How to Install and Monitor Servers with Checkmk on Ubuntu 22.04
On this page
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 - Configure Firewall
- Step 2 - Install Checkmk
- Step 3 - Create Checkmk Site
- Step 4 - Access Checkmk site
- Step 5 - Install SSL
- Step 6 - Configure Apache Server
- Step 7 - Install Monitoring Agent
- Step 8 - Add Host for Monitoring
- Step 9 - Enable Email Notifications
- Step 10 - Upgrade
- Step 11 - Backup and Restore Checkmk Sites
- Conclusion
Checkmk is a server and application monitoring software written in Python and C++. It supports the monitoring of servers, applications, networks, containers, and clouds. It has a wide range of features, including, automated monitoring, agentless monitoring via HTTP/SNMP, over 1900 plugins to collect data, detailed network traffic analysis, customizable dashboards, and Grafana support.
Checkmk comes in four editions. The first version is the open-source Raw edition and uses Nagios as its core. The second version is the free version which has all the features of the standard edition, supports unlimited hosts for the first 30 days, and afterward is limited to 25 hosts. The enterprise standard edition and the enterprise-managed editions are advanced versions with support for unlimited hosts and multiple customers.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install and monitor servers using Checkmk on a Ubuntu 22.04 machine.
Prerequisites
-
A server running Ubuntu 22.04. The Standard edition will give a warning if the number of CPU cores on your server is less than 4. However, you can safely ignore this warning but depending upon the number of hosts you want to monitor, you should opt for a more powerful machine. The Raw edition doesn't perform such a check.
-
A non-root user with sudo privileges.
-
The uncomplicated Firewall(UFW) is enabled and running.
-
A Fully Qualified domain name (FQDN) pointing to the server like,
checkmk.example.com. -
Everything is updated.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Step 1 - Configure Firewall
Before installing any packages, the first step is configuring the firewall to allow HTTP and HTTPS connections.
Check the status of the firewall.
$ sudo ufw status
You should see something like the following.
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Allow HTTP and HTTPs ports.
$ sudo ufw allow http $ sudo ufw allow https
Check the status again to confirm.
$ sudo ufw status Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443 ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 2 - Install Checkmk
For our tutorial, we will be working with the Standard Free edition of Checkmk. You can however use any edition you want. The commands will remain the same.
The first step is to grab the GPG key for Checkmk.
$ wget https://download.checkmk.com/checkmk/Check_MK-pubkey.gpg
Import the key.
$ gpg --import Check_MK-pubkey.gpg
At the time of writing this tutorial, 2.1.0p11 is the latest available version. You can check the official Checkmk download page to grab whichever version/edition of Checkmk you want. Copy the command of the version and edition you want. Since we are installing the Standard edition, our download command will look like the following.
$ wget https://download.checkmk.com/checkmk/2.1.0p11/check-mk-free-2.1.0p11_0.jammy_amd64.deb
Install the Checkmk package.
$ sudo apt install ./check-mk-free-2.1.0p11_0.jammy_amd64.deb
The Checkmk package will install the Apache webserver for you. If you have an existing server on your machine, you can configure it to work as a proxy for Apache.
Confirm whether Checkmk has been installed.
$ omd version OMD - Open Monitoring Distribution Version 2.1.0p11.cfe
The Checkmk monitoring system uses the Open Monitoring Distribution (OMD) project which is managed via the command line using the omd command.
Step 3 - Create Checkmk Site
OMD tool is used to create and manage multiple monitoring sites on a single server. Each site is a self-contained monitoring system running independently of others.
Run the following command to create the Checkmk site.
$ sudo omd create howtoforge
You will get a similar output.
Adding /opt/omd/sites/howtoforge/tmp to /etc/fstab. Creating temporary filesystem /omd/sites/howtoforge/tmp...OK Updating core configuration... Generating configuration for core (type cmc)... Starting full compilation for all hosts Creating global helper config...OK Creating cmc protobuf configuration...OK Executing post-create script "01_create-sample-config.py"...OK Restarting Apache...OK Created new site howtoforge with version 2.1.0p11.cfe. The site can be started with omd start howtoforge. The default web UI is available at http://checkmk/howtoforge/ The admin user for the web applications is cmkadmin with password: 9sWdQemE For command line administration of the site, log in with 'omd su howtoforge'. After logging in, you can change the password for cmkadmin with 'htpasswd etc/htpasswd cmkadmin'.
The above command performs the following steps.
- A system user and a group named
howtoforgeis created. - A home directory
/omd/sites/howtoforgeis created and assigned to the above user. This is called the site directory. - The home directory is populated with configuration files and sub-directories.
- A basic configuration file is created for the site.
- Apache server is configured and restarted.
You can perform the site operations after logging in to the howtoforge user using the following command.
$ sudo omd su howtoforge
This will switch you to its login shell.
OMD[howtoforge]:-$
Alternatively, you can perform the site operations using sudo keyword.
Start the site.
OMD[howtoforge]:-$ omd start Temporary filesystem already mounted Starting agent-receiver...OK Starting mkeventd...OK Starting liveproxyd...OK Starting mknotifyd...OK Starting rrdcached...OK Starting cmc...OK Starting apache...OK Starting dcd...OK Starting redis...OK Initializing Crontab...OK
Use the following command to stop the site.
OMD[howtoforge]:-$ omd stop
Check the site's status using the following command.
OMD[mysite]:~$ omd status agent-receiver: running mkeventd: running liveproxyd: running mknotifyd: running rrdcached: running cmc: running apache: running dcd: running redis: running crontab: running ----------------------- Overall state: running
To change the default password for Checkmk, issue the following command.
OMD[howtoforge]:-$ htpasswd -m etc/htpasswd cmkadmin New password: Re-type new password: Updating password for user cmkadmin
Step 4 - Access Checkmk site
Visit the URL http://<serverIP>/howtoforge or http://checkmk.example.com/howtoforge and you will get the following login page. Log in using the credentials provided in the previous step to log in to the monitoring site.
Once logged in, you will see the Checkmk dashboard.
Step 5 - Install SSL
We need to install Certbot to generate the SSL certificate. We will install Certbot using Snapd.
Ubuntu 22.04 comes with Snapd installed by default. Run the following commands to ensure that your version of Snapd is up to date.
$ sudo snap install core $ sudo snap refresh core
Install Certbot.
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
Use the following command to ensure that the Certbot command can be run by creating a symbolic link to the /usr/bin directory.
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
Run the following command to generate an SSL Certificate.
$ sudo certbot certonly --apache --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d checkmk.example.com
The above command will download a certificate to the /etc/letsencrypt/live/checkmk.example.com directory on your server.
To check whether the SSL renewal is working fine, do a dry run of the process.
$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see no errors, you are all set. Your certificate will renew automatically.
Step 6 - Configure Apache Server
Enable the Apache headers module.
$ sudo a2enmod headers
Enable the mod_ssl apache module.
$ sudo a2enmod ssl
Enable the HTTP/2 module.
$ sudo a2enmod http2
Create and open the file /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/howtoforge.conf for editing.
Paste the following code in it.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName checkmk.example.com
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} !^443$
RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}$1 [L]
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "https"
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName checkmk.example.com
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/checkmk.error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/checkmk.access.log combined
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/checkmk.example.com/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/checkmk.example.com/privkey.pem
SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/checkmk.example.com/chain.pem
Protocols h2 http/1.1
</VirtualHost>
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Create and open the file /etc/apache2/conf-available/ssl-params.conf for editing. Paste the following code in it.
SSLProtocol -all +TLSv1.3 +TLSv1.2 SSLOpenSSLConfCmd Curves X25519:secp521r1:secp384r1:prime256v1 SSLCipherSuite ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 SSLHonorCipherOrder on SSLSessionTickets off SSLCompression off SSLUseStapling On SSLStaplingCache "shmcb:logs/ssl_stapling(32768)" SSLStaplingResponseMaxAge 900
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Deactivate the default site.
$ sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
Activate the Checkmk site.
$ sudo a2ensite howtoforge.conf
Activate the SSL configuration file.
$ sudo a2enconf ssl-params
Verify the configuration.
$ sudo apache2ctl configtest
If you get OK as the response, proceed with restarting the Apache server to activate the Checkmk site.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
You can now access your Checkmk site via the URL https://checkmk.example.com/howtoforge.
Step 7 - Install Monitoring Agent
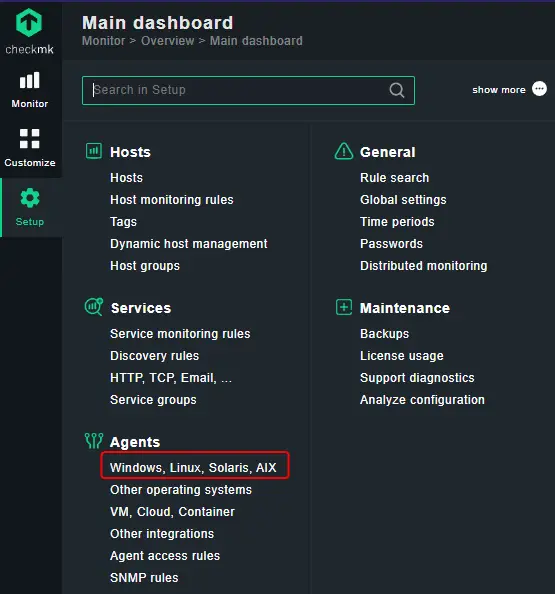
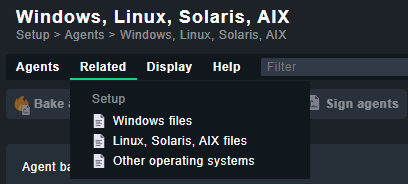
You need to install a monitoring agent to add and monitor other hosts in Checkmk. To install the agent, open the Checkmk site, and go to Setup > Agents > Windows, Linux, Solaris, AIX option.
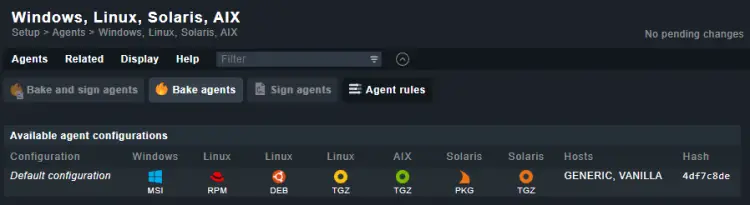
You will be taken to the following page.
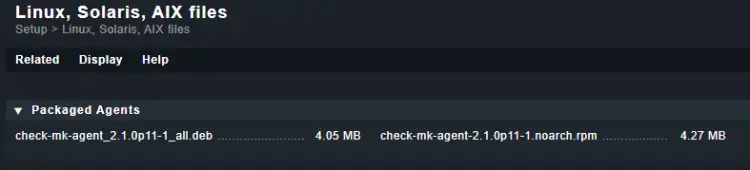
Click the Related menu item on the top and then select Linux, Solaris, AIX files from the dropdown menu.
Copy the download link to the deb file from the following page.
Download the agent using the copied link onto the host server.
$ wget https://checkmk.example.com/howtoforge/check_mk/agents/check-mk-agent_2.1.0p11-1_all.deb
Install the downloaded package.
$ sudo apt install ./check-mk-agent_2.1.0p11-1_all.deb
Verify if the agent is installed.
$ check_mk_agent
You will get a similar output.
$ check_mk_agent <<<check_mk>>> Version: 2.1.0p11 AgentOS: linux Hostname: checkmk AgentDirectory: /etc/check_mk DataDirectory: /var/lib/check_mk_agent SpoolDirectory: /var/lib/check_mk_agent/spool PluginsDirectory: /usr/lib/check_mk_agent/plugins LocalDirectory: /usr/lib/check_mk_agent/local .......
Before proceeding ahead, we need to open port 6556 which is used by the server to connect to the Checkmk host.
$ sudo ufw allow 6556
The next step is to register the host with the server. This step is necessary for a secured Checkmk server. You can skip it if you don't use SSL on your server.
There are some bugs with the latest agent package, therefore, run the following commands as a workaround.
$ sudo /var/lib/cmk-agent/scripts/cmk-agent-useradd.sh $ sudo /var/lib/cmk-agent/scripts/super-server/setup trigger
Restart the following services.
$ sudo systemctl restart cmk-agent-ctl-daemon.service --now $ sudo systemctl restart check-mk-agent.socket --now
Issue the following command to register the host with your Checkmk server.
$ sudo cmk-agent-ctl register --hostname localhost --server checkmk.example.com:443 --site howtoforge --user cmkadmin
You will get a similar output where you will be asked if you want to establish a connection and the password for the Checkmk server.
Attempting to register at checkmk.nspeaks.xyz:443/howtoforge. Server certificate details:
PEM-encoded certificate:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFLTCC...........
.............udEkKI
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Issued by:
R3
Issued to:
checkmk.example.com
Validity:
From Mon, 05 Sep 2022 08:12:29 +0000
To Sun, 04 Dec 2022 08:12:28 +0000
Do you want to establish this connection? [Y/n]
> y
Please enter password for 'cmkadmin'
>
ERROR [cmk_agent_ctl] Error pairing with checkmk.nspeaks.xyz:443/howtoforge
Caused by:
Request failed with code 404 Not Found: <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>404 Not Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Not Found</h1>
<p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p>
</body></html>
You will probably see an error at the end of the command. This is due to the buggy Checkmk agent package at the time of writing this tutorial. But the host is registered successfully with the server.
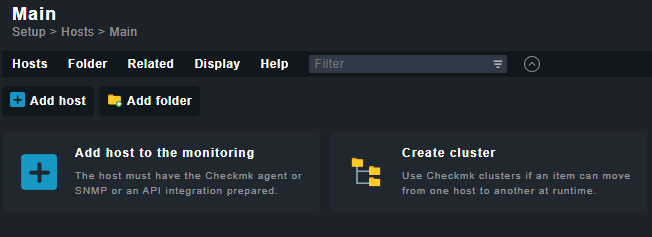
Step 8 - Add Host for Monitoring
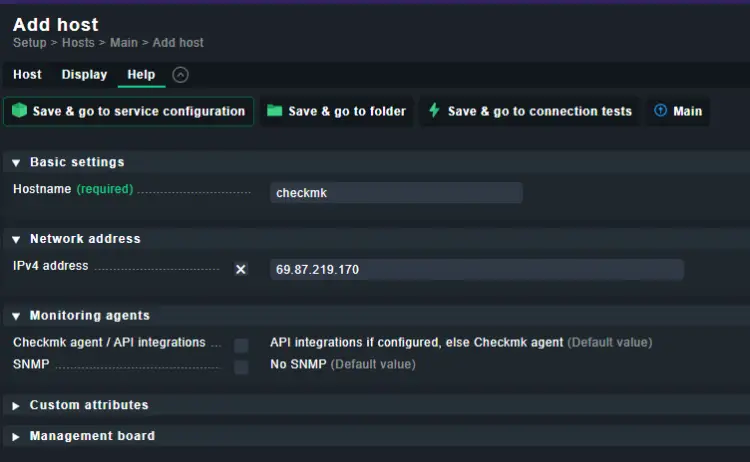
To add your host, visit the Setup option from the left panel and then open the Hosts > Hosts and click Add Host button to proceed.
Enter the hostname and the IP address of the host server, and click the Save & go to service configuration button.
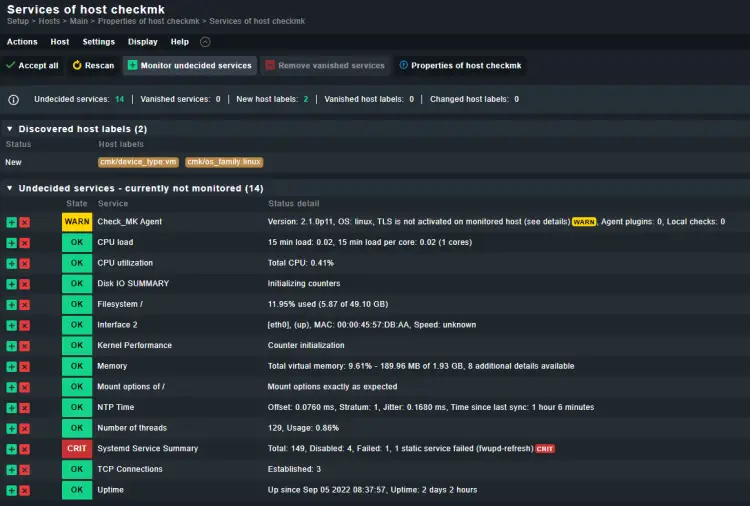
On the services page, you will see a list of all discovered services. If you see any Undecided services, click the Fix all link to fix the issue.
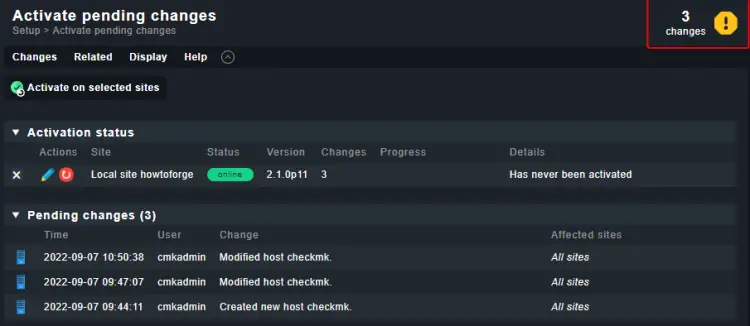
Then, click the yellow-colored sign on the top right corner of the window.
Next, click the Activate on selected sites button.
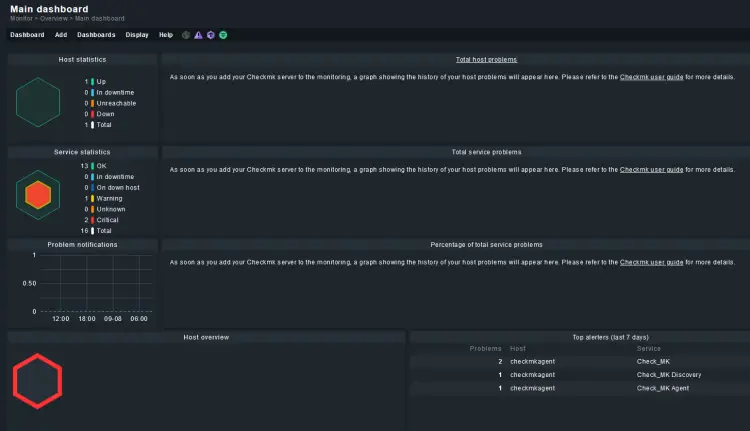
Go back to the homepage and you will notice the Host and service statistics on it. You will need to configure and create custom dashboards to gather more statistics.
Step 9 - Enable Email Notifications
You can enable Checkmk to send out notifications about status changes of your hosts to your email address to get notifications about failures.
Checkmk doesn't ship with an SMTP relay mechanism, therefore, you need to configure an SMTP relay on your server to send email notifications. You can use Postfix, Sendmail, or any other software of your choice. Configuring Postfix and Sendmail is out of the scope of this tutorial, therefore, we will not go into that.
Once you have configured your server for SMTP relay mails, the next step is to configure the server with your email address.
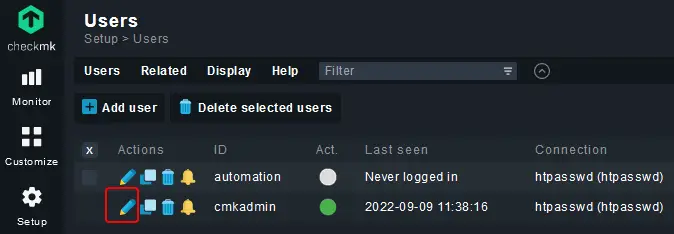
Visit the Setup >> Users >> Users menu and you will be taken to the following page.
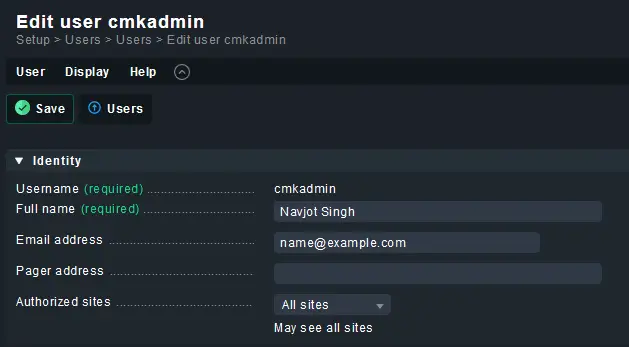
Click the pencil icon against your username to open the User properties page.
Fill in the email address and click the Save button to finish.
Edit Notification Rules
The next step is to set rules based on which, you will receive email notifications. Click the bell icon against your username on the users page.
Click the Add rule button to start creating new rules for your Checkmk user.
On the next page, fill in the notification description.
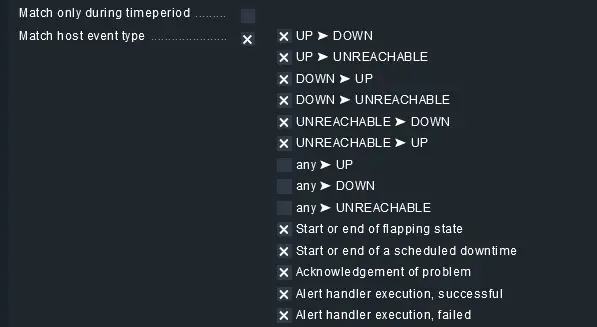
Next, checkmark the condition named Match host event type and select the following options as shown below.
Click the Save button to finish updating the rules.
Click the yellow button on the top right and click the Activate on selected sites button to apply the changes.
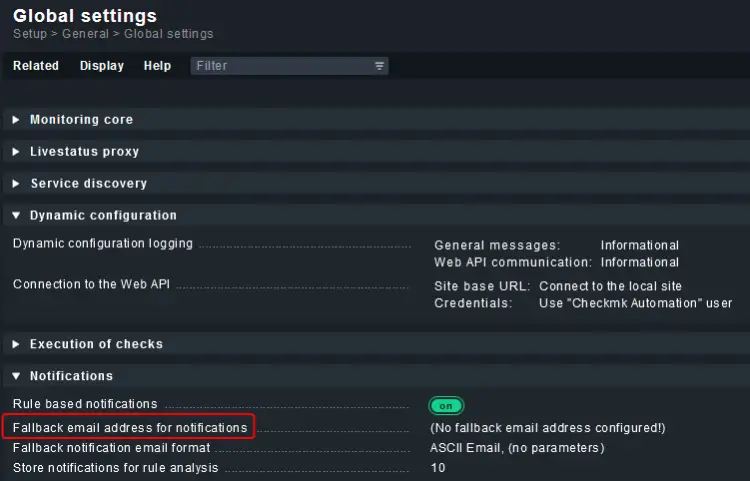
Configure Fallback Email-address for Notifications
When a notification is received and is not matched by any notification rule, it is sent to a globally configured fallback email address.
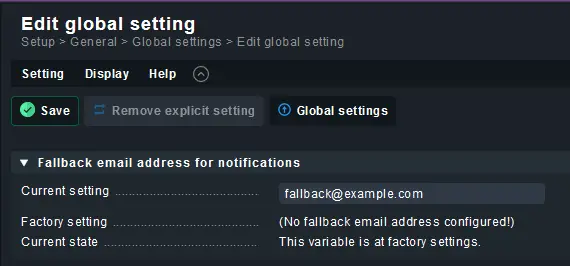
Visit the Global Settings menu from the left panel and click on the Fallback email address for notifications link.
On the next page, enter the email address and click the Save button to update.
Click the yellow icon on the next page and click the Activate on selected sites button to update the email id. Now, you should start receiving emails regarding the status of your host.
Step 10 - Upgrade
Checkmk can run multiple software versions on a single server. And you can assign each site to a specific version. Therefore, updating Checkmk can be a multiple-step process. The first step would be to install the upgraded package. And then, link the upgraded package to the site you want to update.
Installing new version
The first step is to install a new version of Checkmk. The process is the same as installing Checkmk. Grab the newer version from the Archives page of Checkmk and run the apt install command on the package.
Let us grab the raw version of Checkmk.
$ wget https://download.checkmk.com/checkmk/2.1.0p11/check-mk-raw-2.1.0p11_0.jammy_amd64.deb
Install the downloaded package.
$ sudo apt install ./check-mk-raw-2.1.0p11_0.jammy_amd64.deb
List all the available versions using the following command.
$ omd versions 2.1.0p11.cfe 2.1.0p11.cre (default)
The newly downloaded version is set as the default version and any new site created from here on will use that version.
Create a new site with this version.
$ sudo omd create site testsite Adding /opt/omd/sites/testsite/tmp to /etc/fstab. Creating temporary filesystem /omd/sites/testsite/tmp...OK Updating core configuration... Generating configuration for core (type nagios)... Precompiling host checks...OK Executing post-create script "01_create-sample-config.py"...OK Restarting Apache...OK Created new site testsite with version 2.1.0p11.cre. The site can be started with omd start testsite. The default web UI is available at http://checkmk/testsite/ The admin user for the web applications is cmkadmin with password: ZX0NDzY1 For command line administration of the site, log in with 'omd su testsite'. After logging in, you can change the password for cmkadmin with 'htpasswd etc/htpasswd cmkadmin'.
List the sites on your server.
$ omd sites SITE VERSION COMMENTS howtoforge 2.1.0p11.cfe testsite 2.1.0p11.cre default version
Log in to the testsite shell.
$ sudo omd su testsite
Run the following command to update the OMD version of the site.
OMD[testsite]:~$ omd update
You will get the following GUI screen.

Press the Enter key to proceed.
Since we are updating from the free to the Standard edition, you will be prompted again.

Press the Enter key to proceed with updating the site. You will get the following output.
2022-09-09 09:51:15 - Updating site 'testsite' from version 2.1.0p11.cre to 2.1.0p11.cfe... * Installed dir local/lib/python3/cmk/cee * Installed dir local/lib/python3/cmk/cee/dcd * Installed dir local/lib/python3/cmk/cee/dcd/plugins * Installed dir local/lib/python3/cmk/cee/dcd/plugins/connectors * Installed dir var/check_mk/reports * Installed dir var/check_mk/rrd * Installed dir var/check_mk/reports/archive * Installed link etc/rc.d/80-cmc * Installed link etc/rc.d/20-mknotifyd ????????????????????????????? * Installed link etc/rc.d/20-liveproxyd ? You are updating from Raw ? * Installed link etc/rc.d/85-dcd ? Edition to Free Edition. ? * Installed file etc/logrotate.d/mknotifyd ? Is this intended? ? * Installed file etc/logrotate.d/cmc ? ? * Installed file etc/logrotate.d/liveproxyd????????????????????????????? * Installed file etc/logrotate.d/dcd ? < yes > < no > ? * Installed file etc/init.d/mknotifyd ????????????????????????????? * Installed file etc/init.d/cmc * Installed file etc/init.d/liveproxyd * Installed file etc/init.d/dcd Creating temporary filesystem /omd/sites/testsite/tmp...OK Executing update-pre-hooks script "02_cmk-update-config"... -| Initializing application... -| Updating Checkmk configuration... -| ATTENTION: Some steps may take a long time depending on your installation, e.g. during major upgrades. -| 1/26 Rewriting password store... -| 2/26 Migrate Visuals context... -| 3/26 Update global settings... -| 4/26 Rewriting tags... -| 5/26 Rewriting hosts and folders... -| 6/26 Rewriting rulesets... -| Replacing ruleset non_inline_snmp_hosts with snmp_backend_hosts -| 7/26 Rewriting discovered host labels... -| 8/26 Rewriting autochecks... -| 9/26 Cleanup version specific caches... -| 10/26 Migrating fs_used name... -| 11/26 Migrate pagetype topics... -| 12/26 Migrate dashlets... -| 13/26 Migrate LDAP connections... -| 14/26 Rewrite BI Configuration... -| Skipping conversion of bi.mk (already done) -| 15/26 Set version specific user attributes... -| 16/26 Rewriting inventory data... -| Skipping path '/omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/inventory' (empty) -| Skipping path '/omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/inventory_archive' (empty) -| Skipping path '/omd/sites/testsite/tmp/check_mk/status_data' (empty) -| Finished checking for corrupt files -| Creating file '/omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/update_config/py2conversion.done' -| 17/26 Migrate audit log... -| No audit log present. Skipping. -| 18/26 Sanitize audit log (Werk #13330)... -| Wrote audit log backup to /omd/sites/testsite/audit_log_backup. Please check if the audit log in the GUI works as expected. In case of problems you can copy the backup files back to /omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/wato/log. Please check the corresponding files in /omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/wato/log for any leftover passwords and remove them if necessary. If everything works as expected you can remove the backup. For further details please have a look at Werk #13330. -| Sanitizing log files: /omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/wato/log/wato_audit.log -| Finished sanitizing log files -| Wrote sanitization flag file /omd/sites/testsite/var/check_mk/wato/log/.werk-13330 -| 19/26 Rename discovered host label files... -| 20/26 Rewriting host, service or contact groups... -| 21/26 Rewriting notification configuration for ServiceNow... -| 22/26 Renewing certificates without server name extension... -| Skipping (nothing to do) -| 23/26 Adding site CA to trusted CAs... -| 24/26 Rewrite mknotifyd config for central site... -| 25/26 Rewriting InfluxDB connections... -| 26/26 Disabling unsafe EC rules... -| Done OK Executing update-pre-hooks script "01_mkp-disable-outdated"...OK Updating core configuration... Generating configuration for core (type nagios)... Precompiling host checks...OK Finished update.
Confirm the site version.
OMD[testsite]:~$ omd version OMD - Open Monitoring Distribution Version 2.1.0p11.cfe
Congrats. You have successfully updated your site.
Exit the shell.
OMD[testsite]:~$ exit
You can change the OMD's default version with the following command.
$ sudo omd setversion 2.1.0p11.cfe
Step 11 - Backup and Restore Checkmk Sites
You can backup and restore a Checkmk site using both, the GUI and the command line methods.
Log in to the Site's shell.
$ sudo omd su howtoforge
Issue the following command to backup the site to the /tmp folder.
$ OMD[howtoforge]:~$ omd backup /tmp/howtoforge.tar.gz
You can take a backup without logging into the shell.
$ sudo omd backup howtoforge /tmp/howtoforge.tar.gz
If you don't want the historical events to be backed up with the site, you can take a backup without it.
$ sudo omd backup howtoforge -N /tmp/howtoforge.N.tar.gz
Restore a Checkmk site
Restoring a Checkmk site completely empties and refills it. Therefore, the site should be stopped before restoring.
$ sudo omd stop howtoforge
Run the restore.
$ sudo omd restore howtoforge /tmp/howtoforge.tar.gz
You can combine the stopping and restoring commands into one using the --kill flag.
$ sudo omd restore howtoforge --kill /tmp/howtoforge.tar.gz
You can restore the backup as a new site with a different name.
$ sudo omd restore howtoforge1 /tmp/howtoforge.tar.gz
Start the restored site.
$ sudo omd start howtoforge
Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on installing and using Checkmk to monitor servers on Ubuntu 22.04. If you have any questions, post them in the comments below.