Firewall Access Policy Rulesets, Part 3
| Author: [email protected] http://www.fwbuilder.org |
This article continues the series of articles on Firewall Builder, a graphical firewall configuration and management tool that supports many Open Source firewall platforms as well as Cisco IOS access lists and Cisco ASA (PIX). Firewall Builder was introduced on this site earlier with articles Getting Started With Firewall Builder, Using Firewall Object In Firewall Builder. Firewall Access Policy Rulesets, Part 1. Firewall Access Policy Rulesets, Part 2.
This article continues with examples of Access Policy rules and demonstrates generated configurations for iptables, PF and Cisco PIX.
More information on Firewall Builder, pre-built binary packages and source code, documentation can be found on the project web site at http://www.fwbuilder.org/. Numerous examples of iptables, pf and other rules are available in Firewall Builder Users Guide. Follow Firewall Builder Project Blog for announcements and articles on all aspects of using Firewall Builder.
Controlling access to the firewall
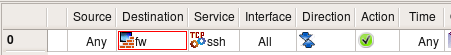
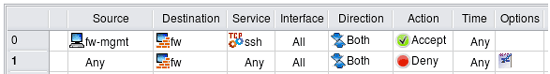
Suppose we need to permit SSH access to the firewall. In the simplest case we just create a rule with firewall object (fw) in Destination and a service object SSH in Service. Service object SSH can be found in the Standard objects tree, under Services/TCP. Here is the rule:
This almost trivial rule compiles into configurations using entirely different concepts depending on the chosen target firewall platform. Generated iptables rule is rather simple:
# Rule 0 (global) # $IPTABLES -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT
Generated PF configuration uses tables to list all ip addresses that belong to the firewall:
table <tbl.r0.d> { 192.0.2.1 , 192.168.1.1 }
# Rule 0 (global)
#
pass in quick inet proto tcp from any to <tbl.r0.d> port 22 keep state
Iptables has concept of chains that separate different packet flow paths inside netfilter engine and packets headed for the firewall itself are always processed in the INPUT chain. This means generated iptables script could be optimized. If comparison is done in the INPUT chain, the script does not have to verify destination address to make sure it belongs to the firewall since this has already been done by the kernel. PF does not have mechanism like this, therefore generated PF configuration must compare destination address of the packet with all addresses of the firewall. This can be done in a more elegant way using PF tables, but still, we make the firewall compare destination address of the packet against a list of addresses.
Ipfw offers a shortcut for this, it is called configuration option "me". Here is how generated ipfw script looks like for the same simple rule controlling ssh access to the firewall:
# Rule 0 (global) # "$IPFW" add 10 set 1 permit tcp from any to me 22 in setup keep-state || exit 1
"me" here means any address that belongs to the firewall.
The rule #0 in the screenshot above matches service ssh which has special meaning in case of PIX. There, control to the firewall for protocols such as ssh and telnet is configured using special configuration commands "ssh" and "telnet" instead of generic access lists. Here is what we get when we compile exactly the same rule for PIX:
! Rule 0 (global) ! ssh 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 outside ssh 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 dmz50 ssh 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 inside
The rule in this example leaves source address "any", which is why generated PIX commands match "0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0". Fwbuilder generated "ssh" command for all interfaces of the PIX for the same reason.
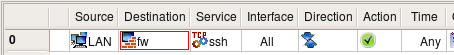
Obviously this rule makes our firewall too open because it permits SSH connections to it from any host on the Internet. It would be a good idea to restrict it so that it permitted connections only from the internal LAN. This is easy, we just put object "LAN" in the source of the corresponding rule:
Generated configuration for all supported firewall platforms will follow the same pattern but add matching of the source address of the packet to make sure it comes from local LAN. In case of PIX, there is only one "ssh" command attached to the internal interface because the program determined that network object used in "Source" of the rule matches only this interface of the firewall:
! Rule 0 (global) ! ssh 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 inside
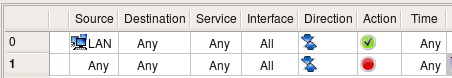
This is better, but we should be careful not to permit more protocols to the firewall than we really intend to. Let's look at the simple rule permitting connects from internal LAN to the Internet (rule #0 on the screenshot below):
Logic says that destination "any" should match any address, including the ones that belong to the firewall itself. In Firewall Builder this can actually be changed using a checkbox in the
We are now using negation in the destination; the meaning of this rule is "permit connections on any protocols from machines on the network 'LAN' to any host except the firewall". We still need a rule described above to permit ssh to the firewall, but the rule permitting access from LAN to anywhere does not open additional access to the firewall anymore. I am going to demonstrate generated iptables and pf configurations for rules with negation like this later.
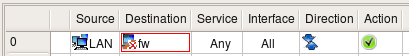
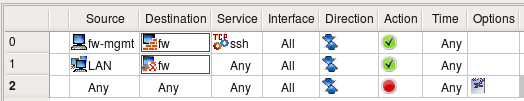
But is there any way to make it even more restrictive? Of course there is. It is always a good idea to restrict access to the firewall to just one machine and use that machine to compile the policy and manage the firewall. Let's call this machine a management station "fw-mgmt". Here is more restrictive combination of rules that permits ssh access to the firewall only from fw-mgmt, permits access from LAN to anywhere except the firewall on any protocol and blocks everything else. This combination of rules works the same regardless of the setting of the option "Assume firewall is part of any".
Three rules shown above are very good at restricting access to the firewall from all sources except for the dedicated management workstation. The problem with them is that the firewall policy is never this simple and short. As you add more rules, you can add a rule with a side effect of permitting access to the firewall sooner or later. This is one of the reason many administrators prefer to keep option "Assume firewall is part of any" turned off. In any case, it may be a good idea to build rules for the access to the firewall explicitly and group them together. It would look like something like this:
I do not include generated iptables, pf, pix code because it should be clear by now how should it look like. It is more important that rules in Firewall Builder GUI look exactly the same regardless of the chosen target firewall platform.
Policy rules demonstrated in these examples are good at restricting access to the firewall while making it possible to manage it remotely via ssh. The problem with these rules is that administrator has to be careful to not break them in any way. One would think it should be hard to make an error in a policy fragment consisting of two rules, but this happens. These two rules are just a small part of a much larger rule set and may not be located in a prominent place right on top of it. As new rules are added to the policy, at some point some rule located above may block access to the whole network or range of addresses that accidentally includes management address of the firewall. This means even though the rules are there, the access to the firewall gets blocked as soon as updated policy is uploaded and activated. This is really bad news if the firewall machine is located far away in a remote office or data center.
To help avoid this bad (but all too familiar) situation, Firewall Builder offers yet another feature. To access it, select firewall object in the tree and open it in the editor, then click "Firewall Settings" button. This was described in more details in Using Firewall Object In Firewall Builder on this site. In the dialog that appears, locate controls shown below:
Enter single IP as shown on the screenshot or subnet definition in the input field and hit "OK", then recompile the policy. Here is what gets added on the top of the generated iptables script:
$IPTABLES -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
$IPTABLES -A OUTPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
$IPTABLES -A FORWARD -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# backup ssh access
#
$IPTABLES -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp -s 192.168.1.110/255.255.255.255 \
--dport 22 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
$IPTABLES -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp -d 192.168.1.110/255.255.255.255 \
--sport 22 -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
I included rules matching "ESTABLISHED,RELATED" states in the screenshot to demonstrate that automatic rule for ssh access is added right after them. In other words, the ssh access rule is added at the very beginning of the script before any other rule. There are actually two rules, one to permit inbound packets in chain INPUT, it matches protocol tcp, destination port 22 and states "NEW,ESTABLISHED". The other rule permits outbound packets in chain OUTPUT, also protocol tcp, source port 22 and states "ESTABLISHED,RELATED". The purpose of this complexity is to make sure not only newly established ssh sessions are permitted, but also "old" ones, established before iptables rules are purged and reinstalled during firewall configuration reload. This helps ensure ssh session used to activate updated firewall policy does not get blocked and stall in the middle of the policy update process.
The same option is provided in the "Firewall settings" dialog for all supported firewall platforms. Firewall Builder always generates command to permit ssh to the firewall and makes it the very first in the access control rule set.
Now all administrator needs to do is enter ip address of the management workstation or address block it belongs to in the "Firewall Settings" dialog, then recompile and update generated policy on the firewall. There is no need to remember to add special rule to permit ssh to the firewall in the policy ruleset since this rule is now generated automatically. Generated rule is always on top of all other rules, so any mistake in the policy rule set will never block ssh access to the firewall. This is a good way to reduce the risk of locking yourself out of your own firewall. Using this feature is highly recommended.