How to Install Mailtrain Newsletter Software on Ubuntu 18.04
Mailtrain is a free, open-source and self-hosted newsletter application built from Node.js which supports MySQL/MariaDB database backends. Mailtrain allows you to add subscribers manually, through the API, or import from a CSV file. Mailtrain comes with a rich set of features including, Template Editors, Automation, Custom Fields, RSS campaign, HTML code editor and much more. If you have a long list of subscribers and want to manage it easily then Mailtrain is the best choice for you.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Mailtrain newsletter application with Docker on Ubuntu 18.04 server.
Requirements
- A server running Ubuntu 18.04.
- A valid domain name pointed with your server IP.
- A root password is configured on your server.
Getting Started
Before starting, you will need to update your system with the latest version. You can do this by running the following command:
apt-get update -y
apt-get upgrade -y
Next, restart your system to apply the changes.
Install Docker and Docker Compose
By default, the latest version of Docker is not available in the Ubuntu 18.04 default repository. So, you will need to add Docker repository to your system.
First, install the required packages with the following command:
apt-get install curl git apt-transport-https ca-certificates -y
Next, download and add the Docker’s PGP key with the following command:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | apt-key add -
Next, add the Docker CE repository by editing /etc/apt/sources.list file:
nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Add the following line at the end of the file:
deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable
Save and close the file when you are finished. Then, update the repository and install Docker CE with the following commands:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install docker-ce -y
Once the installation has been completed successfully, you can check the status of Docker service with the following command:
systemctl status docker
You should see the following output:
Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2019-10-24 16:15:25 UTC; 21min ago
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 1402 (dockerd)
Tasks: 45
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
?? 1402 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
??10312 /usr/bin/docker-proxy -proto tcp -host-ip 0.0.0.0 -host-port 3000 -container-ip 172.18.0.4 -container-port 3000
Oct 24 16:23:04 ubuntu1804 dockerd[1402]: time="2019-10-24T16:23:04.817021656Z" level=info msg="Layer sha256:b875b006eb8ffb0434ce3a26cb04c9017c
Oct 24 16:24:09 ubuntu1804 dockerd[1402]: time="2019-10-24T16:24:09.879265134Z" level=info msg="ignoring event" module=libcontainerd namespace=
Oct 24 16:24:10 ubuntu1804 dockerd[1402]: time="2019-10-24T16:24:10.065610315Z" level=warning msg="20676b10252b4a484e32a7d7534b3b386cc2a1e5efd1
Oct 24 16:25:52 ubuntu1804 dockerd[1402]: time="2019-10-24T16:25:52.649551513Z" level=info msg="Layer sha256:903ab9000f0a93e49537d5d00c5c8a8cab
Oct 24 16:26:47 ubuntu1804 dockerd[1402]: time="2019-10-24T16:26:47.428865652Z" level=info msg="Layer sha256:903ab9000f0a93e49537d5d00c5c8a8cab
Oct 24 16:27:41 ubuntu1804 dockerd[1402]: time="2019-10-24T16:27:41.603287585Z" level=info msg="Layer sha256:903ab9000f0a93e49537d5d00c5c8a8cab
Next, install the latest version of docker compose with the pip command as shown below:
apt-get install python-pip
apt-get install docker-compose
Once the installation has been completed, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Mailtrain with Docker
First, download the latest version of the Mailtrain from the Git repository with the following command:
git clone git://github.com/Mailtrain-org/mailtrain.git
Next, change the directory to mailtrain and rename the default docker-compose file:
cd mailtrain
mv docker-compose.override.yml.tmpl docker-compose.override.yml
Next, start the Mailtrain docker containers with the following command:
docker-compose up -d
This command will download and start mailtrain, mysql and redis containers as shown below:
Creating network "mailtrain_default" with the default driver Creating volume "mailtrain_mailtrain-node-config" with default driver Creating volume "mailtrain_mailtrain-node-data" with default driver Creating volume "mailtrain_mailtrain-redis-data" with default driver Creating volume "mailtrain_mailtrain-node-reports" with default driver Creating volume "mailtrain_mailtrain-mysq-data" with default driver Pulling redis (redis:3.0)... 3.0: Pulling from library/redis f5cc0ee7a6f6: Pull complete 5fc25ed18e87: Pull complete e025bc8872f6: Pull complete 77c68b51b836: Pull complete 7c403ece3755: Pull complete 0a653bd338f4: Pull complete 31531fd948c6: Pull complete Digest: sha256:730b765df9fe96af414da64a2b67f3a5f70b8fd13a31e5096fee4807ed802e20 Status: Downloaded newer image for redis:3.0 Pulling mysql (mysql:5.7)... 5.7: Pulling from library/mysql 80369df48736: Pull complete e8f52315cb10: Pull complete cf2189b391fc: Pull complete cc98f645c682: Pull complete 27a27ac83f74: Pull complete fa1f04453414: Pull complete d45bf7d22d33: Pull complete c7d49ffebc56: Pull complete 511a8052b204: Pull complete 5d5df4c12444: Pull complete d482603a2922: Pull complete Digest: sha256:44b33224e3c406bf50b5a2ee4286ed0d7f2c5aec1f7fdb70291f7f7c570284dd Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:5.7 Building mailtrain : : Removing intermediate container 20676b10252b ---> 0abdb4121f54 Step 6/9 : COPY . /app ---> c8af7560e844 Step 7/9 : EXPOSE 3000 ---> Running in 3ff55179a229 Removing intermediate container 3ff55179a229 ---> d83b49d4b24b Step 8/9 : ENTRYPOINT ["bash", "/app/docker-entrypoint.sh"] ---> Running in e5baf6a1ea2e Removing intermediate container e5baf6a1ea2e ---> c4f899a0f8f9 Step 9/9 : CMD ["node", "index.js"] ---> Running in fe94519d2bd3 Removing intermediate container fe94519d2bd3 ---> 2808c2972f20 Successfully built 2808c2972f20 Successfully tagged mailtrain:latest WARNING: Image for service mailtrain was built because it did not already exist. To rebuild this image you must use `docker-compose build` or `docker-compose up --build`. Creating mailtrain_redis_1 ... done Creating mailtrain_mysql_1 ... done Creating mailtrain_mailtrain_1 ... done
You can now check all the running containers with the following command:
docker ps
You should see the following output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 0e837c586c39 mailtrain:latest "bash /app/docker-en…" About a minute ago Up 55 seconds 0.0.0.0:3000->3000/tcp mailtrain_mailtrain_1 49a4e69a09c6 mysql:5.7 "docker-entrypoint.s…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 3306/tcp, 33060/tcp mailtrain_mysql_1 a1449b64a196 redis:3.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 6379/tcp mailtrain_redis_1
Access Mailtrain Web Interface
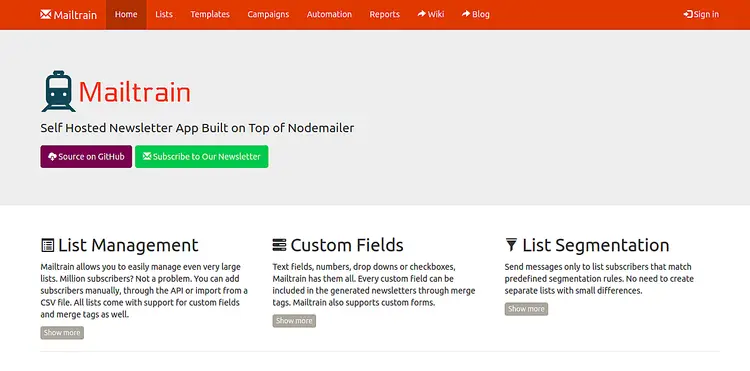
Mailtrain container is now started and listening on port 3000. Next, open your web browser and type the URL http://your-server-ip:3000. You should see the Mailtrain default dashboard in the following page:
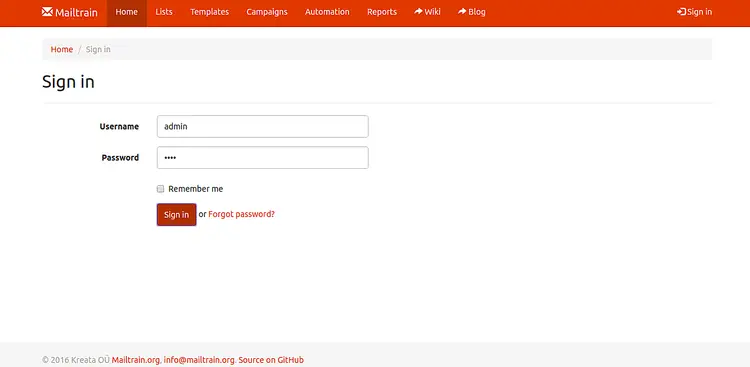
Now, click on the Sign in button. You should see the following page:
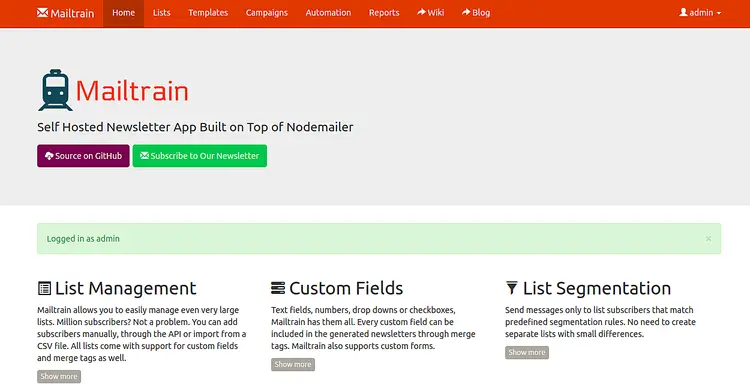
Provide default username and password as admin/admin and click on the Sign in button. You should see the Mailtrain default dashboard in the following page:
Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy for Mailtrain
Next, you will need to create an Nginx as a reverse proxy for Mailtrain on port 3000. To do so, first install the Nginx web server by running the following command:
apt-get install nginx -y
Next, create an Nginx virtual host configuration file with the following command:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mailtrain.conf
Add the following lines:
upstream mailtrain {
server 127.0.0.1:3000 weight=100 max_fails=5 fail_timeout=5;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://mailtrain/;
}
}
Save and close the file when you are finished. Then, check the Nginx for any syntax error with the following command:
nginx -t
You should see the following output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Next, enable the Nginx virtual host file with the following command:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mailtrain.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Finally, restart the Nginx webserver to apply the configuration:
systemctl restart nginx
Secure Mailtrain with Let's Encrypt
Next, you will need to install Certbot client to secure Mailtrain with Let's Encrypt free SSL. By default, the latest version of Certbot is not available in the Ubuntu 18.04 default repository. So add the Certbot repository by running the following command:
add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
Next, update the repository and install Certbot with the following command:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install certbot python-certbot-nginx -y
Once installed, run the following command to download the Let's Encrypt free SSL for your domain example.com and configure Nginx to use this certificate.
certbot --nginx -d example.com
Provide your email address and agree the Terms of Service. Once the certificate has been installed successfully, you should see the following output:
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://example.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=example.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem Your key file has been saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem Your cert will expire on 2020-01-22. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again with the "certonly" option. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal. - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
You can now access your Mailtrain application securely using the URL https://example.com.
Conclusion
In the above tutorial, we learned how to install Mailtrain with docker on Ubuntu 18.04 server. We also learned how to configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for Mailtrain and secure Mailtrain with Let's Encrypt free SSL. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.