Learning C/C++ Step-By-Step - Page 12
12. Step-by-Step CorC++ --- C Programming - Files
File Handling
Introduction
Let’s find the output of the following program.
 |
Yes, it accepts a record of student information and displays it.
Here is the same program, but included statements with a few modifications.
 |
Above two programs are same, but the second program contains a highlighted statement (FILE *fp = fopen(“stud.dat”, “a+”); ) and a few modifications like ‘fprintf’, ‘fp’. Only few modifications included. These modifications affect data to transfers from console to diskette in the file stud.dat. This process is known as file control/file management/file organization.
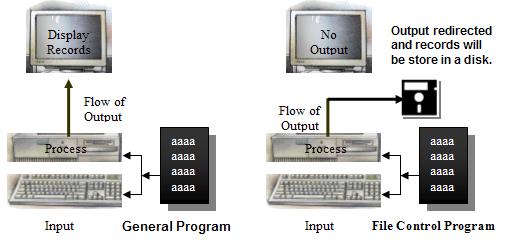 |
Actually file processing involved with a lot of operations as well as methods to implement. Here is the actual process to handle files.
File Handling
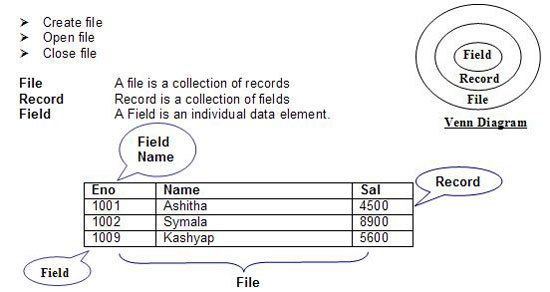
Generally every program has to present the resulted values on the screen (1st program illustrates this). But those values are removed from the memory whenever the program is terminated. If we want to keep records permanently, save them in a file. Every file has a few operations, here is a few;
 |
 |
File Operations
fopen |
Opens the stream filename in the mode mode & if succeeded, Returns a pointer to the newly open stream; or Null other wise. |
Syntax |
FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode); |
E.g. |
FILE *fp = fopen("stud.dat", "r"); /* Read from file */ |
|
Mode: Mode Description r Open for reading only To specify that a given file is being opened or created in text mode, |
fclose |
Closes the file pointed to by fp & returns 0 on success, EOF is returned in case of error |
Syntax |
Int fclose(FILE *fp); |
e.g. |
Fclose(fp); fclose(stud); fcloseall(); |
fprintf |
Sends formatted output to a stream. Uses the same format specifiers as printf, but sends output to the specified stream. Returns the number of bytes output or EOF in case of error. |
Syntax |
Fprintf(fptr, “Control String”, list); |
E.g |
Fprintf(fp, “%d %s %d %d %d”, sno, name, sub1, sub2, sub3); |
fscanf |
This function is used to read a formatted data from a specified file. |
Syntax: |
Fscanf(fptr, “Control String”, list); |
E.g |
Fscanf(fp, “%d %s %d %d %d”, &sno, name, &sub1, &sub2, &sub3); |
fwrite |
Fwrite appends a specified number of equal-sized data items to an output file. |
Syntax: |
Size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t n, FILE*stream); |
fread |
Fread retrieves a specified number of equal-sized data items from an input file. |
Syntax |
Size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t n, FILE*stream); |
rewind |
Repositions file pointer to stream's beginning |
Syntax |
Void rewind(FILE *stream); |
fseek |
The file pointer for the stream is positioned at offset number of bytes calculated from the position specified by whence. Offset may be zero, negative, or positive. The defined symbols SEEK_CUR, SEEK_SET & SEEK_END are used as whence specifiers to indicate current position. BOF & EOF respectively. Returns 0 if successful or nonzero on failure. |
Syntax |
Int fssek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence); |
ftell |
Returns the current file pointer position on success or Negative value on error. |
Syntax |
Long ftell(FILE *stream); |
feof |
It is a macro to return nonzero if end-of-file has been reached on the stream. |
Syntax |
Int feof(FILE *stream); |
eof |
Checks whether the position marker in the file given by its handle is at the end-of-file. If yes, returns 0, 1 is returned if position marker is NOT at eof & an error is indicated by setting of errno & return value of –1. |
Syntax |
Int eof(int handle); |
fgets / |
The function fgets/fputs gets/puts a string(of size n bytes) on the file pointed to by stream and returns end-of-file on error. |
Syntax |
Char *fgets(char *s, int n, FILE *stream); |
fgetc/fputc |
Reads/writes a character from a stream. |
fgetchar/ |
These are equivalent to the above fgetc/fputc. |
Write a program to read a student data and store it in a data file.
/* Program to create a student data file */ |
Write a program to retrieve data from a student data file.
/* Program to retrieve data from a student data file */ |

