How to Install Apache Kafka Distributed Streaming Platform on Ubuntu
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
On this page
Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform developed by Apache Software Foundation and written in Java and Scala. Apache Kafka was originally developed by LinkedIn, and was open sourced in 2011.
Apache Kafka is used for building real-time streaming data pipeline that reliably gets data between system and applications. It provides a unified, high-throughput, and low-latency data processing in real-time.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to step-by-step install and configure Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 18.04. This guide will cover the Apache Kafka and Apache Zookeeper installation and configuration.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Root privileges
What we will do?
- Install Java OpenJDK 8
- Install Apache Zookeeper
- Download and Configure Apache Kafka
- Configure Apache Kafka and Zookeeper as s Service
- Testing
Step 1 - Install Java OpenJDK 8
Apache Kafka has been written in Java and Scala, so we need to install java on the server.
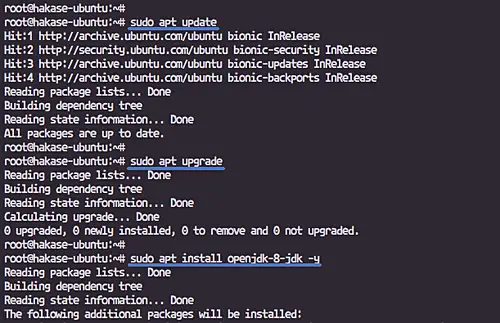
Before installing any packages, update the repository and upgrade all packages.
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Now install the Java OpenJDK 8 from the Ubuntu repository using the apt command below.
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk -y
After the installation is complete, check the java installed version.
java -version
Now you will see the java OpenJDK 8 installed on Ubuntu 18.04.
Step 2 - Install Apache Zookeeper
Apache Kafka uses zookeeper for the electing controller, cluster membership, and topics configuration. Zookeeper s a distributed configuration and synchronization service.
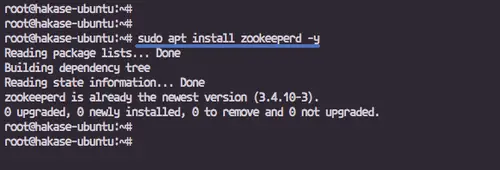
In this step, we will install Zookeeper from the Ubuntu repository.
Run the apt command below.
sudo apt install zookeeperd -y
Wait until the installation is complete.
Step 3 - Download and Configure Apache Kafka
In this step, we will install the Apache Kafka using the binary files that can be downloaded from the Kafka website. We will install and configure apache Kafka and run it as a non-root user.
Add a new user named 'kafka'.
useradd -d /opt/kafka -s /bin/bash kafka
passwd kafka
Now go to the '/opt' directory and download the Apache Kafka binary files using wget.
cd /opt
wget http://www-eu.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.0.0/kafka_2.11-2.0.0.tgz
Now create a new kafka directory.
mkdir -p /opt/kafka
Extract the kafka_*.tar.gz file to the 'kafka' directory and change the owner of directory to the 'kafka' user and group.
tar -xf kafka_2.11-2.0.0.tgz -C /opt/kafka --strip-components=1
sudo chown -R kafka:kafka /opt/kafka
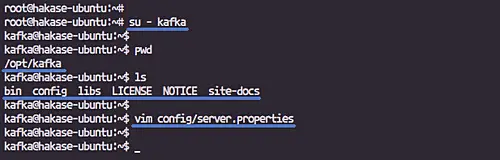
Now login to the 'kafka' user and edit the server.properties configuration.
su - kafka
vim config/server.properties
Paste the following configuration to the end of the line.
delete.topic.enable = true
Save and exit.
The Apache Kafka configuration has been completed.
Step 4 - Configure Apache Kafka and Zookeeper as Services
In this step, we will configure the Apache Kafka as a service and configure the customs service configuration for the zookeeper.
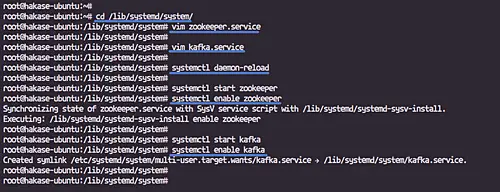
Go to the '/lib/systemd/system' directory and create a new service file 'zookeeper.service'.
cd /lib/systemd/system/
vim zookeeper.service
Paste the configuration below.
[Unit] Requires=network.target remote-fs.target After=network.target remote-fs.target [Service] Type=simple User=kafka ExecStart=/opt/kafka/bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh /opt/kafka/config/zookeeper.properties ExecStop=/opt/kafka/bin/zookeeper-server-stop.sh Restart=on-abnormal [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and exit.
Now create the Apache Kafka service file 'kafka.service'.
vim kafka.service
Paste the configuration below.
[Unit] Requires=zookeeper.service After=zookeeper.service [Service] Type=simple User=kafka ExecStart=/bin/sh -c '/opt/kafka/bin/kafka-server-start.sh /opt/kafka/config/server.properties' ExecStop=/opt/kafka/bin/kafka-server-stop.sh Restart=on-abnormal [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and exit.
Reload the systemd manager configuration.
systemctl daemon-reload
Now start Apache Zookeeper and Apache Kafka services.
systemctl start zookeeper
systemctl enable zookeeper
systemctl start kafka
systemctl enable kafka
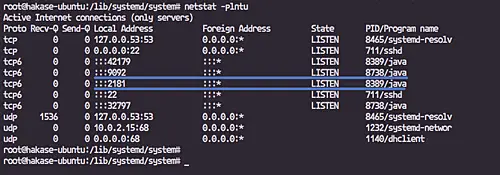
The apache zookeeper and Kafka are up and running.
Zookeeper running under port '2181', and Kafka on port '9092', check it using the netstat command below.
netstat -plntu
Step 5 - Testing Apache Kafka
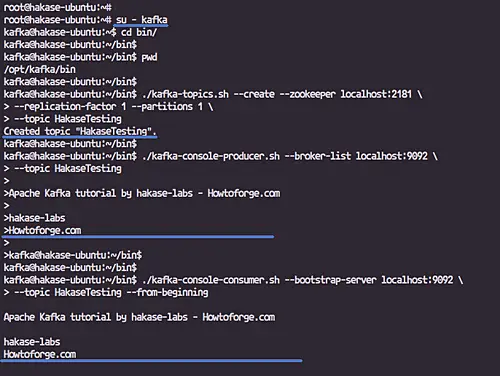
Login to the 'kafka' user and go to the 'bin/' directory.
su - kafka
cd bin/
Now create a new topic named 'HakaseTesting' using the 'kafka-topics.sh' executable file.
./kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 \
--replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 \
--topic HakaseTesting
And run the 'kafka-console-producer.sh' with the 'HakaseTesting' topic.
./kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 \
--topic HakaseTesting
Now open a new terminal and log in to the server, then login to the 'kafka' user.
Run 'kafka-console-consumer.sh' for the 'HakaseTesting' topic.
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--topic HakaseTesting --from-beginning
And when you type any input from the 'kafka-console-producer.sh' shell, you will get the same result on the 'kafka-console-consumer.sh' shell.
The installation and configuration for Apache Kafka on Ubuntu 18.04 has been completed successfully.