How to Install Apache Tomcat 9 with Nginx Proxy on Debian 10
Tomcat is a free, open-source and lightweight application server used to deploy Java-based applications. It can be used as a standalone server or combined with other servers like Apache and Nginx. It provides the extended functionality to interact with Java Servlets and also implements several technical specifications of the Java platform. Currently, Tomcat is one of the most widely used application servers for Java.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install Tomcat 9 with Nginx on Debian 10.
Prerequisites
- A server running Debian 10.
- A valid domain name pointed with your server IP.
- A root password is configured on your server.
Getting Started
Before starting, it is a good idea to update your APT cache to the latest version. You can update it by running the following command:
apt-get update -y
Once your system package cache are up-to-date, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Java
Tomcat is a java-based application so Java must be installed in your server. If not installed, you can install it with the following command:
apt-get install default-jdk -y
Once the Java is installed, you can verify the Java version with the following command:
java --version
You should get the following output:
openjdk 11.0.9.1 2020-11-04 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.9.1+1-post-Debian-1deb10u2) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.9.1+1-post-Debian-1deb10u2, mixed mode, sharing)
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Install Tomcat
First, you will need to create a dedicated user to run the Tomcat server. You can create it with the following command:
useradd -m -U -d /opt/tomcat -s /bin/false tomcat
Next, download the latest version of Tomcat using the following command:
wget https://www-eu.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.45/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.45.tar.gz
Once the download is completed, extract the downloaded file with the following command:
tar -xvzf apache-tomcat-9.0.45.tar.gz
Next, move the extracted directory to the /opt with the following command:
mv apache-tomcat-9.0.45 /opt/tomcat/tomcat
Next, set proper permission and ownership with the following command:
chown -R tomcat:tomcat /opt/tomcat/tomcat
chmod -R 755 /opt/tomcat/tomcat
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Create a Systemd Service File for Tomcat
Next, you will need to create a systemd service file to manage the Tomcat service. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit] Description=Tomcat 9.0 servlet container After=network.target [Service] Type=forking User=tomcat Group=tomcat Environment="JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/default-java" Environment="JAVA_OPTS=-Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom" Environment="CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat/tomcat" Environment="CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat/tomcat" Environment="CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid" Environment="CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M -server -XX:+UseParallelGC" ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/tomcat/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file then reload the systemd daemon with the following command:
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start the Tomcat service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start tomcat
systemctl enable tomcat
You can also verify the status of Tomcat with the following command:
systemctl status tomcat
You should get the following output:
? tomcat.service - Tomcat 9.0 servlet container
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2021-04-14 05:41:21 UTC; 42s ago
Process: 5784 ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/tomcat/bin/startup.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 5791 (java)
Tasks: 30 (limit: 4701)
Memory: 159.1M
CGroup: /system.slice/tomcat.service
??5791 /usr/lib/jvm/default-java/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/tomcat/tomcat/conf/logging.properties -Djava.util.log
Apr 14 05:41:21 debian systemd[1]: Starting Tomcat 9.0 servlet container...
Apr 14 05:41:21 debian startup.sh[5784]: Tomcat started.
Apr 14 05:41:21 debian systemd[1]: Started Tomcat 9.0 servlet container.
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Configure Tomcat Web Interface
Next, you will need to define a user to access the Tomcat web interface. You can define it using the tomcat-users.xml file:
nano /opt/tomcat/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Find the
<role rolename="admin-gui"/> <role rolename="manager-gui"/> <user username="tomcatadmin" password="password" roles="admin-gui,manager-gui"/>
Save and close the file when you are finished.
By default, the Tomcat web interface is configured to access only from the localhost. So you will need to configure it for external access.
For the Manager app, edit the following line:
nano /opt/tomcat/tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
For the Host Manager app, edit the following file:
nano /opt/tomcat/tomcat/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
Remove the following line:
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve"
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" />
Save and close the file then restart the Tomcat service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart tomcat
Once you are finished, you can proceed to the next step.
Configure Nginx for Tomcat
Next, you will need to install and configure the Nginx as a reverse proxy for Tomcat. First, install the Nginx package with the following command:
apt-get install nginx -y
Once the Nginx has been installed, you will need to create a new Nginx virtual host configuration file for Tomcat. You can create it using the following command:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/tomcat.conf
Add the following lines:
server {
listen 80;
server_name tomcat.example.com;
root /opt/tomcat/tomcat/webapps/;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
}
}
Save and close the file then verify the Nginx for any syntax error:
nginx -t
You should see the following output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Next, restart the Nginx service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart nginx
Next, verify the status of the Nginx service with the following command:
systemctl status nginx
You should see the following output:
? nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2021-04-14 05:57:03 UTC; 1min 38s ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Process: 6852 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 6853 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 6854 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4701)
Memory: 4.0M
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??6854 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
??6855 nginx: worker process
??6856 nginx: worker process
Apr 14 05:57:03 debian systemd[1]: Starting A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server...
Apr 14 05:57:03 debian systemd[1]: Started A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server.
At this point, Nginx is configured to access the Tomcat. You can now proceed to the next step.
Access Tomcat Web UI
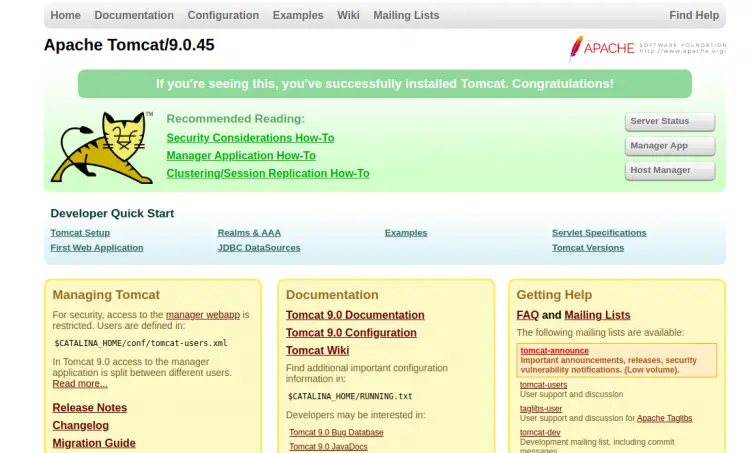
Now, open your web browser and access the Tomcat web UI using the URL http://tomcat.example.com. You should see the following page:
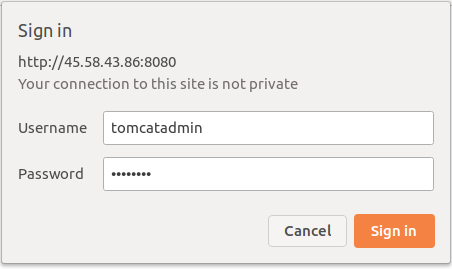
Click on the Manager App, you should see the following page:
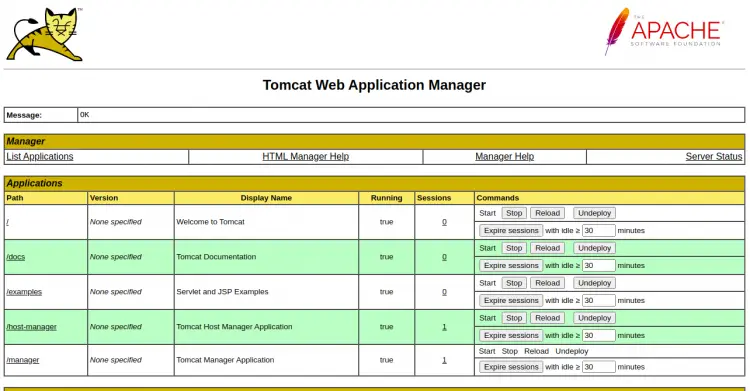
Provide your Manager App admin username, password and click on the Sign In button. You should see the following page:
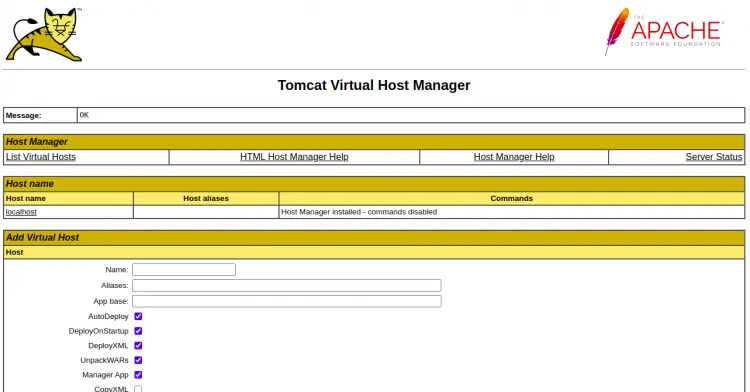
You can also click on the Host Manager to access the Host Manager App as shown below:
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed Tomcat with Nginx as a reverse proxy on Debian 10. You can now deploy your Java application easily with Tomcat. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.