How to Setup IKEv2 VPN Using Strongswan and Let's Encrypt on CentOS 8
Strongswan is an open-source multiplatform IPSec implementation. It's an IPSec-based VPN solution that focuses on strong authentication mechanisms. Strongswan offers support for both IKEv1 and IKEv2 key exchange protocols, authentication based on X.509 certificates or pre-shared keys, and secure IKEv2 EAP user authentication.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install an IPSec VPN server using Strongswan. We will create an IKEv2 VPN server with the 'EAP-MSCHAPv2' authentication and be using Letsencrypt certificates on CentOS 8 server.
Prerequisites
- CentOS 8 Server
- Root privileges
What we will do?
- Install Strongswan on CentOS 8
- Generate SSL Letsencrypt
- Configure Strongswan
- Enable NAT Firewall
- Enable Port-Forwarding
- Testing
Step 1 - Install Strongswan on CentOS 8
In this first step, we will install the strongswan IPsec implement software and all packages needed from the EPEL repository.
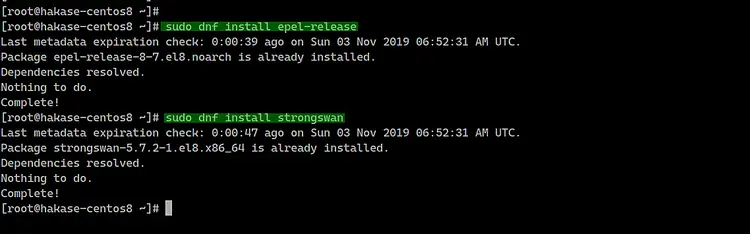
Before installing the strongswan package, you must add the EPEL repository to the CentOS 8 system.
Add the EPEL repository for CentOS 8 server.
sudo dnf install epel-release
After that, install the strongswan package from the EPEL repository using the dnf command below.
sudo dnf install strongswan
Wait for the strongswan package to be installed.
Step 2 - Generate SSL Certificate with Let's encrypt
For this guide, we're going to create the IKEv2 VPN server using a domain name 'vpn.hakase-labs.io' and use certificates generated from letsencrypt.
In this step, we will install the letsencrypt tool 'certbot' manually and generate certificates for the server domain name 'vpn.hakase-labs.io'.
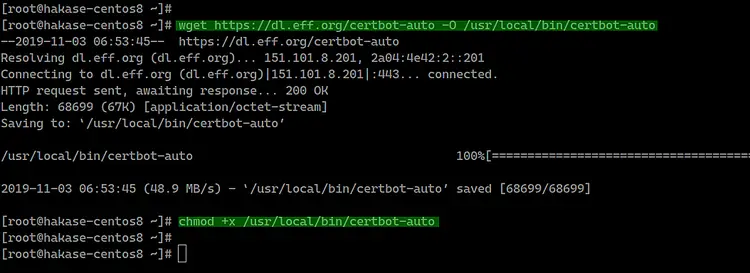
Download the certbot binary file from GitHub using the wget command below.
wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto -O /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
After that, make it an executable by changing the permission of the file.
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/certbot-auto
And the certbot tool for generating Letsencrypt certificates has been installed.
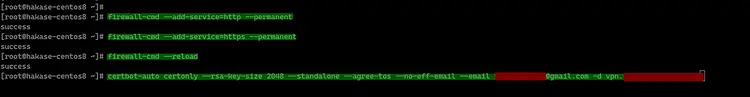
Before generating the Letsencrypt certificates, we need to open the HTTP and HTTPS ports of the server using firewall-cmd.
Add the HTTP and HTTPS services to the firewalld service list by running firewall-cmd commands below.
firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
firewall-cmd --add-service=https --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
Now we can generate new SSL certificate files using the letsencrypt tool certbot-auto.
Change the email address and the domain name with your own and run the 'certbot-auto' command below.
certbot-auto certonly --rsa-key-size 2048 --standalone --agree-tos --no-eff-email --email [email protected] -d vpn.hakase-labs.io
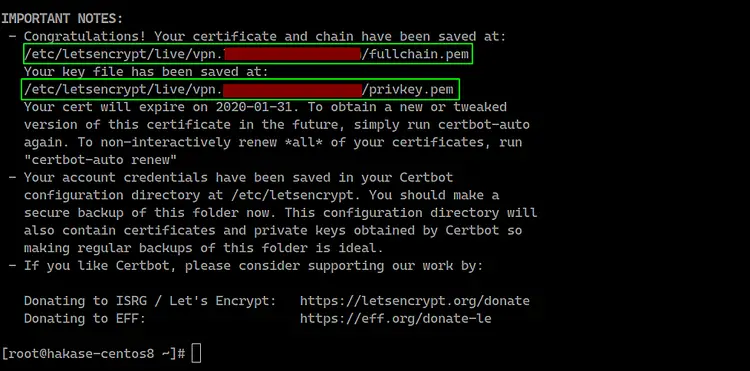
Once it's complete, you will get the result as below.
All certificates of your domain name are generated to the '/etc/letsencrypt/live/domain.com' directory.
Next, we need to copy the certificate files 'fullchain.pem', 'privkey.pem', and the 'chain.pem' to the '/etc/strongswan/ipsec.d/' directory.
cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/vpn.hakase-labs.io/fullchain.pem /etc/strongswan/ipsec.d/certs/
cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/vpn.hakase-labs.io/privkey.pem /etc/strongswan/ipsec.d/private/
cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/vpn.hakase-labs.io/chain.pem /etc/strongswan/ipsec.d/cacerts/
All letsencrypt certificates for the Strongswan VPN named 'vpn.hakase-labs.io' have been generated and copied to the '/etc/strongswan/ipsec.d' directory.
tree /etc/strongswan/ipsec.d/
Step 3 - Configure Strongswan
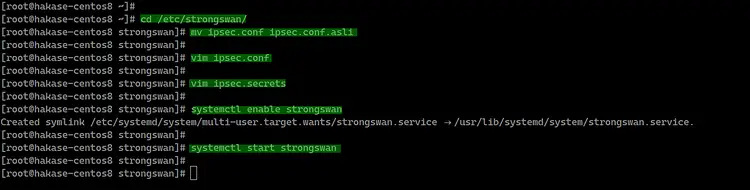
Go to the '/etc/strongswan' directory and backup the default 'ipsec.conf 'configuration file.
cd /etc/strongswan/
mv ipsec.conf ipsec.conf.asli
Create a new one 'ipsec.conf' using vim editor.
vim ipsec.conf
And paste the following configuration.
config setup
uniqueids=never # allow multiple connections per user
charondebug="ike 2, knl 2, cfg 2, net 2, esp 2, dmn 2, mgr 2"
conn %default
fragmentation=yes
closeaction=restart
rekey=no
dpdaction=clear
keyexchange=ikev2
compress=yes
dpddelay=35s
lifetime=3h
ikelifetime=12h
ike=aes256gcm16-prfsha512-ecp384!
esp=aes256gcm16-ecp384!
left=%any
[email protected]
leftcert=fullchain.pem
leftsendcert=always
leftsubnet=0.0.0.0/0
right=%any
rightid=%any
rightauth=eap-mschapv2
rightsourceip=10.15.1.0/24
rightdns=1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8
rightsendcert=never
eap_identity=%identity
conn ikev2-pubkey
auto=add
Save and exit.
Next, we need to edit the 'ipsec.secrets' file to define the RSA server private key and EAP user password credentials.
Edit the 'ipsec.secrets' file.
vim ipsec.secrets
Paste the configuration below.
: RSA "privkey.pem"
hakase : EAP "hakase321@"
tensai : EAP "tensai321@"
Save and exit.
And the strongswan IPSec configuration has been completed. Add the strongswan service to startup boot time and then start the service.
systemctl enable strongswan
systemctl start strongswan
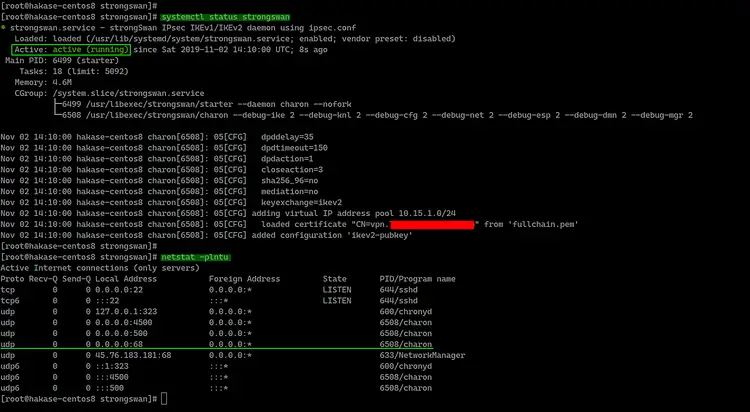
The strongswan service is up and running on CentOS 8 server, check it using the following command.
systemctl status strongswan
netstat -plntu
And you will be shown the result as below.
Step 4 - Enable NAT in Firewalld
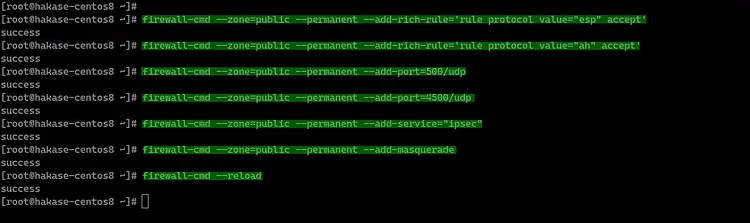
In this step, we will enable the NAT masquerading and add the IPSec protocols Authentication Header (AH) and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) on Firewalld using the 'rich-rule' configuration.
Add 'AH' and 'ESP' for authentication and encryption protocols to the firewalld.
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule protocol value="esp" accept'
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule protocol value="ah" accept'
Add the ipsec UDP ports and service.
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=500/udp
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=4500/udp
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service="ipsec"
Now enable the NAT mode masquerade and reload the firewalld configuration rules.
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-masquerade
firewall-cmd --reload
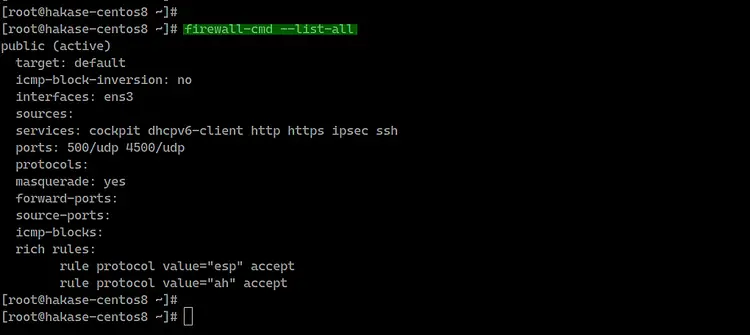
The NAT mode on firewalld has been enabled, check using the command below.
firewall-cmd --list-all
Following is the result.
Step 5 - Enable Port-Forwarding
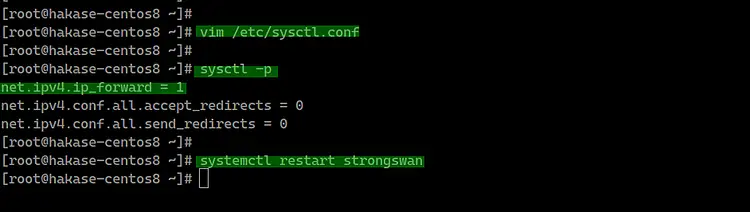
To enable port-forwarding, we need to edit the 'sysctl.conf' file.
Edit the '/etc/sysctl.conf' file using vim editor.
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
Paste the following configuration there.
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
Save and exit, now reload using the sysctl command below.
sysctl -p
Port-forwarding has been enabled. Now restart the strongswan service.
systemctl restart strongswan
Step 6 - Testing Strongswan IPSec VPN
In this case, we will do the test on the MacOS X and android phone.
On MacOS
- Open the 'System Preferences' and click the 'Network' menu.
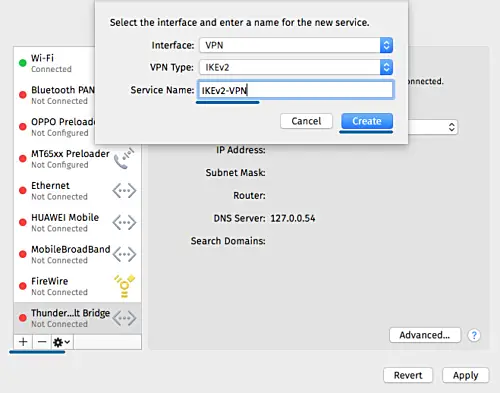
Click the '+' button to create a new VPN connection.
- Interface: 'VPN'
- VPN Type: 'IKEv2'
- Service Name: 'IKEv2-vpn
- On the 'Server Address' and 'Remote ID', type the VPN domain name 'ikev2.hakase-labs.io'.
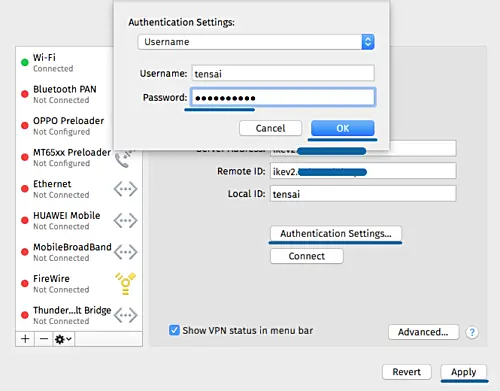
- Click 'Authentication Settings'.
- Authentication using a 'Username'.
- Type the username 'tensai' with password 'tensai321@'
- Click 'OK' and click 'Apply'.
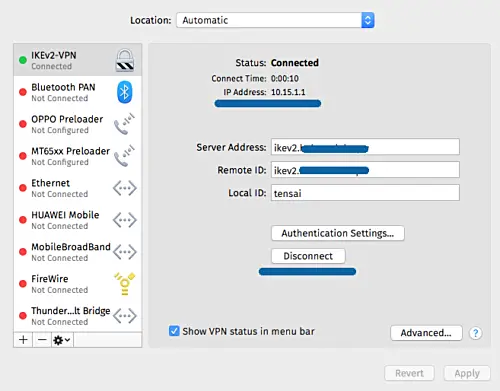
New IKEv2 VPN connection has been created on the client. Now click the connect button.
And the client has been connected to the strongswan VPN server and has an internal/private IP address 10.15.1.1.
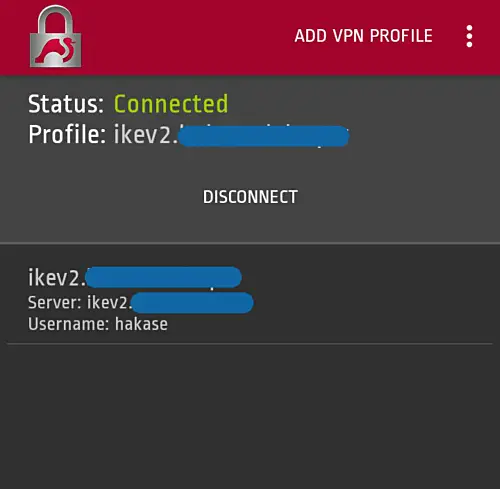
On Android
- Download and install the native strongswan android application from Google-Play.
- Add new VPN profile
- Type the server domain name 'ikev2.hakase-labs.io' and use the IKEv2 EAP Username and Password authentication.
Following is the result when we connect to the VPN server.
The IKEv2 IPSec-based VPN server has been created using Strongswan and Letsencrypt on CentOS 8 server.