Virtualization With KVM On A Fedora 12 Server - Page 2
On this page
5 Connecting To The Guest
Fedora 12 Desktop:
The KVM guest will now boot from the Debian Lenny Netinstall CD and start the Debian installer - that's why we need to connect to the graphical console of the guest. You can do this with virt-manager on the Fedora 12 desktop.
Run
virt-manager
on the desktop to start virt-manager (this is exactly the same on an Ubuntu desktop).
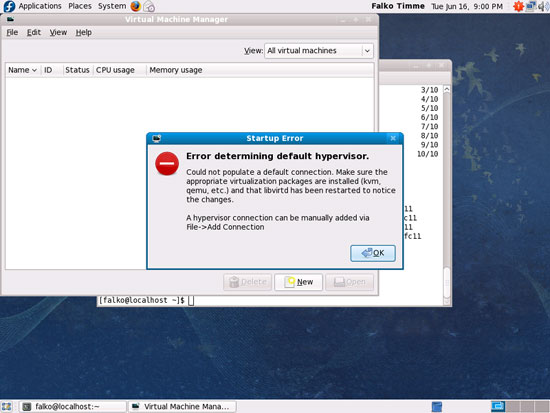
When you start virt-manager for the first time, you will most likely see the following message (Error determining default hypervisor.). Click on OK...
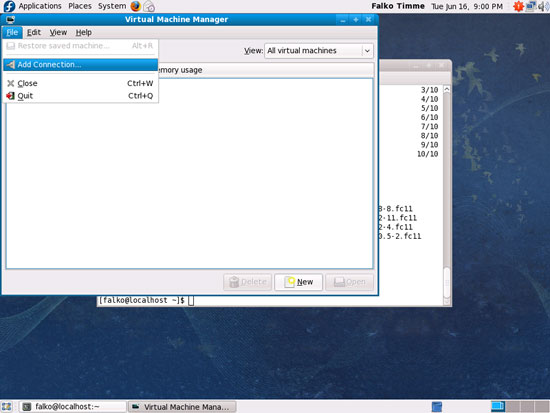
... and go to File > Add Connection... to connect to our Fedora 12 KVM host:
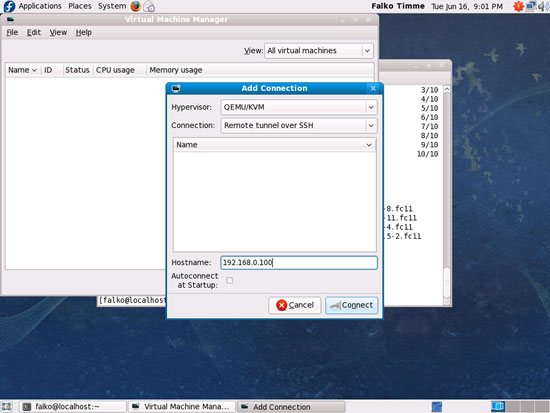
Select QEMU/KVM as Hypervisor, Remote tunnel over SSH as Connection, and type in the hostname (server1.example.com) or IP address (192.168.0.100) of the Fedora 12 KVM host. Then click on Connect:
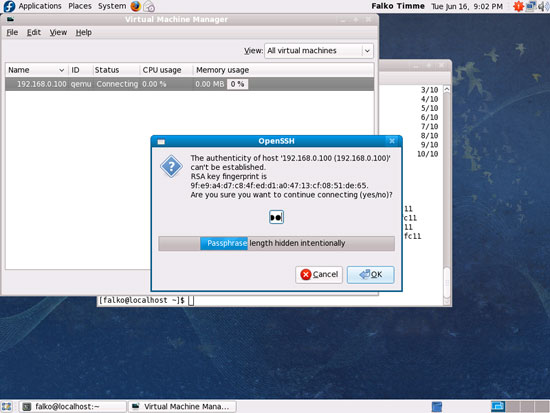
If this is the first connection to the remote KVM server, you must type in yes and click on OK:
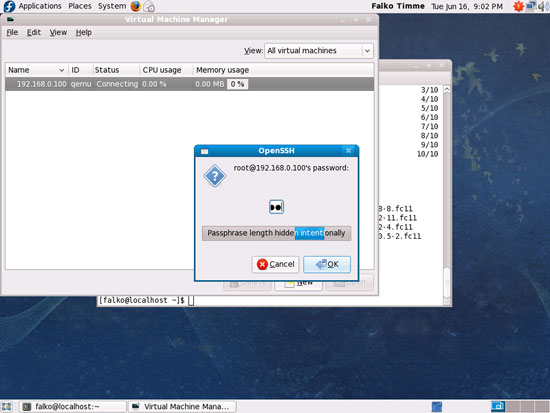
Afterwards type in the root password of the Fedora 12 KVM host:
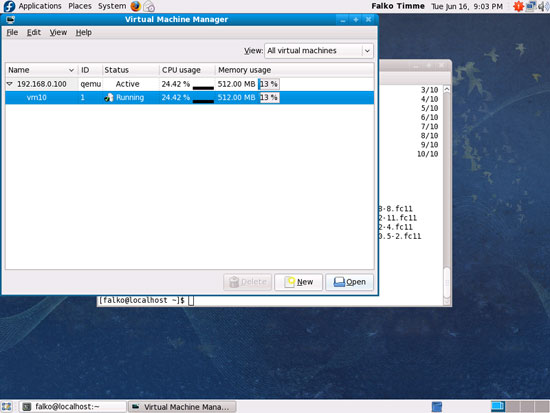
You should see vm10 as running. Mark that guest and click on the Open button to open the graphical console of the guest:
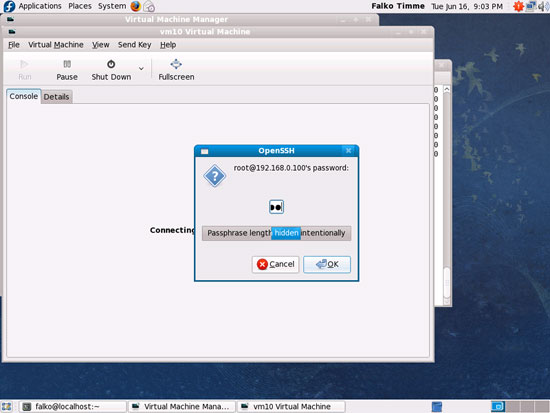
Type in the root password of the KVM host again:
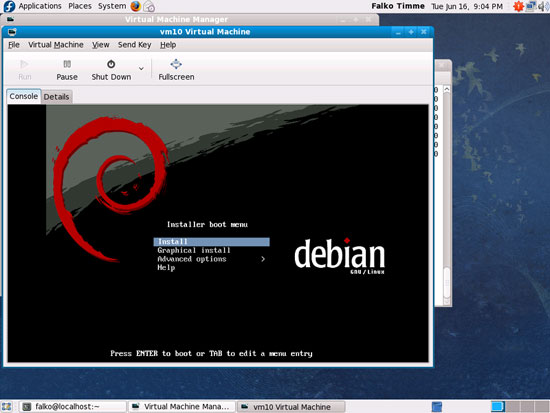
You should now be connected to the graphical console of the guest and see the Debian installer:
Now install Debian as you would normally do on a physical system. Please note that at the end of the installation, the Debian guest needs a reboot. The guest will then stop, so you need to start it again, either with virt-manager or like this on our Fedora 12 KVM host command line:
Fedora 12 KVM Host:
virsh --connect qemu:///system
start vm10
quit
Afterwards, you can connect to the guest again with virt-manager and configure the guest. If you install OpenSSH (package openssh-server) in the guest, you can connect to it with an SSH client (such as PuTTY).
6 Managing A KVM Guest
Fedora 12 KVM Host:
KVM guests can be managed through virsh, the "virtual shell". To connect to the virtual shell, run
virsh --connect qemu:///system
This is how the virtual shell looks:
[root@server1 ~]# virsh --connect qemu:///system
Welcome to virsh, the virtualization interactive terminal.
Type: 'help' for help with commands
'quit' to quit
virsh #
You can now type in commands on the virtual shell to manage your guests. Run
help
to get a list of available commands:
virsh # help
Commands:
help print help
attach-device attach device from an XML file
attach-disk attach disk device
attach-interface attach network interface
autostart autostart a domain
capabilities capabilities
connect (re)connect to hypervisor
console connect to the guest console
create create a domain from an XML file
start start a (previously defined) inactive domain
destroy destroy a domain
detach-device detach device from an XML file
detach-disk detach disk device
detach-interface detach network interface
define define (but don't start) a domain from an XML file
domid convert a domain name or UUID to domain id
domuuid convert a domain name or id to domain UUID
dominfo domain information
domname convert a domain id or UUID to domain name
domstate domain state
domblkstat get device block stats for a domain
domifstat get network interface stats for a domain
dumpxml domain information in XML
edit edit XML configuration for a domain
find-storage-pool-sources discover potential storage pool sources
find-storage-pool-sources-as find potential storage pool sources
freecell NUMA free memory
hostname print the hypervisor hostname
list list domains
migrate migrate domain to another host
net-autostart autostart a network
net-create create a network from an XML file
net-define define (but don't start) a network from an XML file
net-destroy destroy a network
net-dumpxml network information in XML
net-edit edit XML configuration for a network
net-list list networks
net-name convert a network UUID to network name
net-start start a (previously defined) inactive network
net-undefine undefine an inactive network
net-uuid convert a network name to network UUID
nodeinfo node information
nodedev-list enumerate devices on this host
nodedev-dumpxml node device details in XML
nodedev-dettach dettach node device its device driver
nodedev-reattach reattach node device its device driver
nodedev-reset reset node device
pool-autostart autostart a pool
pool-build build a pool
pool-create create a pool from an XML file
pool-create-as create a pool from a set of args
pool-define define (but don't start) a pool from an XML file
pool-define-as define a pool from a set of args
pool-destroy destroy a pool
pool-delete delete a pool
pool-dumpxml pool information in XML
pool-edit edit XML configuration for a storage pool
pool-info storage pool information
pool-list list pools
pool-name convert a pool UUID to pool name
pool-refresh refresh a pool
pool-start start a (previously defined) inactive pool
pool-undefine undefine an inactive pool
pool-uuid convert a pool name to pool UUID
quit quit this interactive terminal
reboot reboot a domain
restore restore a domain from a saved state in a file
resume resume a domain
save save a domain state to a file
schedinfo show/set scheduler parameters
dump dump the core of a domain to a file for analysis
shutdown gracefully shutdown a domain
setmem change memory allocation
setmaxmem change maximum memory limit
setvcpus change number of virtual CPUs
suspend suspend a domain
ttyconsole tty console
undefine undefine an inactive domain
uri print the hypervisor canonical URI
vol-create create a vol from an XML file
vol-create-as create a volume from a set of args
vol-delete delete a vol
vol-dumpxml vol information in XML
vol-info storage vol information
vol-list list vols
vol-path convert a vol UUID to vol path
vol-name convert a vol UUID to vol name
vol-key convert a vol UUID to vol key
vcpuinfo domain vcpu information
vcpupin control domain vcpu affinity
version show version
vncdisplay vnc display
virsh #
list
shows all running guests;
list --all
shows all guests, running and inactive:
virsh # list --all
Id Name State
----------------------------------
2 vm10 running
virsh #
If you modify a guest's xml file (located in the /etc/libvirt/qemu/ directory), you must redefine the guest:
define /etc/libvirt/qemu/vm10.xml
Please note that whenever you modify the guest's xml file in /etc/libvirt/qemu/, you must run the define command again!
To start a stopped guest, run:
start vm10
To stop a guest, run
shutdown vm10
To immediately stop it (i.e., pull the power plug), run
destroy vm10
Suspend a guest:
suspend vm10
Resume a guest:
resume vm10
These are the most important commands.
Type
quit
to leave the virtual shell.