How to Install Sails.js Framework with Nginx on Ubuntu 22.04
On this page
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 - Configure Firewall
- Step 2 - Install Node Version Manager (NVM)
- Step 3 - Install Node.js
- Step 4 - Install Sails.js
- Step 5 - Create a Demo application
- Step 6 - Create a systemd service file
- Step 7 - Install Nginx
- Step 8 - Install SSL
- Step 9 - Configure Nginx
- Step 10 - Access Sails.js App
- Conclusion
Sails.js is a full-stack MVC JavaScript framework for Node.js. It is used for developing real-time web applications. It is inspired by Ruby on Rails, but with support for data-driven APIs and scalable, service-oriented architecture. It uses a powerful Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) called Waterline that allows it to be used with databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis, etc.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install the Sails.js framework to create a test app and deploy it using the Nginx server along with Let's Encrypt SSL on a Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Prerequisites
-
A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
-
A non-root user with sudo privileges.
-
The Uncomplicated Firewall(UFW) is enabled and running.
-
A Fully Qualified domain name pointed to the server. For our tutorial, we will be using the domain
sails.example.com. -
Everything is updated.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Step 1 - Configure Firewall
The first step before installing any packages is to configure the firewall to allow HTTP and HTTPS connections.
Check the status of the firewall.
$ sudo ufw status
You should see something like the following.
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Allow HTTP and HTTPs ports.
$ sudo ufw allow http $ sudo ufw allow https
Check the status again to confirm.
$ sudo ufw status Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443 ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 2 - Install Node Version Manager (NVM)
We will install Node using Node Version Manager (nvm) application. You can use NVM to install multiple versions of Node and switch between them with ease. Run the following command to download and install NVM.
Check the latest version of NVM from the Github releases page. At the time of writing this tutorial, v0.39.1 is the latest available version.
$ NVMVERSION=0.39.1 $ curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/$NVMVERSION/install.sh | bash
Refresh the terminal.
$ source ~/.bashrc
Verify that NVM is installed.
$ command -v nvm
You should see the following output on successful installation.
nvm
Step 3 - Install Node.js
We will install the latest version of the LTS (Long term support) release of Node.js. Run the following command to do that.
$ nvm install --lts
Verify that Node.js is installed.
$ node --version v16.17.0
Step 4 - Install Sails.js
Now that Node.js is installed, it is time to install the Sails.js framework. Run the following command to install it globally.
$ npm -g install sails
Verify that the Sails.js framework is installed.
$ sails --version 1.5.3
You can check other commands available with the sails command line application by using the --help flag.
$ sails --help
You will receive the following output.
Usage: sails [command]
Options:
-v, --version output the version number
-h, --help output usage information
Commands:
version
lift|l [options]
new [options] [path_to_new_app]
generate
upgrade
migrate
console|c [options]
www
debug (for Node v5 and below)
inspect (for Node v6 and above)
run
test
lint
deploy
debug-console|dc
help [command]
Step 5 - Create a Demo application
Run the following command to generate a demo application.
$ sails new howtoforge-app
You will get the following two options.
Choose a template for your new Sails app: 1. Web App · Extensible project with auth, login, & password recovery 2. Empty · An empty Sails app, yours to configure (type "?" for help, or <CTRL+C> to cancel)
You can type 1 to go with a pre-defined template for a full-fledged application with authentication, a login page, and a password recovery feature. If you want to start with a blank slate, go with option 2.
We will go with option 1. You will need to wait for a few minutes for the process to complete.
? 1 info: Installing dependencies... Press CTRL+C to cancel. (to skip this step in the future, use --fast) info: Created a new Sails app `howtoforge-app`!
Switch to the working directory of the newly created application. The directory name is the same as your application.
$ cd howtoforge-app
Check the folder listing. The folder will have all essential files and packages installed to get you started with the application.
$ ls total 944 drwxrwxr-x 9 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:14 . drwxr-x--- 8 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 .. drwxrwxr-x 8 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 api -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 1841 Aug 23 07:13 app.js drwxrwxr-x 8 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 assets drwxrwxr-x 4 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 config -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 1046 Aug 23 07:13 .editorconfig -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 44 Aug 23 07:13 .eslintignore -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 4228 Aug 23 07:13 .eslintrc -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 3531 Aug 23 07:13 .gitignore -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 669 Aug 23 07:13 Gruntfile.js -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 709 Aug 23 07:13 .htmlhintrc -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 2162 Aug 23 07:13 .lesshintrc drwxrwxr-x 510 navjot navjot 20480 Aug 23 07:14 node_modules -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 369 Aug 23 07:13 .npmrc -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 6151 Aug 23 07:13 package.json -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 854958 Aug 23 07:14 package-lock.json -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 1732 Aug 23 07:13 README.md -rw-rw-r-- 1 navjot navjot 123 Aug 23 07:13 .sailsrc drwxrwxr-x 2 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 scripts drwxrwxr-x 4 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 tasks drwxrwxr-x 5 navjot navjot 4096 Aug 23 07:13 views
Run the Sails application. The following command will start the application in development mode. Sails.js uses the Grunt tool to monitor the /assets folder. If you change anything in that folder, it will be reflected automatically in the browser. You can also change your view files without restarting Sails because the templates are not cached in memory.
$ sails lift
You will get the following output on the successful starting of the application.
info: Starting app... info: Initializing project hook... (`api/hooks/custom/`) info: Initializing `apianalytics` hook... (requests to monitored routes will be logged!) info: ·• Auto-migrating... (alter) info: Hold tight, this could take a moment. info: ? Auto-migration complete. debug: Running v0 bootstrap script... (looks like this is the first time the bootstrap has run on this computer) info: info: .-..-. info: info: Sails <| .-..-. info: v1.5.3 |\ info: /|.\ info: / || \ info: ,' |' \ info: .-'.-==|/_--' info: `--'-------' info: __---___--___---___--___---___--___ info: ____---___--___---___--___---___--___-__ info: info: Server lifted in `/home/navjot/howtoforge-app` info: To shut down Sails, press <CTRL> + C at any time. info: Read more at https://sailsjs.com/support. debug: ------------------------------------------------------- debug: :: Tue Aug 23 2022 09:01:32 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time) debug: Environment : development debug: Port : 1337 debug: -------------------------------------------------------
Sails.js exposes your app to port 1337. You will need to open the port to access the application. Launch another terminal to your server and run the following command to open the port.
$ sudo ufw allow 1337
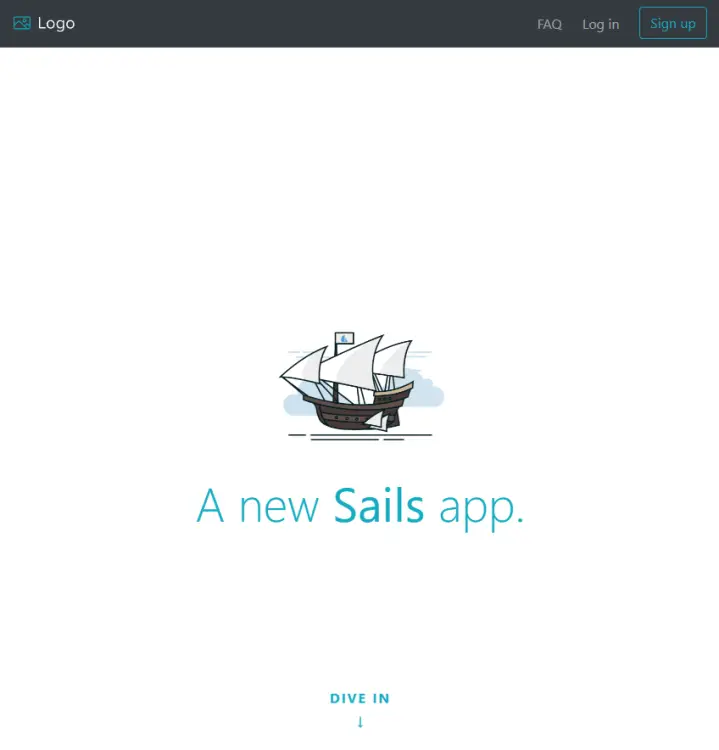
Launch the URL http://<serverIP>:1337 in your browser. You will get the following page.
Press Ctrl + C on the terminal to shut down the Sails application.
Step 6 - Create a systemd service file
Right now, the Sails app is working only if the terminal is active. To keep it persistent across reboots, we need to create a systemd service file for Sails.
Create and open the howtoforge-app.service file for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/howtoforge-app.service
Paste the following code in it.
[Unit] After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=navjot WorkingDirectory=/home/navjot/howtoforge-app ExecStart=/home/navjot/.nvm/versions/node/v16.17.0/bin/node app.js Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Replace the values for the User, WorkingDirectory and ExecStart variables with your system's username, application path, and the path to your node application. To locate the path to Node.js, you can use the following command.
$ which node /home/navjot/.nvm/versions/node/v16.17.0/bin/node
We are using Node.js instead of the Sails CLI application because it is easier to configure and run it via a system script. Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Reload the system daemon to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Start the Sails.js service and enable it to start at system boot.
$ sudo systemctl enable howtoforge-app --now
Check the status of the service.
$ sudo systemctl status howtoforge-app
? howtoforge-app.service - Sails.js Howtoforge App
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/howtoforge-app.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-08-23 11:52:58 UTC; 5s ago
Main PID: 15385 (node)
Tasks: 22 (limit: 2237)
Memory: 123.8M
CPU: 3.894s
CGroup: /system.slice/howtoforge-app.service
??15385 /home/navjot/.nvm/versions/node/v16.17.0/bin/node app.js
??15392 grunt "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" "" ">
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: info: ____---___--___---___--___---___--___-__
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: info:
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: info: Server lifted in `/home/navjot/howtoforge-app`
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: info: To shut down Sails, press <CTRL> + C at any time.
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: info: Read more at https://sailsjs.com/support.
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: debug: -------------------------------------------------------
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: debug: :: Tue Aug 23 2022 11:53:01 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time)
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: debug: Environment : development
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: debug: Port : 1337
Aug 23 11:53:01 sails node[15385]: debug: -------------------------------------------------------
You can verify the service by opening the URL http://<serverIP>:1337 in your browser.
Step 7 - Install Nginx
Ubuntu 22.04 ships with an older version of Nginx. To install the latest version, you need to download the official Nginx repository.
Import Nginx's signing key.
$ curl https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor \ | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
Add the repository for Nginx's stable version.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg arch=amd64] \ http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Update the system repositories.
$ sudo apt update
Install Nginx.
$ sudo apt install nginx
Verify the installation.
$ nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
Step 8 - Install SSL
We need to install Certbot to generate the SSL certificate. You can either install Certbot using Ubuntu's repository or grab the latest version using the Snapd tool. We will be using the Snapd version.
Ubuntu 22.04 comes with Snapd installed by default. Run the following commands to ensure that your version of Snapd is up to date.
$ sudo snap install core $ sudo snap refresh core
Install Certbot.
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
Use the following command to ensure that the Certbot command can be run by creating a symbolic link to the /usr/bin directory.
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
Run the following command to generate an SSL Certificate.
$ sudo certbot certonly --standalone --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d sails.example.com
The above command will download a certificate to the /etc/letsencrypt/live/sails.example.com directory on your server.
Generate a Diffie-Hellman group certificate.
$ sudo openssl dhparam -dsaparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 4096
Open the file /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/sails.example.com.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/sails.example.com.conf
Paste the following code at the bottom.
pre_hook = systemctl stop nginx post_hook = systemctl start nginx
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
We have generated the SSL certificate using the standalone option of Certbot. It runs its web server to create the certificate which means Nginx should be shut off during the renewal. The pre_hook and post_hook commands run before and after the renewal to automatically shut and restart the Nginx server thereby requiring no manual intervention.
To check whether the SSL renewal is working fine, do a dry run of the process.
$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see no errors, you are all set. Your certificate will renew automatically.
Step 9 - Configure Nginx
Open the file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Add the following line before the line include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;.
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Create and open the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/sails.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/sails.conf
Paste the following code in it. Replace sails.example.com with your domain name. Make sure the value of the client_max_body_size is set to 10MB. Change it according to your requirements.
upstream backend {
server 127.0.0.1:1337;
keepalive 32;
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name sails.example.com;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name sails.example.com;
http2_push_preload on; # Enable HTTP/2 Server Push
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/sails.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/sails.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/sails.example.com/chain.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
# Enable TLS versions (TLSv1.3 is required upcoming HTTP/3 QUIC).
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
# Enable TLSv1.3's 0-RTT. Use $ssl_early_data when reverse proxying to
# prevent replay attacks.
#
# @see: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_ssl_module.html#ssl_early_data
ssl_early_data on;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
# OCSP Stapling ---
# fetch OCSP records from URL in ssl_certificate and cache them
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
add_header X-Early-Data $tls1_3_early_data;
access_log /var/log/nginx/sails.access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/sails.error.log;
location / {
client_max_body_size 10M;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
# This block is useful for debugging TLS v1.3. Please feel free to remove this
# and use the `$ssl_early_data` variable exposed by NGINX directly should you
# wish to do so.
map $ssl_early_data $tls1_3_early_data {
"~." $ssl_early_data;
default "";
}
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Verify your Nginx configuration.
$ sudo nginx -t
Restart the Nginx server.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Step 10 - Access Sails.js App
Launch the URL https://sails.example.com in your browser and you will be greeted with the Sails homepage.
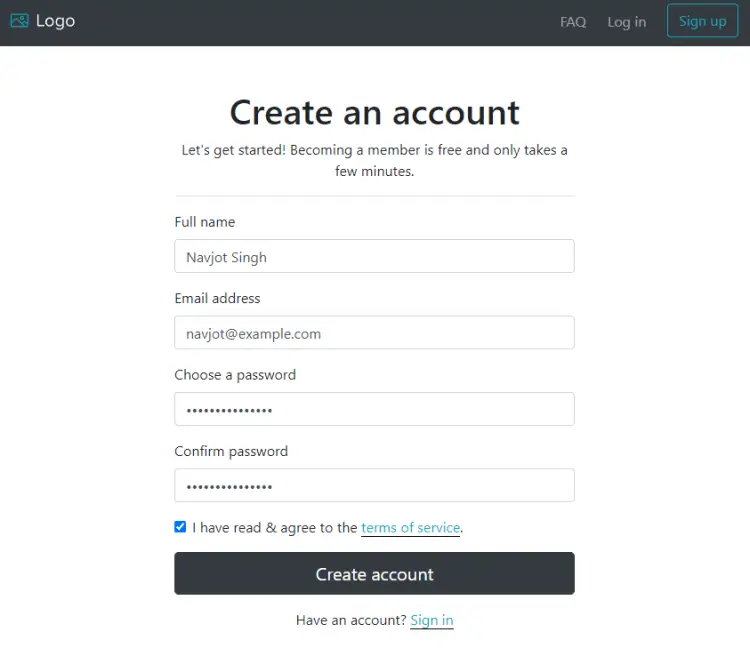
Click the Sign up button at the top right to create a new account.
Fill in your account details and click the Create account button to finish.
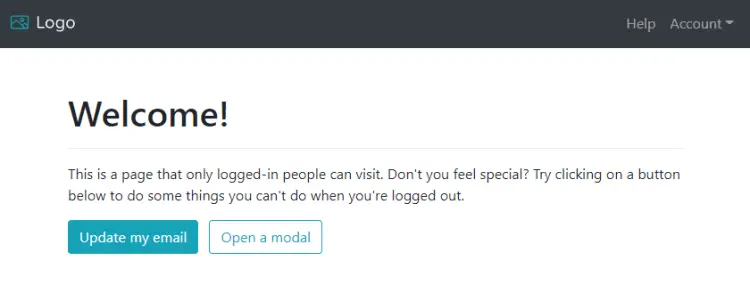
You will be immediately taken to the welcome screen.
You can now start using the application to build a dynamic application with user authentication, database support, and an in-built payment gateway powered by Stripe.
Conclusion
This completes the tutorial where you learned how to install the Sails.js framework and created a demo application. You also learned how to set up a systemd service for it and use the Nginx proxy server with Let's Encrypt to launch a secure web application. If you have any questions, post them in the comments below.