Create and Store Secrets like Passwords, OAuth Tokens, and SSH Keys in Kubernetes
On this page
In Kubernetes, we can store and manage sensitive information, such as passwords, OAuth tokens, and ssh keys using Kubernetes Secrets. In Kubernetes, secrets can be defined as Kubernetes Objects. It is safer to store credentials in Kubernetes Secrets that in Pods or in Docker Images.
There are multiple ways of generating secrets in Kubernetes:
- Creating from a text file
- Creating from a yml file
Once the secrets are available they can be used in the following ways:
- Environment Variable
- Volume
- Using imagePullSecrets field
To know more about Kubernetes Secrets, click here.
In this article, we will create secrets using .yml file and access them in the Pod as Environment Variables.
Pre-requisites
- Kubernetes Cluster with at least 1 worker node.
If you want to learn to create a Kubernetes Cluster, click here. This guide will help you create a Kubernetes cluster with 1 Master and 2 Nodes on AWS Ubuntu 18l04 EC2 Instances.
What we will do
- Create Secrets
Create secrets
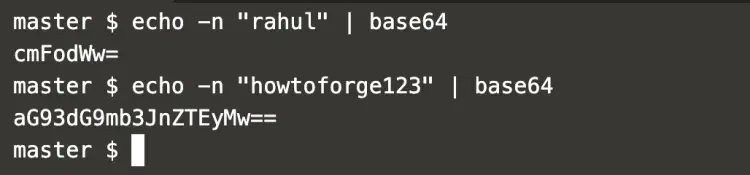
To create new secrets in Kubernetes, first encrypt them as shown below using base64 encoding method.
Here,
username=rahul and password=howtoforge123.
echo -n "rahul" | base64
echo -n "howtoforge123" | base64
In the above screenshot, it can be seen that the credentials have been encrypted.
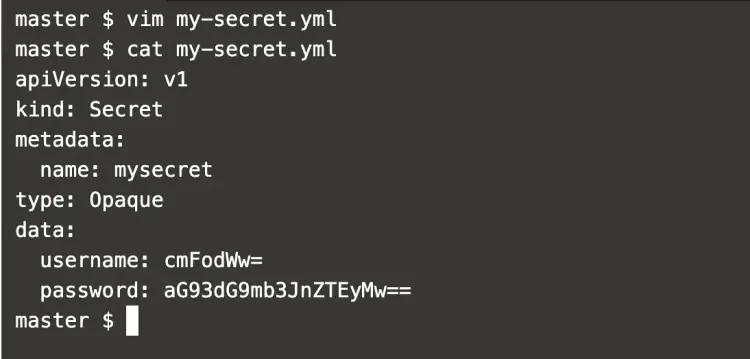
Create a secret definition file as follows, this file holds the base64 value of the credentials generated in the above step,.
vim my-secret.yml
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: mysecret type: Opaque data: username: cmFodWw= password: aG93dG9mb3JnZTEyMw==
Now, let's create a pod in which these secrets and can be accessed.
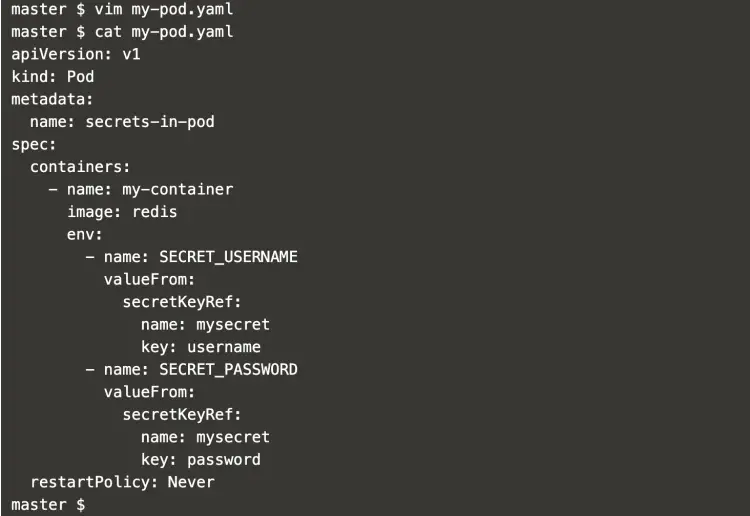
Create a new file that will contain the pod definition as follows.
vim my-pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: secrets-in-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: redis
env:
- name: SECRET_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: username
- name: SECRET_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: password
restartPolicy: Never
Let's create secrets using the following command.
kubectl create -f my-secret.yml
kubectl get secret | grep mysecret
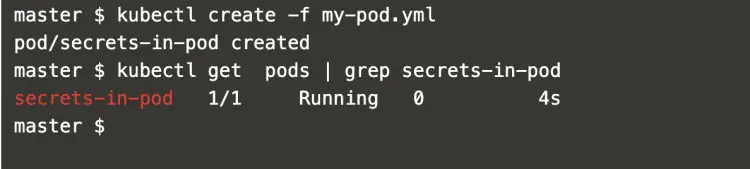
 Now, create a pod using the following pod definition to access the previously created secrets.
Now, create a pod using the following pod definition to access the previously created secrets.
kubectl create -f my-pod.yml
kubectl get pods | grep secrets-in-pod
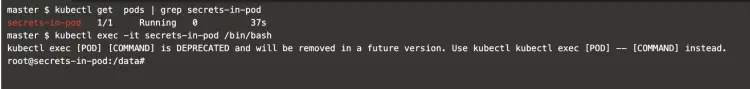
Login into the pod using the following command.
kubectl get pods | grep secrets-in-pod
kubectl exec -it secrets-in-pod /bin/bash
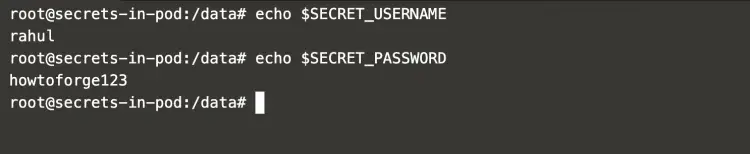
Once you login to the pod, the secrets can be accessed as Environment Variable using the following command.
echo $SECRET_USERNAME
echo $SECRET_PASSWORD
In the above screenshot, it can be seen that the secrets are available as Environment variables.
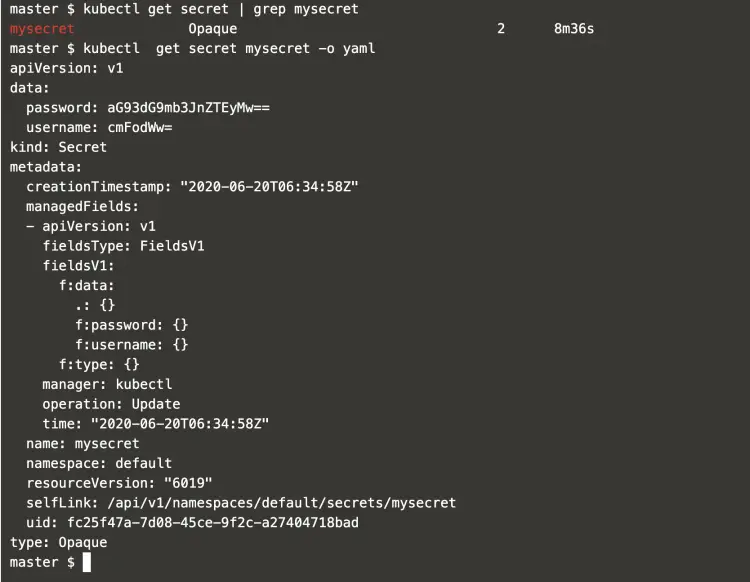
To see details of the secret object, execute the following command.
kubectl get secret | grep mysecret
kubectl get secret mysecret -o yaml
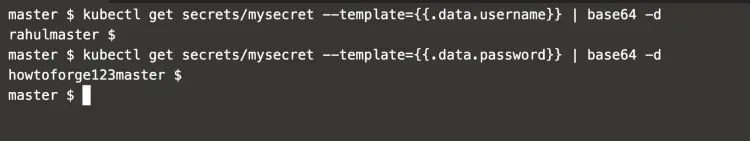
These secrete can also be decoded from the command line using the following commands.
kubectl get secrets/mysecret --template={{.data.username}} | base64 -d
kubectl get secrets/mysecret --template={{.data.password}} | base64 -d
In the above screenshot, it can be seen that the credentials are extracted from the Secrets and decrypted on the command line using base64.
Conclusion
In this article, we saw the steps to create and store secrets in Kubernetes from a .yml file. We tried to access these secrets in Pod as Environment variables. We also saw the command to decrypt the secrets on the command line.