Server Monitoring With munin And monit On Debian Squeeze - Page 2
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- Debian 10 (Buster)
- Debian 8 (Jessie)
- Debian 7 (Wheezy)
- Debian 6 (Squeeze)
- 0
- Debian 3.1 (Sarge)
On this page
4 Install And Configure monit
To install monit, we do this:
apt-get install monit
Now we must edit /etc/monit/monitrc. The default /etc/monit/monitrc has lots of examples, and you can find more configuration examples on http://mmonit.com/monit/documentation/. However, in my case I want to monitor proftpd, sshd, mysql, apache, and postfix, I want to enable the monit web interface on port 2812, I want a https web interface, I want to log in to the web interface with the username admin and the password test, and I want monit to send email alerts to root@localhost, so my file looks like this (I've added examples for other daemons to the configuration so that you can adjust the file to your needs):
cp /etc/monit/monitrc /etc/monit/monitrc_orig
cat /dev/null > /etc/monit/monitrc
vi /etc/monit/monitrc
set daemon 60
set logfile syslog facility log_daemon
set mailserver localhost
set mail-format { from: [email protected] }
set alert root@localhost
set httpd port 2812 and
SSL ENABLE
PEMFILE /var/certs/monit.pem
allow admin:test
check process proftpd with pidfile /var/run/proftpd.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/proftpd start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/proftpd stop"
if failed port 21 protocol ftp then restart
if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
check process sshd with pidfile /var/run/sshd.pid
start program "/etc/init.d/ssh start"
stop program "/etc/init.d/ssh stop"
if failed port 22 protocol ssh then restart
if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
check process mysql with pidfile /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
group database
start program = "/etc/init.d/mysql start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/mysql stop"
if failed host 127.0.0.1 port 3306 then restart
if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
check process apache with pidfile /var/run/apache2.pid
group www
start program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 stop"
if failed host www.example.com port 80 protocol http
and request "/monit/token" then restart
if cpu is greater than 60% for 2 cycles then alert
if cpu > 80% for 5 cycles then restart
if totalmem > 500 MB for 5 cycles then restart
if children > 250 then restart
if loadavg(5min) greater than 10 for 8 cycles then stop
if 3 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
check process postfix with pidfile /var/spool/postfix/pid/master.pid
group mail
start program = "/etc/init.d/postfix start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/postfix stop"
if failed port 25 protocol smtp then restart
if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#check process nginx with pidfile /var/run/nginx.pid
# start program = "/etc/init.d/nginx start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/nginx stop"
# if failed host 127.0.0.1 port 80 then restart
#
#check process memcached with pidfile /var/run/memcached.pid
# start program = "/etc/init.d/memcached start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/memcached stop"
# if failed host 127.0.0.1 port 11211 then restart
#
#check process pureftpd with pidfile /var/run/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.pid
# start program = "/etc/init.d/pure-ftpd-mysql start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/pure-ftpd-mysql stop"
# if failed port 21 protocol ftp then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process named with pidfile /var/run/named/named.pid
# start program = "/etc/init.d/bind9 start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/bind9 stop"
# if failed host 127.0.0.1 port 53 type tcp protocol dns then restart
# if failed host 127.0.0.1 port 53 type udp protocol dns then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process ntpd with pidfile /var/run/ntpd.pid
# start program = "/etc/init.d/ntp start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/ntp stop"
# if failed host 127.0.0.1 port 123 type udp then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process mailman with pidfile /var/run/mailman/mailman.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/mailman start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/mailman stop"
#
#check process amavisd with pidfile /var/run/amavis/amavisd.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/amavis start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/amavis stop"
# if failed port 10024 protocol smtp then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process courier-imap with pidfile /var/run/courier/imapd.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/courier-imap start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/courier-imap stop"
# if failed host localhost port 143 type tcp protocol imap then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process courier-imap-ssl with pidfile /var/run/courier/imapd-ssl.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/courier-imap-ssl start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/courier-imap-ssl stop"
# if failed host localhost port 993 type tcpssl sslauto protocol imap then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process courier-pop3 with pidfile /var/run/courier/pop3d.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/courier-pop start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/courier-pop stop"
# if failed host localhost port 110 type tcp protocol pop then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process courier-pop3-ssl with pidfile /var/run/courier/pop3d-ssl.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/courier-pop-ssl start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/courier-pop-ssl stop"
# if failed host localhost port 995 type tcpssl sslauto protocol pop then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
#
#check process dovecot with pidfile /var/run/dovecot/master.pid
# group mail
# start program = "/etc/init.d/dovecot start"
# stop program = "/etc/init.d/dovecot stop"
# if failed host localhost port 993 type tcpssl sslauto protocol imap then restart
# if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
|
The configuration file is pretty self-explaining; if you are unsure about an option, take a look at the monit documentation: http://mmonit.com/monit/documentation/monit.html
In the apache part of the monit configuration you find this:
if failed host www.example.com port 80 protocol http
and request "/monit/token" then restart
|
which means that monit tries to connect to www.example.com on port 80 and tries to access the file /monit/token which is /var/www/www.example.com/web/monit/token because our web site's document root is /var/www/www.example.com/web. If monit doesn't succeed it means Apache isn't running, and monit is going to restart it. Now we must create the file /var/www/www.example.com/web/monit/token and write some random string into it:
mkdir /var/www/www.example.com/web/monit
echo "hello" > /var/www/www.example.com/web/monit/token
Next we create the pem cert (/var/certs/monit.pem) we need for the SSL-encrypted monit web interface:
mkdir /var/certs
cd /var/certs
We need an OpenSSL configuration file to create our certificate. It can look like this:
vi /var/certs/monit.cnf
# create RSA certs - Server RANDFILE = ./openssl.rnd [ req ] default_bits = 2048 encrypt_key = yes distinguished_name = req_dn x509_extensions = cert_type [ req_dn ] countryName = Country Name (2 letter code) countryName_default = MO stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name) stateOrProvinceName_default = Monitoria localityName = Locality Name (eg, city) localityName_default = Monittown organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company) organizationName_default = Monit Inc. organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) organizationalUnitName_default = Dept. of Monitoring Technologies commonName = Common Name (FQDN of your server) commonName_default = server.monit.mo emailAddress = Email Address emailAddress_default = [email protected] [ cert_type ] nsCertType = server |
Now we create the certificate like this:
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -nodes -config ./monit.cnf -out /var/certs/monit.pem -keyout /var/certs/monit.pem
openssl gendh 512 >> /var/certs/monit.pem
openssl x509 -subject -dates -fingerprint -noout -in /var/certs/monit.pem
chmod 700 /var/certs/monit.pem
Afterwards we edit /etc/default/monit to enable the monit daemon. Change startup to 1:
vi /etc/default/monit
# Defaults for monit initscript # sourced by /etc/init.d/monit # installed at /etc/default/monit by maintainer scripts # Stefan Alfredsson <[email protected]> # You must set this variable to for monit to start startup=1 # You can change the location of the state file here # It can also be set in monitrc # STATEFILE="/var/lib/monit/monit.state" # To change the intervals which monit should run, # edit the configuration file /etc/monit/monitrc # It can no longer be configured here. |
Finally, we can start monit:
/etc/init.d/monit start
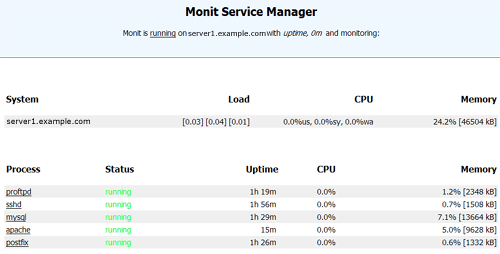
Now point your browser to https://www.example.com:2812/ (make sure port 2812 isn't blocked by your firewall), log in with admin and test, and you should see the monit web interface. It should look like this:
(Main Screen)
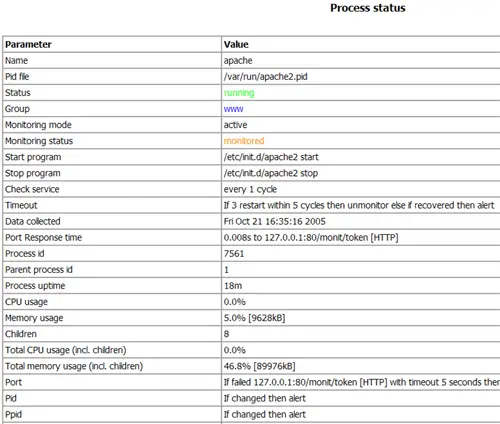
(Apache Status Page)
Depending on your configuration in /etc/monit/monitrc monit will restart your services if they fail and send notification emails if process IDs of services change, etc.
Have fun!
5 Links
- munin: http://munin-monitoring.org/
- monit: http://mmonit.com/monit/