PSAD installation and configuration on Debian 8 (Jessie)
On this page
In this tutorial, I will show you the installation and configuration of the PSAD (Port Scan Attack Detection) tool on Debian 8 (Jessie). As per project website: PSAD provides intrusion detection and log-analysis with IPtables (Linux firewall). The PSAD tool is used to change an IDS (Intrusion Detection) system into an IPS (Intrusion Prevention System). It uses the rules of the well-known open source IDS "SNORT" for the detection of intrusion events. The VM or server is continuously monitored by the tool for any active attacks such as port scans and it can block malicious IP addresses in the Linux firewall automatically. Another similar project is Guardian, which has very limited features. PSAD will be installed on a Debian-8 (Jessie) VM and the scanning tool "Nmap" will be used to check open ports on the VM. In the end, a DOS attack will be launched on the web server (Apache) to see the behavior of PSAD tool.
PSAD Installation
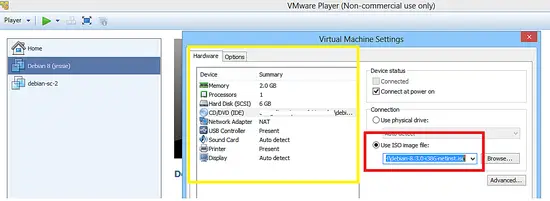
Debian Jessie will be installed on the VMware VM using net installer (debian-8.3.0-i386-netinst.iso).
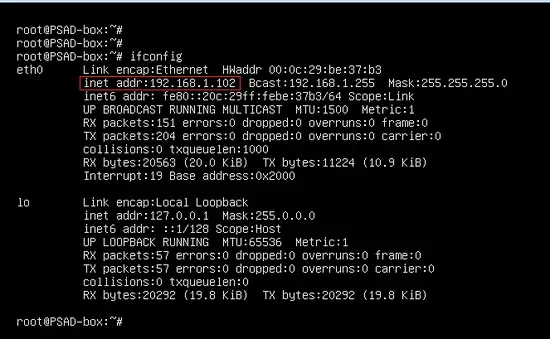
The Debian installation process is described in the previous article. The IP address of the PSAD machine is 192.168.1.102/24.
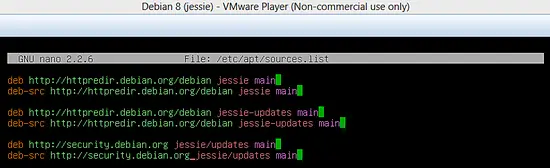
The PSAD tool can be installed from source code or from the Debian package repository. I will install it from the Debian repository. First of all, add the following in the sources.list file (or check if the lines are already there) and run the apt command to update the repository list.
deb http://httpredir.debian.org/debian jessie main deb-src http://httpredir.debian.org/debian jessie main deb http://httpredir.debian.org/debian jessie-updates main deb-src http://httpredir.debian.org/debian jessie-updates main deb http://security.debian.org/ jessie/updates main deb-src http://security.debian.org/ jessie/updates main
Sources list for Debian Jessie
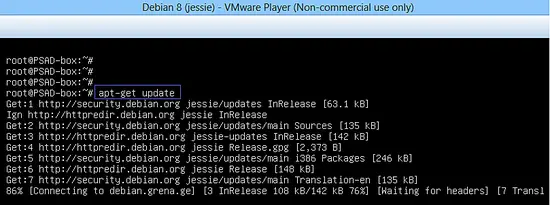
apt-get update
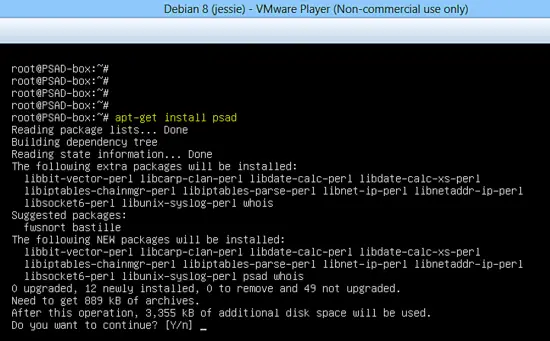
Run the following command to install PSAD in the VM.
apt-get install psad
Several Perl packages are required during installation of PSAD tool. The package dependencies will be automatically resolved by the Debian package manager.
The Firewalling feature on the Linux platform is provided by the IPtables package. It is a well known Linux firewall and already installed in all Linux distributions.
PSAD and Firewall Configuration
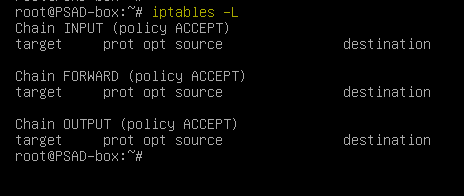
By default, there will be no rules in the IPtables chains on the Debian platform. Run the following command to list chains rules.
iptables -L
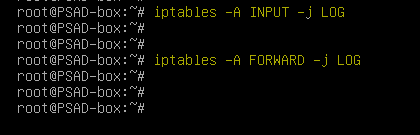
Enable logging on the input and forward chains of IPtables so that PSAD daemon can detect any abnormal activity.
iptables -A INPUT -j LOGiptables -A FORWARD -j LOG
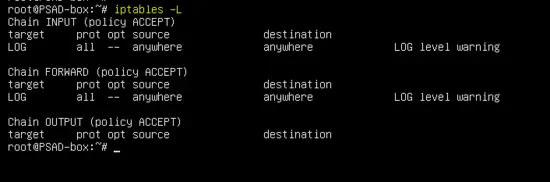
The output of "iptables -L" command will be similar as shown below now.
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination LOG all -- anywhere anywhere LOG level warning Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination LOG all -- anywhere anywhere LOG level warning Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
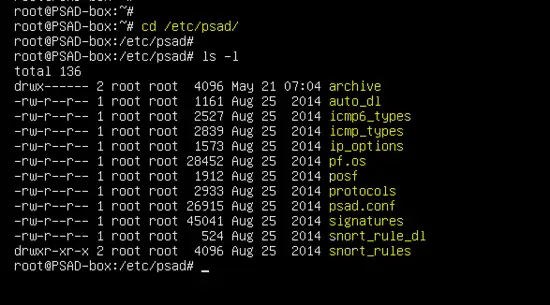
On the Debian distribution, the PSAD tool stores configuration files and rules in the /etc/psad directory.
The main PSAD configuration file is /etc/psad/psad.conf. In this tutorial, the IPS feature will be used to detects DOS attacks on the web server.
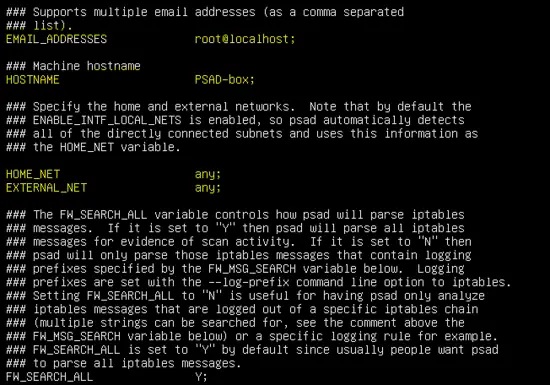
The basic settings for PSAD are given below.
EMAIL_ADDRESSES root@localhost;
HOSTNAME PSAD-box;
HOME_NET any;
EXTERNAL_NET any;
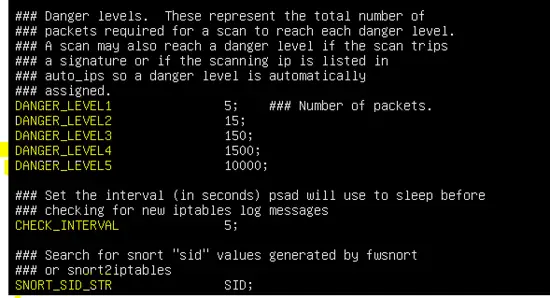
The default danger level setting, PSAD check interval and usage of SID is shown in the following figure.
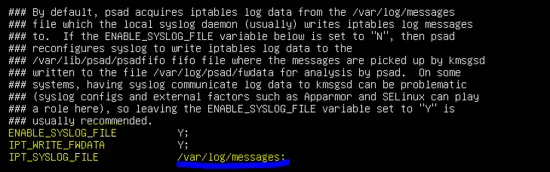
By default, the PSAD daemon searches for logs in /var/log/messages file. Therefore, change IPT_SYSLOG_FILE parameter in the PSAD configuration.
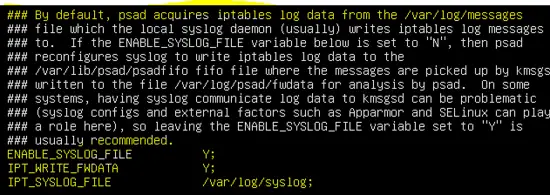
Debian based distributations store syslog messages in /var/log/syslog file.
ENABLE_SYSLOG_FILE Y;
IPT_WRITE_FWDATA Y;
IPT_SYSLOG_FILE /var/log/syslog;
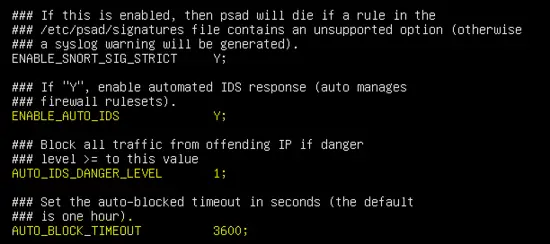
By default, PSAD works in IDS mode, the IPS parameter is disabled in the configuration file. Enable the following parameters to enable the IPS feature and danger level. After enabling the parameter in the configuration file, the PSAD daemon will automatically block the attacker by adding his IP address in the IPtables chains.
ENABLE_AUTO_IDS Y;
AUTO_IDS_DANGER_LEVEL 1;
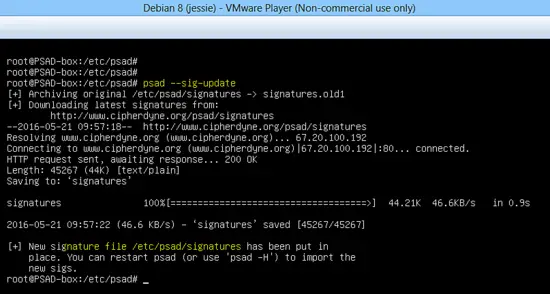
Now run the following command to update the signature database for detection of attacks.
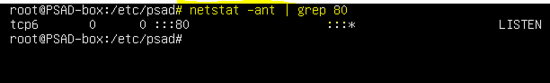
psad --sig-updateCurrently, Apache server is listening on port 80 as shown below.
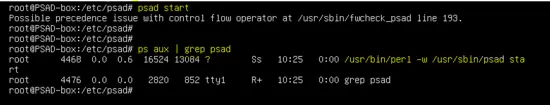
Start PSAD using the following command and check status.
psad start
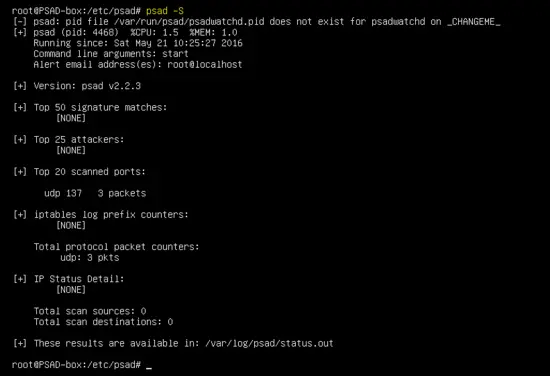
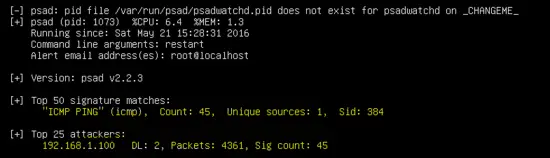
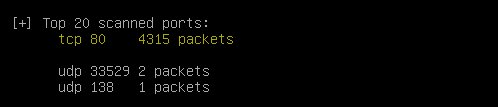
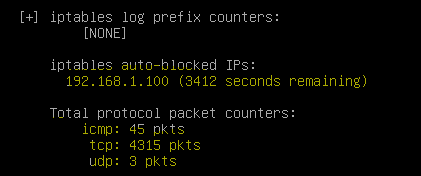
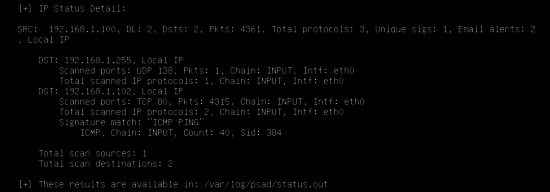
psad -S
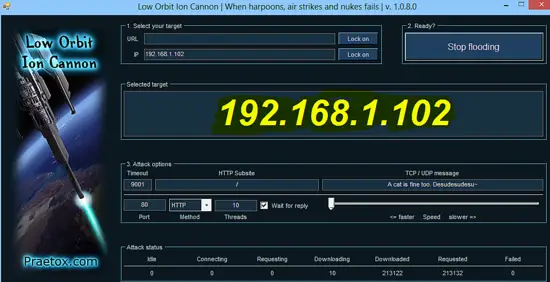
A DOS attack is launched using LOIC (Low Orbit Ion Cannon ) tool on the VM to test PSAD as shown below.
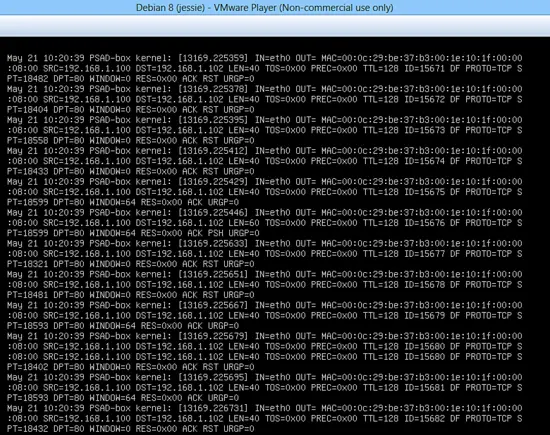
Syslog shows the DOS traffic generated using LOIC tool.
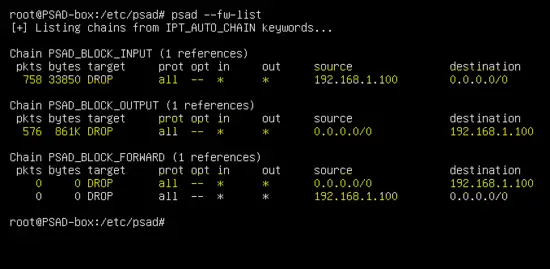
The IP address of the simulated attacker 192.168.1.100 is blocked by the PSAD daemon as shown below. Run the following command to view the dynamic rules added by PSAD.
psad --fw-list
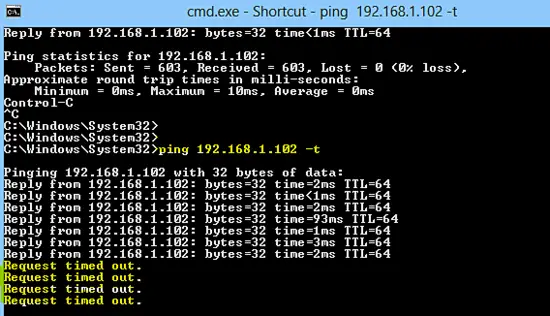
The following screenshot shows that attacker can not ping the victim IP addressa nymore, so he has been blocked successfully by PSAD.
Run the following command to see the detailed output of PSAD.
psad -S
1. Signature matched and attacker IP address
2. Traffic for specific ports
3. The attacker's IP address in the IPtables chains.
4. Details about communication between attacker and victim.
Conclusion
PSAD is a well-known open source tool for blocking port scan attacks on Linux servers. It has both IDS and IPS features and is able to dynamically block malicious IP addresses using IPtables.