How To Enable NTFS Write Support (ntfs-3g) On Ubuntu Feisty Fawn - Page 2
On this page
3 Using ntfs-3g
Before you plug in and switch on your NTFS drive, open the NTFS Configuration Tool (Applications > System Tools > NTFS Configuration Tool):
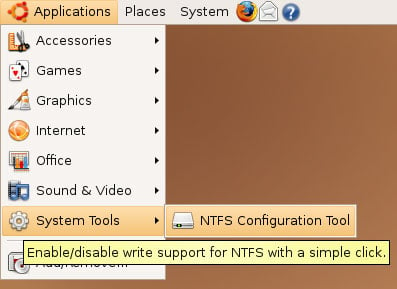
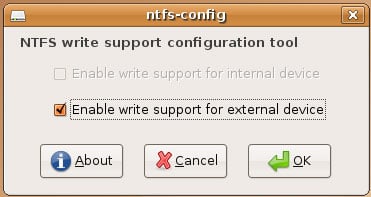
In the NTFS Configuration Tool, you can specify for what NTFS drives you want to enable write support. I'm using an external NTFS drive, so I select Enable write support for external device (my system doesn't have any internal NTFS devices, so the other option is greyed out). Then click on OK:
Now while you're sitting in front of your Ubuntu Feisty Fawn desktop, plug in your external NTFS drive and switch it on.
After a few seconds (if nothing goes wrong), you should see a desktop icon for your NTFS drive (mine is called BACKUP), and a file explorer window should come up with the contents of the drive:
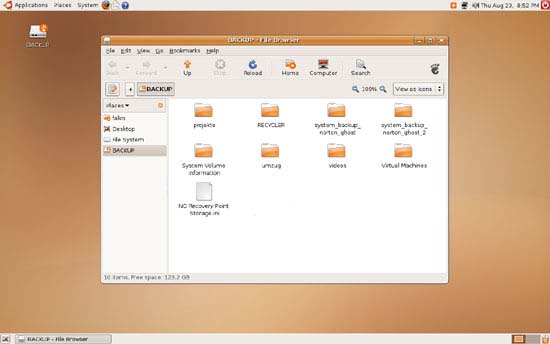
This means that we can at least read from the NTFS drive, but of course we want to know if the write support is working. To test this, you can go to any subfolder (or stay in the root folder) of the NTFS drive, right-click on the free space, and select Create Folder (you could as well select Create Document):
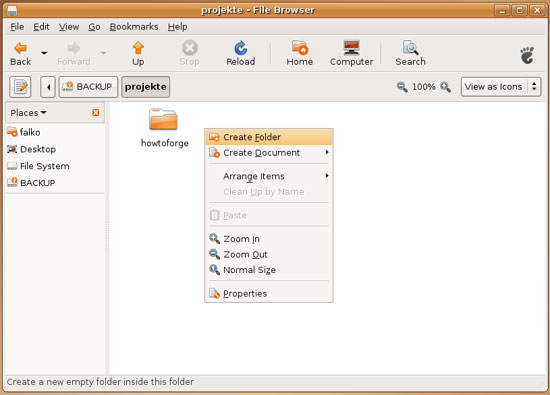
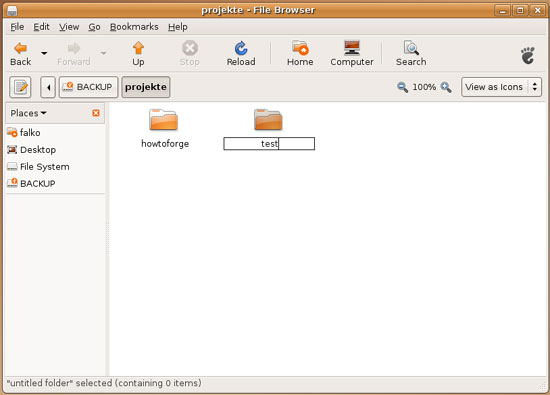
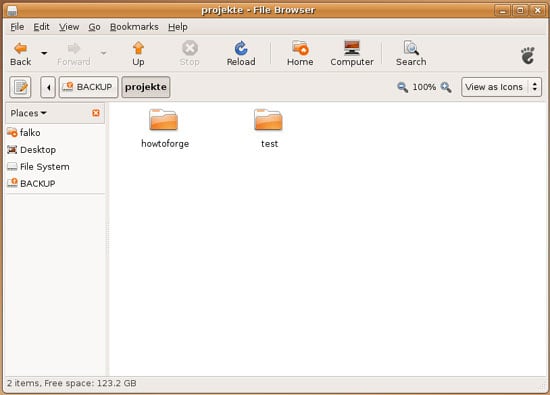
Type in the name of the new folder. If the folder is created without errors, this means that write support is working for our NTFS drive!
Before you switch off/disconnect your NTFS drive from your Ubuntu system, you must unmount it (or you risk filesystem damage!). To do this, right-click on the drive's desktop icon and select Eject:
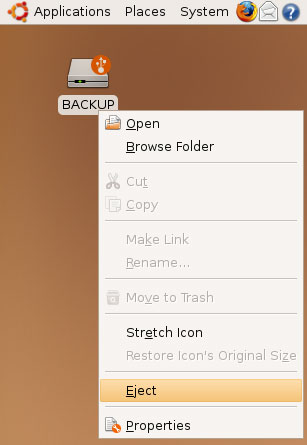
After the drive's desktop icon has disappeared, you can unplug and switch off the drive.
4 Troubleshooting
If you plug in your NTFS drive, and it doesn't get mounted, but you see an error message saying something like:
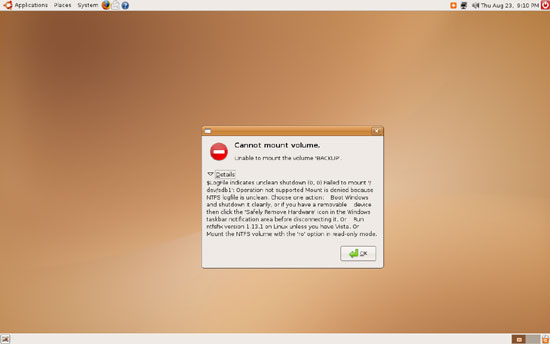
Cannot mount volume.
Unable to mount the volume 'BACKUP'.
$LogFile indicates unclean shutdown (0, 0) Failed to mount '/dev/sdb1': Operation not supported Mount is denied because NTFS logfile is unclean. Choose one action: Boot Windows and shutdown it cleanly, or if you have a removable device then click the 'Safely Remove Hardware' icon in the Windows taskbar notification area before disconnecting it. Or Run ntfsfix version 1.13.1 on Linux unless you have Vista. Or Mount the NTFS volume with the 'ro' option in read-only mode.
this means that the NTFS drive wasn't safely removed from your Windows system before.
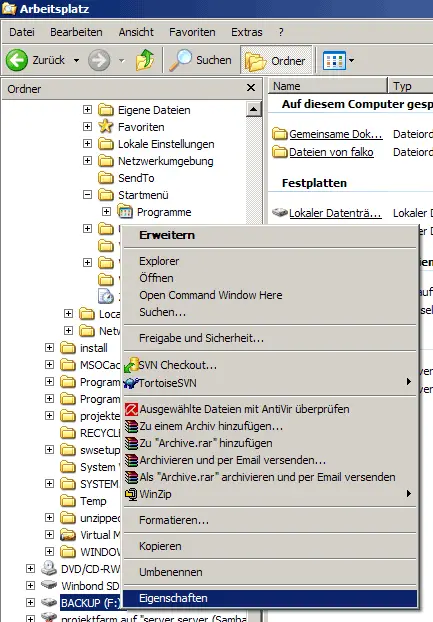
To fix this, we must boot into our Windows system again and plug in our NTFS drive. In the Windows Explorer, right-click on the drive and select Properties:
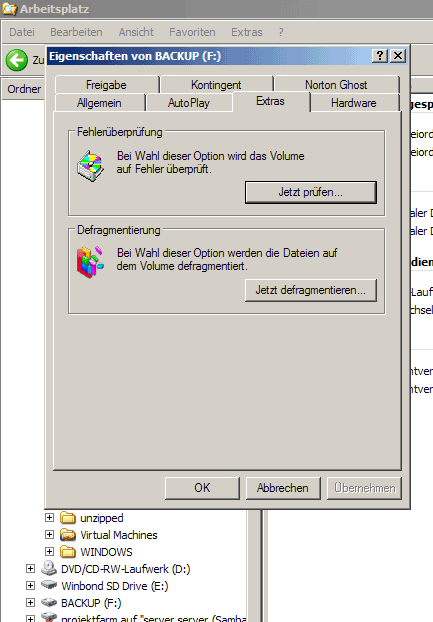
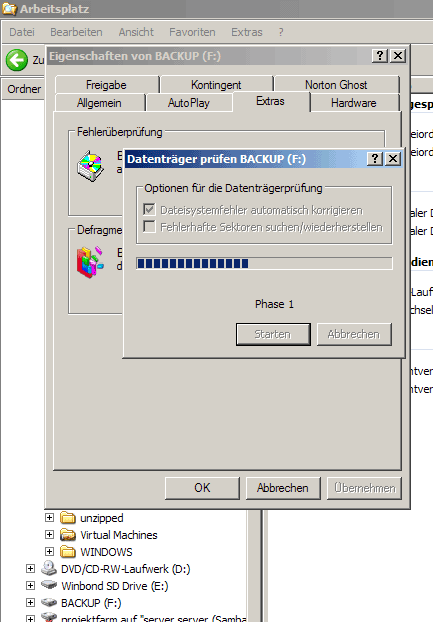
Then go to the Extras tab and select to check the drive for errors (it's the first button saying Jetzt prüfen... in this screenshot (I got a German Windows...)):
Select the option to automatically correct filesystem errors (Dateisystemfehler automatisch korrigieren):
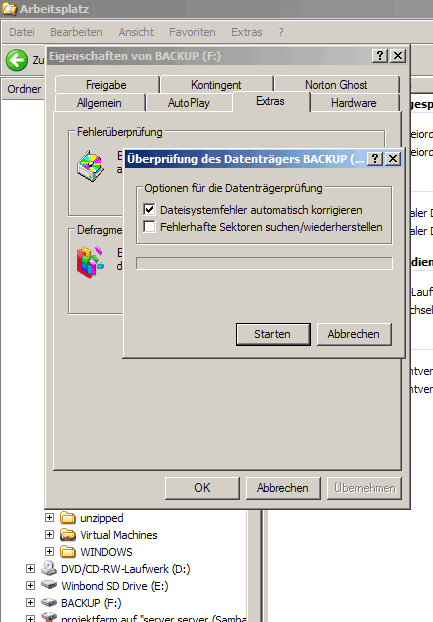
The drive is now being checked:
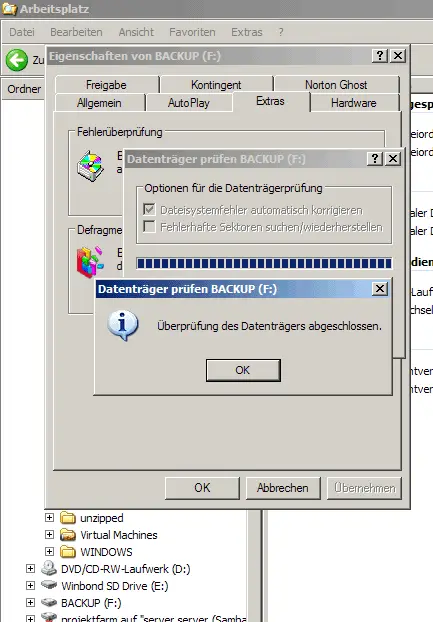
Click on OK afterwards:
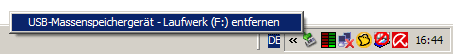
Afterwards, you must safely remove the drive by clicking on the green arrow in the task bar. You should always use this option from now on instead of simply unplugging the drive, because if you simply unplug the drive, you'll get the Cannot mount volume error again in Ubuntu.
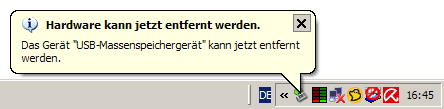
A few seconds after you've selected to safely remove the drive, Windows tells you that the drive can now be disconnected:
Afterwards, you can connect the drive to your Ubuntu system, and it should now be mounted without errors.
5 Links
- ntfs-3g: http://www.ntfs-3g.org
- Ubuntu: http://www.ubuntu.com

