How To Install Cacti Monitoring Tool on Ubuntu 22.04
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
On this page
Cacti is an open-source network monitoring and graphing tool written in PHP. It is web-based and uses the MySQL database to store all of the necessary information to create graphs and populate them. It has the ability to poll network devices as well as track bandwidth usage and graph it very nicely. It uses SNMP protocol to gather information about remote devices, including switches and routers. With Cacti, you can monitor bandwidth utilization and network traffic via a web browser.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install the Cacti monitoring tool on Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Install Required Dependencies
First, you will need to update the APT package index to the latest version. You can update it with the following command:
apt-get update -y
After updating the APT package index, install other required dependencies by running the following command:
apt-get install snmp php-snmp rrdtool librrds-perl unzip curl git gnupg2 -y
After installing all the dependencies, you can proceed to install the LAMP server.
Install LAMP Server
Next, you will need to install the Apache web server, MariaDB, PHP and other required PHP extensions to your server. You can install all of them by running the following command:
apt-get install apache2 mariadb-server php php-mysql libapache2-mod-php php-xml php-ldap php-mbstring php-gd php-gmp -y
Once all the packages are installed, edit the PHP configuration file and modify default settings:
nano /etc/php/8.1/apache2/php.ini
Change the following lines:
memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 60 date.timezone = UTC
Save and close the file, then edit another PHP configuration file change the default settings:
nano /etc/php/8.1/cli/php.ini
Change the following lines:
memory_limit = 512M max_execution_time = 60 date.timezone = UTC
Save and close the file when you are finished. Then, restart the Apache service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart apache2
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Create a Database
Cacti uses MariaDB as a database backend. So you will need to create a database and user for Cacti.
First, edit the MariaDB default configuration file and tweak some default settings:
nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Add / Modify the following lines inside [mysqld] section:
collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_ci max_heap_table_size = 128M tmp_table_size = 64M join_buffer_size = 64M innodb_file_format = Barracuda innodb_large_prefix = 1 innodb_buffer_pool_size = 512M innodb_flush_log_at_timeout = 3 innodb_read_io_threads = 32 innodb_write_io_threads = 16 innodb_io_capacity = 5000 innodb_io_capacity_max = 10000 innodb_doublewrite = OFF
Save and close the file, then restart the MariaDB service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart mariadb
Next, log in to the MariaDB shell with the following command:
mysql
Once login, create a database and user for Cacti with the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database cactidb;
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON cactidb.* TO cactiuser@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Next, flush the privileges and exit from the MariaDB shell with the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
MariaDB [(none)]> exit;
Next, you will need to import timezone data to the MySQL database. You can import it with the following command:
mysql mysql < /usr/share/mysql/mysql_test_data_timezone.sql
Next, log in to the MariaDB shell and grant the required privileges on the MySQL timezone with the following command:
mysql
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT SELECT ON mysql.time_zone_name TO cactiuser@localhost;
Next, flush the privileges and exit from the MariaDB shell with the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges;
MariaDB [(none)]> exit;
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Install and Configure Cacti
Download the latest version of Cacti from its official website using the following command:
wget https://www.cacti.net/downloads/cacti-latest.tar.gz
Once the download is completed, extract the downloaded file with the following command:
tar -zxvf cacti-latest.tar.gz
Next, move the extracted directory to the Apache root directory with the following command:
mv cacti-1* /var/www/html/cacti
Next, import the database to the Cacti database with the following command:
mysql cactidb < /var/www/html/cacti/cacti.sql
Next, edit the Cacti config.php file and define your database settings:
nano /var/www/html/cacti/include/config.php
Change the following lines:
$database_type = 'mysql'; $database_default = 'cactidb'; $database_hostname = 'localhost'; $database_username = 'cactiuser'; $database_password = 'password'; $database_port = '3306';
Save and close the file, then create a log file for Cacti.
touch /var/www/html/cacti/log/cacti.log
Next, set the ownership and permission of the cacti directory with the following command:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/cacti/
chmod -R 775 /var/www/html/cacti/
Next, create a new Cacti cron job file with the following command:
nano /etc/cron.d/cacti
Add the following line:
*/5 * * * * www-data php /var/www/html/cacti/poller.php > /dev/null 2>&1
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Create an Apache Virtual Host for Cacti
Next, you will need to create an Apache virtual host configuration file for Cacti. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/cacti.conf
Add the following lines:
Alias /cacti /var/www/html/cacti
<Directory /var/www/html/cacti>
Options +FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
<IfVersion >= 2.3>
Require all granted
</IfVersion>
<IfVersion < 2.3>
Order Allow,Deny
Allow from all
</IfVersion>
AddType application/x-httpd-php .php
<IfModule mod_php.c>
php_flag magic_quotes_gpc Off
php_flag short_open_tag On
php_flag register_globals Off
php_flag register_argc_argv On
php_flag track_vars On
# this setting is necessary for some locales
php_value mbstring.func_overload 0
php_value include_path .
</IfModule>
DirectoryIndex index.php
</Directory>
Save and close the file, then enable the virtual host file with the following command:
a2ensite cacti
Next, restart the Apache service to apply the configuration changes:
systemctl restart apache2
You can also verify the status of the Apache service with the following command:
systemctl status apache2
You should get the following output:
? apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor prese>
Active: active (running) since Sun 2022-07-24 03:58:11 UTC; 7s ago
Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
Process: 12847 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/apachectl start (code=exited, status=0/S>
Main PID: 12851 (apache2)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 2242)
Memory: 13.7M
CPU: 103ms
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
??12851 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??12852 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??12853 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??12854 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??12855 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
??12856 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
Jul 24 03:58:11 ubuntu systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Launch Cacti Web Installation Wizard
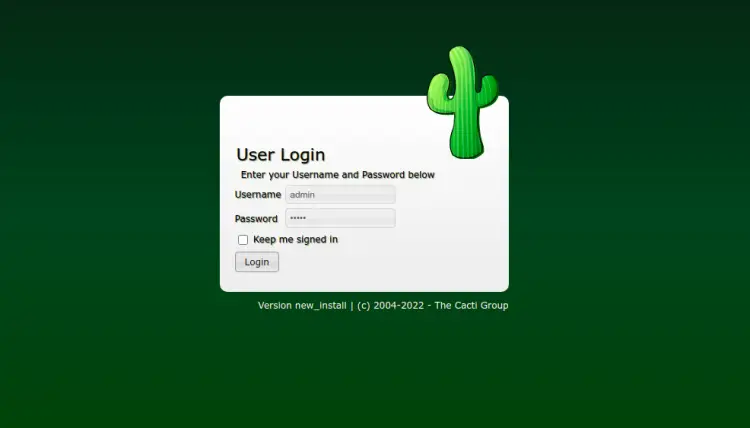
Now, open your web browser and access the Cacti installation using the URL http://your-server-ip/cacti. You will be redirected to the Cacti login page:
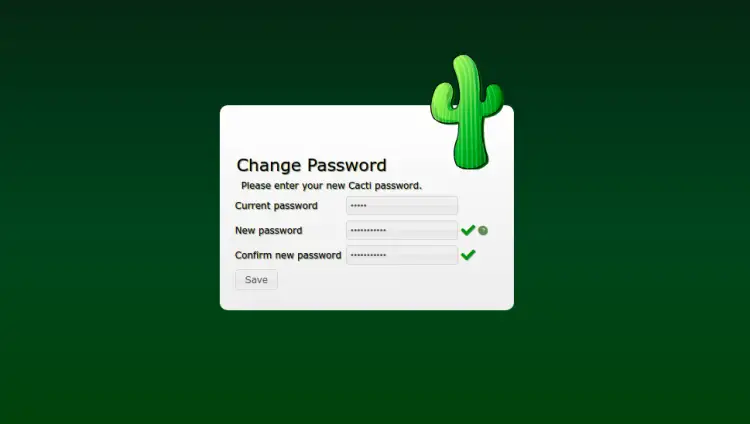
Provide default admin username and password as admin and click on the Login button. You should see the password reset screen:
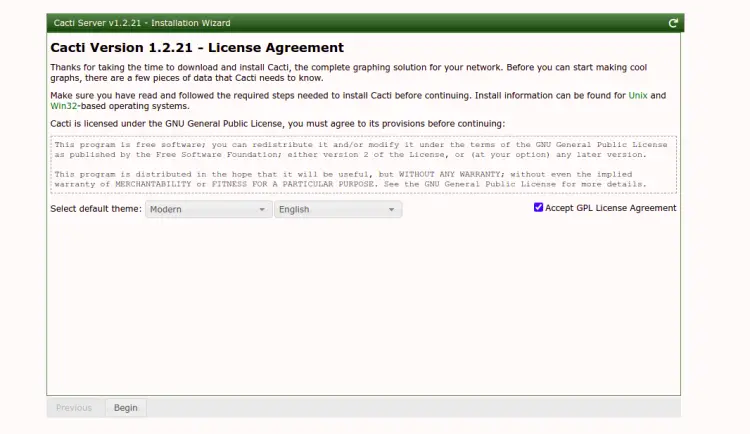
Change your default password and click on the Save button. You should see the License agreement page:
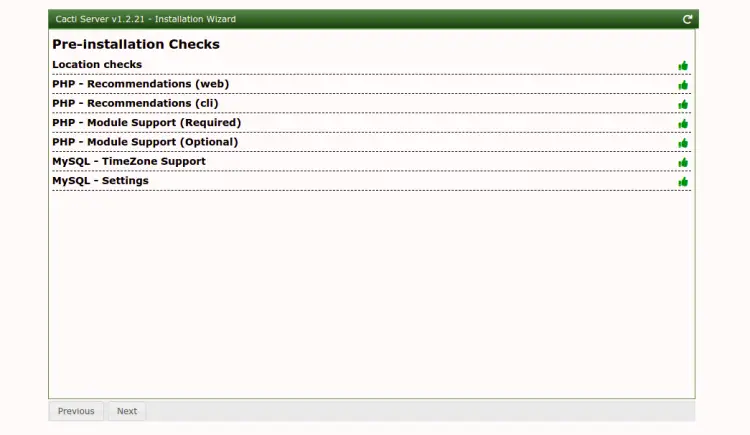
Accept the agreement and click on the Begin button. You should see the pre-installation check screen:
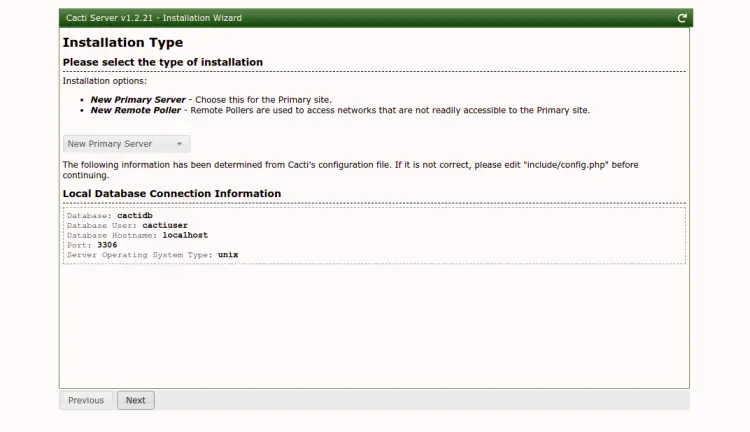
Click on the Next button. You should see the Installation Type screen:
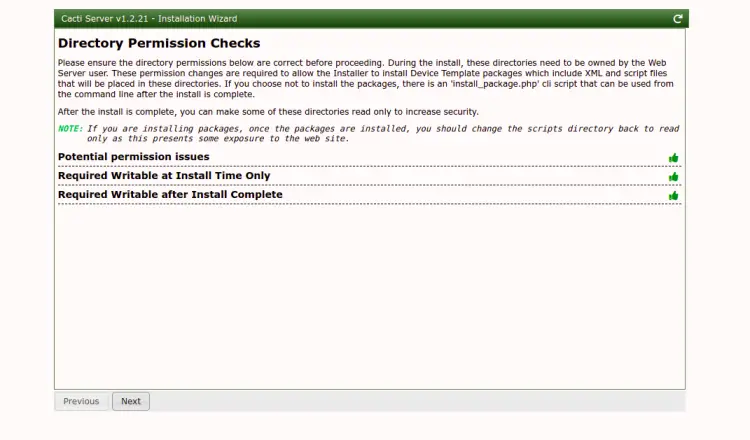
Select your desired installation type and click on the Next button. You should see the Directory Permission check screen:
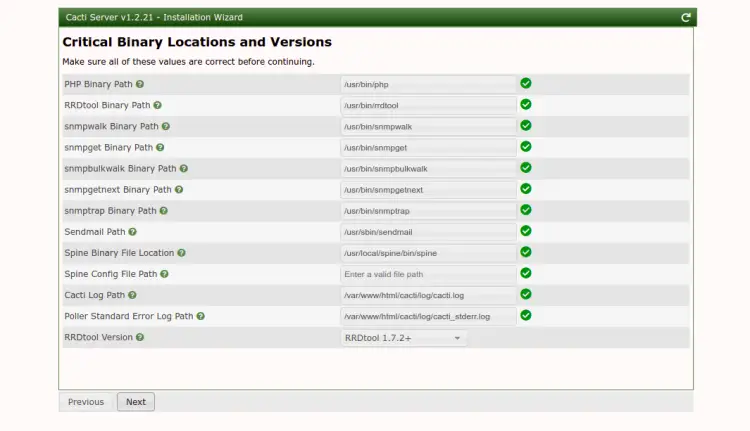
Click on the Next button. You should see the Binary Locations and Versions check screen:
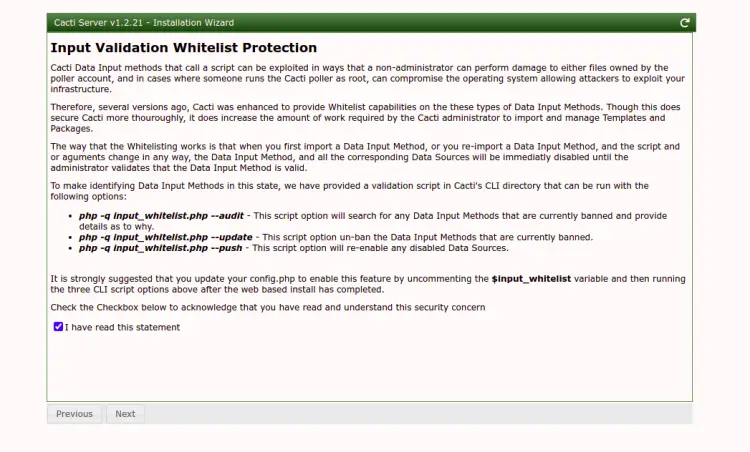
Click on the Next button. You should see the following screen:
Check the "I have read this statement" and click on the Next button. You should see the following screen:
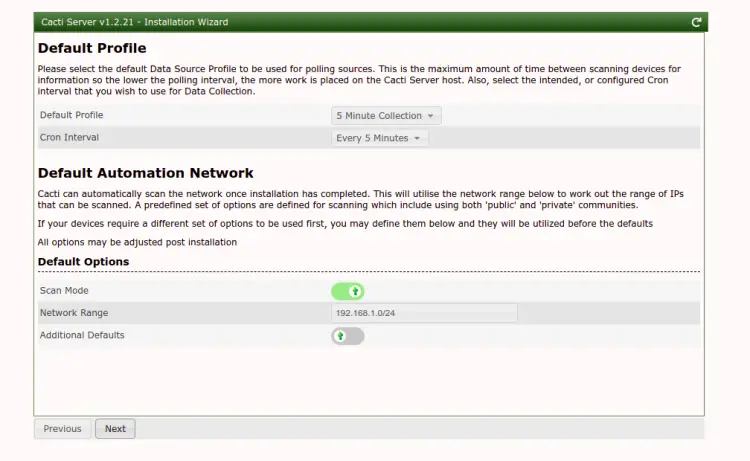
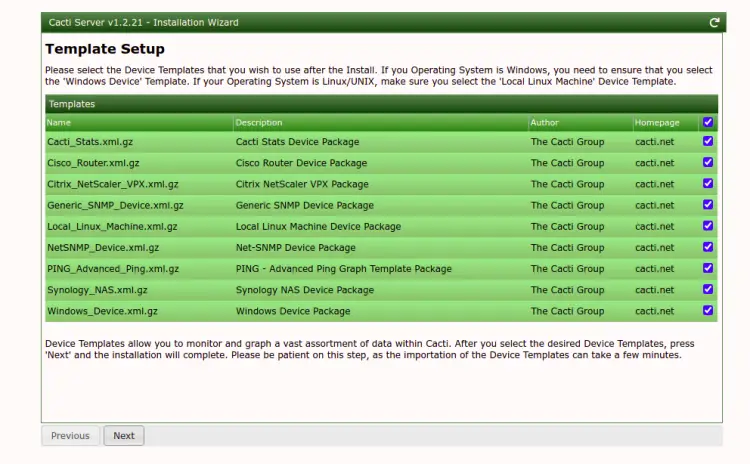
Select your desired options and click on the Next button. You should see the template setup screen:
Click on the Next button. You should see the following screen:
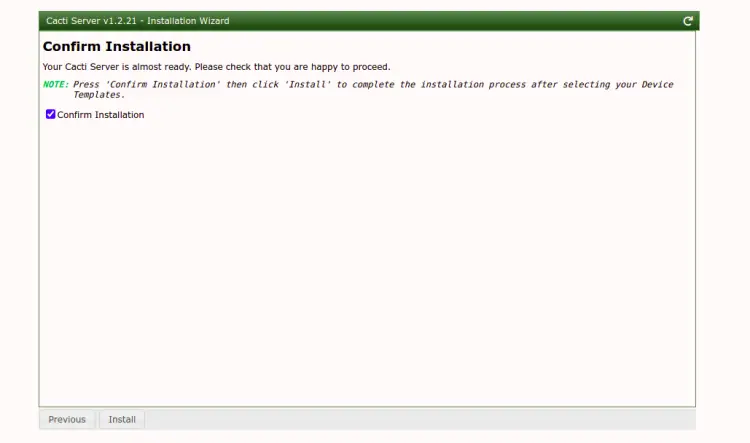
Click on the Next button. You should see the Confirm installation screen:
Check the "Confirm Installation" and click on the Install button. Once the installation has been completed, you should see the following screen:
Click on the Get Started button. You should see the Cacti dashboard on the following screen:
Conclusion
In this post, we explained how to install and configure the Cacti monitoring tool on Ubuntu 22.04 server. You can now add network devices from the Cacti dashboard and start monitoring them from the web browser. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.