How to Install Apache Spark on Debian 11
Apache Spark is a free, open-source, general-purpose and distributed computational framework that is created to provide faster computational results. It supports several APIs for streaming, graph processing including, Java, Python, Scala, and R. Generally, Apache Spark can be used in Hadoop clusters, but you can also install it in standalone mode.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Apache Spark framework on Debian 11.
Prerequisites
- A server running Debian 11.
- A root password is configured on the server.
Install Java
Apache Spark is written in Java. So Java must be installed in your system. If not installed, you can install it using the following command:
apt-get install default-jdk curl -y
Once the Java is installed, verify the Java version using the following command:
java --version
You should get the following output:
openjdk 11.0.12 2021-07-20 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.12+7-post-Debian-2) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.12+7-post-Debian-2, mixed mode, sharing)
Install Apache Spark
At the time of writing this tutorial, the latest version of Apache Spark is 3.1.2. You can download it using the following command:
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/spark/spark-3.1.2/spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz
Once the download is completed, extract the downloaded file with the following command:
tar -xvzf spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2.tgz
Next, move the extracted directory to the /opt with the following command:
mv spark-3.1.2-bin-hadoop3.2/ /opt/spark
Next, edit the ~/.bashrc file and add the Spark path variable:
nano ~/.bashrc
Add the following lines:
export SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark export PATH=$PATH:$SPARK_HOME/bin:$SPARK_HOME/sbin
Save and close the file then activate the Spark environment variable using the following command:
source ~/.bashrc
Start Apache Spark
You can now run the following command to start the Spark master service:
start-master.sh
You should get the following output:
starting org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master, logging to /opt/spark/logs/spark-root-org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master-1-debian11.out
By default, Apache Spark listens on port 8080. You can verify it using the following command:
ss -tunelp | grep 8080
You will get the following output:
tcp LISTEN 0 1 *:8080 *:* users:(("java",pid=24356,fd=296)) ino:47523 sk:b cgroup:/user.slice/user-0.slice/session-1.scope v6only:0 <->
Next, start the Apache Spark worker process using the following command:
start-slave.sh spark://your-server-ip:7077
Access the Apache Spark Web UI
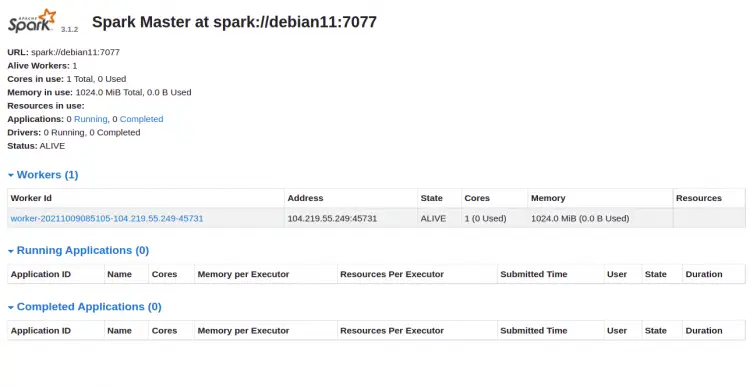
You can now access the Apache Spark web interface using the URL http://your-server-ip:8080. You should see the Apache Spark master and slave service on the following screen:
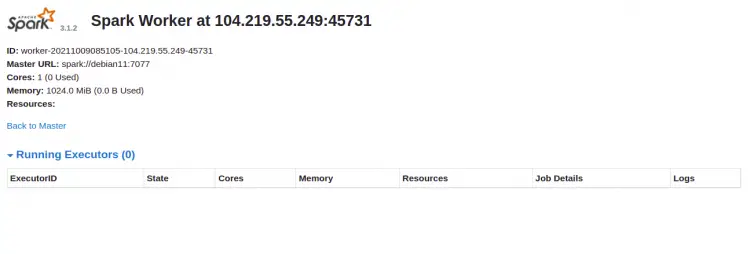
Click on the Worker id. You should see the detailed information of your Worker on the following screen:
Connect Apache Spark via Command-line
If you want to connect to Spark via its command shell, run the commands below:
spark-shell
Once you are connected, you will get the following interface:
Spark session available as 'spark'.
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/___/ .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 3.1.2
/_/
Using Scala version 2.12.10 (OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM, Java 11.0.12)
Type in expressions to have them evaluated.
Type :help for more information.
scala>
If you want to use Python in Spark. You can use pyspark command-line utility.
First, install the Python version 2 with the following command:
apt-get install python -y
Once installed, you can connect the Spark with the following command:
pyspark
Once connected, you should get the following output:
To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/__ / .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 3.1.2
/_/
Using Python version 3.9.2 (default, Feb 28 2021 17:03:44)
Spark context Web UI available at http://debian11:4040
Spark context available as 'sc' (master = local[*], app id = local-1633769632964).
SparkSession available as 'spark'.
>>>
Stop Master and Slave
First, stop the slave process using the following command:
stop-slave.sh
You will get the following output:
stopping org.apache.spark.deploy.worker.Worker
Next, stop the master process using the following command:
stop-master.sh
You will get the following output:
stopping org.apache.spark.deploy.master.Master
Conclusion
Congratulations! you have successfully installed Apache Spark on Debian 11. You can now use Apache Spark in your organization to process large datasets