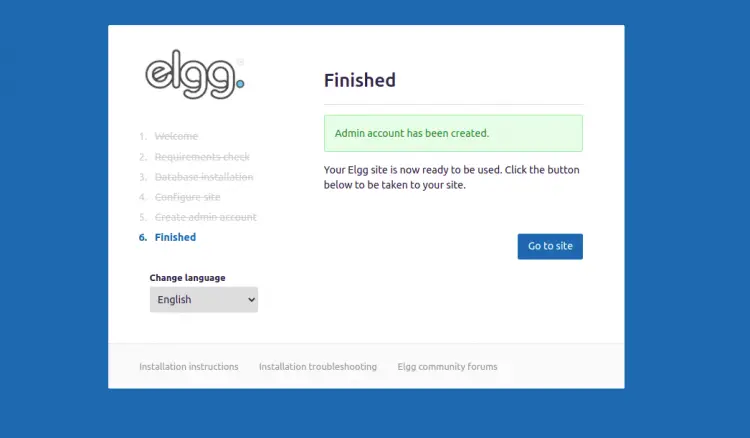
Provide your admin username, email, password, and click on the Next button. Once the installation has been completed successfully, you should see the following page:
Click on the Go to site. You should see the Elgg login page:
Provide your admin username, password and click on the Log in button. You should see the Elgg dashboard on the following page:
Secure Elgg with Let's Encrypt SSL
It is always a good idea to secure your website with Let's Encrypt SSL. First, install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client in your server with the following command:
apt-get install python3-certbot-nginx -y
Once installed, secure your website with Let's Encrypt SSL by running the following command:
certbot --nginx -d elgg.domain.com
You will be asked to provide a valid email address and accept the term of service as shown below:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): [email protected] - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (A)gree/(C)ancel: A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (Y)es/(N)o: Y Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for elgg.domain.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/conf.d/elgg.conf
Next, choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS as shown below:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2
Type 2 and hit Enter to finish the installation. You should see the following output:
Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/conf.d/elgg.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://elgg.domain.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=elgg.domain.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/elgg.domain.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/elgg.domain.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2021-05-30. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le - We were unable to subscribe you the EFF mailing list because your e-mail address appears to be invalid. You can try again later by visiting https://act.eff.org.
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed Elgg with Nginx and Let's Encrypt SSL on Ubuntu 20.04. You can now easily implement your own social networking platform on your campus easily.