How to Install Cachet Status Page System on CentOS 7
On this page
- Requirements
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 - Install PHP
- Step 2 - Install MariaDB and create a database for Cachet
- Step 3 - Install Acme.sh client and obtain Let's Encrypt certificate (optional)
- Step 4 - Install and configure NGINX
- Step 5 - Install Composer
- Step 6 - Install Cachet
- Step 7 - Complete the Cachet setup
- Links
Cachet is a beautiful and powerful open source status page system written in PHP that allows you to better communicate downtime and system failures to your customers, teams, and shareholders. The application offers many features, the most important of which are: a powerful JSON API, event reports, metrics, transcription support for event messages, subscriber notifications via email, two-factor authentication. In this tutorial, we will install the Cachet status page system using PHP, Nginx, MySQL, and Composer on the CentOS 7 system.
Requirements
To run Cachet on your CentOS 7 system you will need a couple of things:
- PHP version 7.1 or greater
- HTTP server with PHP support (eg: Nginx, Apache, Caddy)
- Composer
- A supported database: MySQL, PostgreSQL or SQLite
- Git
Prerequisites
- A CentOS 7 operating system.
- A non-root user with sudo privileges.
Initial steps
Check your CentOS version:
cat /etc/centos-release
Set up the timezone:
timedatectl list-timezones
sudo timedatectl set-timezone 'Region/City'Update your operating system packages (software). This is an important first step because it ensures you have the latest updates and security fixes for your operating system's default software packages:
sudo yum upgdate -yInstall some essential packages that are necessary for basic administration of the CentOS operating system:
sudo yum install -y curl wget vim git unzip socat bash-completionStep 1 - Install PHP
Setup the Webtatic YUM repo:
sudo rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpmInstall PHP, as well as the necessary PHP extensions:
sudo yum install -y php72w-cli php72w-fpm php72w-common php72w-xml php72w-gd php72w-zip php72w-mbstring php72w-mysqlnd php72w-pgsql php72w-sqlite3 php72w-opcache php72w-apcu php72w-jsonTo show PHP compiled in modules, you can run:
php -m
ctype
curl
exif
fileinfo
. . .
. . .Check the PHP version:
php --version
Start and enable PHP-FPM service:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm.service
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm.serviceWe can move on to the next step, which is the database installation and setup.
Step 2 - Install MariaDB and create a database for Cachet
Cachet supports MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL and SQLite databases. In this tutorial, we will use MariaDB as the database server.
Create MariaDB 10.2 YUM repository for CentOS:
sudo vim /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repoCopy and paste the following text into it:
# MariaDB 10.2 CentOS repository list - created 2017-12-11 23:19 UTC
# http://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/
[mariadb]
name=MariaDB
baseurl=https://yum.mariadb.org/10.2/centos7-amd64
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1After the file is in place, install MariaDB by running:
sudo yum install -y MariaDB-server MariaDB-clientCheck the MariaDB version:
mysql --version
# mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.2.21-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using readline 5.1Start and enable MariaDB service:
sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.serviceRun mysql_secure installation script to improve MariaDB security and set the password for MariaDB root user:
sudo mysql_secure_installationAnswer each of the questions:
Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD plugin? N
New password: your_secure_password
Re-enter new password: your_secure_password
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] YConnect to MariaDB shell as the root user:
sudo mysql -u root -p
# Enter password
Create an empty MariaDB database and user for Cachet and remember the credentials:
MariaDB> CREATE DATABASE dbname;
MariaDB> GRANT ALL ON dbname.* TO 'username' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
MariaDB> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Exit from MariaDB:
MariaDB> exitReplace dbname, username and password with your own names.
Step 3 - Install Acme.sh client and obtain Let's Encrypt certificate (optional)
Securing your website with HTTPS is not necessary, but it is a good practice to secure your site traffic. In order to obtain a TLS certificate from Let's Encrypt we will use acme.sh client. Acme.sh is a pure UNIX shell software for obtaining TLS certificates from Let's Encrypt with zero dependencies.
Download and install acme.sh:
sudo su - root
git clone https://github.com/Neilpang/acme.sh.git
cd acme.sh
./acme.sh --install --accountemail [email protected]
source ~/.bashrc
cd ~Check acme.sh version:
acme.sh --version
# v2.8.0Obtain RSA and ECC/ECDSA certificates for your domain/hostname:
# RSA 2048
acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength 2048
# ECDSA
acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength ec-256If you want fake certificates for testing you can add --staging flag to the above commands.
After running the above commands, your certificates and keys will be in:
- For RSA:
/home/username/example.comdirectory. - For ECC/ECDSA:
/home/username/example.com_eccdirectory.
To list your issued certs you can run:
acme.sh --listCreate a directory to store your certs. We will use the /etc/letsencrypt directory.
mkdir -p /etc/letsecnrypt/example.comsudo mkdir -p /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc
Install/copy certificates to /etc/letsencrypt directory.
# RSA
acme.sh --install-cert -d example.com --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/fullchain.pem --reloadcmd "sudo systemctl reload nginx.service"
# ECC/ECDSA
acme.sh --install-cert -d example.com --ecc --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/fullchain.pem --reloadcmd "sudo systemctl reload nginx.service"All the certificates will be automatically renewed every 60 days.
After obtaining certs exit from root user and return back to normal sudo user:
exitStep 4 - Install and configure NGINX
Cachet can work fine with many web servers. In this tutorial, we selected NGINX. If you prefer Apache web server over NGINX, visit https://docs.cachethq.io/docs/installing-cachet#section-running-cachet-on-apache to learn more.
Install NGINX:
sudo yum install -y nginxCheck the NGINX version:
sudo nginx -v
Start and enable NGINX service:
sudo systemctl start nginx.service
sudo systemctl enable nginx.serviceConfigure NGINX for Cachet by running:
sudo vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/cachet.confAnd populate the file with the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:443 ssl;
server_name status.example.com;
root /var/www/cachet/public;
index index.php;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/status.example.com/fullchain.cer;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/status.example.com/status.example.com.key;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/status.example.com_ecc/fullchain.cer;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/status.example.com_ecc/status.example.com.key;
location / {
try_files $uri /index.php$is_args$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
}
}Test NGINX configuration:
sudo nginx -tReload NGINX:
sudo systemctl reload nginx.serviceStep 5 - Install Composer
Install Composer, the PHP dependency manager globally:
php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
php -r "if (hash_file('sha384', 'composer-setup.php') === '48e3236262b34d30969dca3c37281b3b4bbe3221bda826ac6a9a62d6444cdb0dcd0615698a5cbe587c3f0fe57a54d8f5') { echo 'Installer verified'; } else { echo 'Installer corrupt'; unlink('composer-setup.php'); } echo PHP_EOL;"
php composer-setup.php
php -r "unlink('composer-setup.php');"
sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composerCheck Composer version:
composer --version
# Composer version 1.8.4 2019-02-11 10:52:10Step 6 - Install Cachet
Create a document root directory where Cachet should reside in:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/cachet
Change ownership of the /var/www/cachet directory to {jour_user}:
sudo chown -R {your_user}:{your_user} /var/www/cachet
NOTE: Replace {jour_user} with your initially created non-root user username.
Navigate to the document root directory:
cd /var/www/cachetDownload the Cachet source code with Git:
git clone -b 2.4 --single-branch https://github.com/cachethq/Cachet.git .
Copy .env.example to .env file and configure database and APP_URL settings in .env file:
cp .env.example .env
vim .envInstall Cachet dependencies with Composer:
composer install --no-dev -oSet up the application key by running:
php artisan key:generateInstall Cachet:
php artisan cachet:installProvide the appropriate ownership:
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/cachetRun sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf and set the user and group to nginx. Initially, they will be set to apache:
sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
# user = nginx
# group = nginxOpen your site in a web browser and follow the instructions on the screen to finish Cachet installation.
Step 7 - Complete the Cachet setup
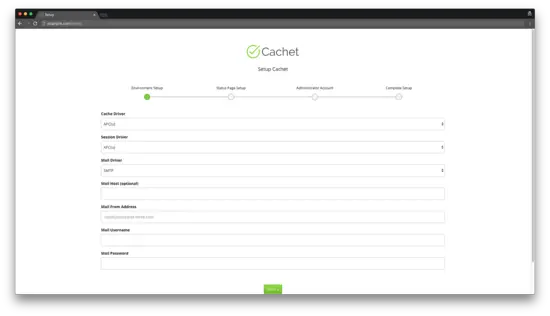
Select cache and session drivers and configure mail options:
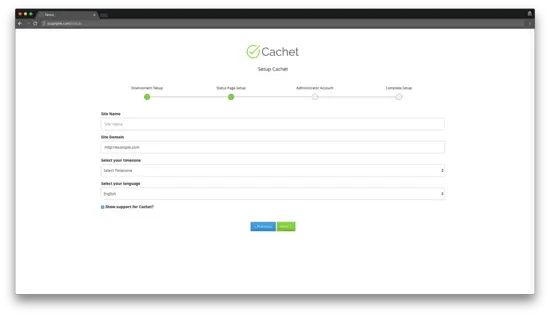
Configure general site settings like site name, site domain, timezone and language:
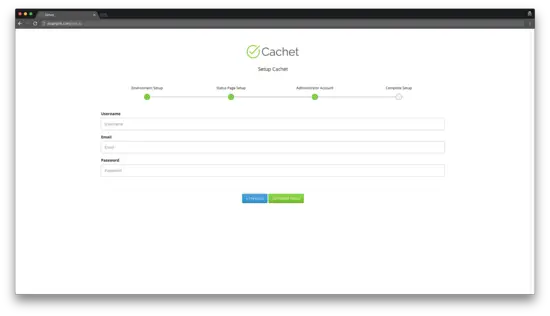
Create an administrative user account:
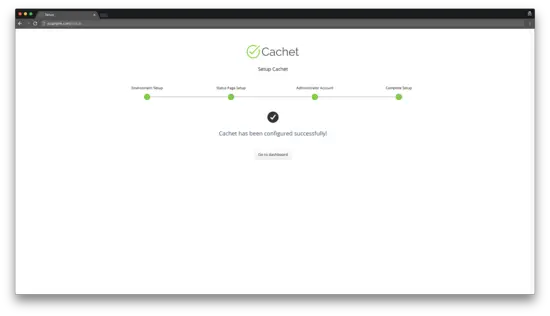
After that, you should get a message that Cachet has been configured successfully. You can open the Cachet dashboard by pressing the "Go to dashboard" button:
Cachet installation and setup has been completed.
To access Cachet dashboard append /dashboard to your website URL.