How to Install Nextcloud with Nginx and PHP7-FPM on CentOS 7
This tutorial exists for these OS versions
- CentOS 8
- CentOS 7
On this page
- Step 1 - Install Nginx and PHP7-FPM on CentOS 7
- Step 2 - Configure PHP7-FPM
- Step 3 - Install and Configure MariaDB
- Step 4 - Generate a Self-signed SSL Certificate for Nextcloud
- Step 5 - Download and Install Nextcloud
- Step 6 - Configure Nextcloud Virtual Host in Nginx
- Step 7 - Configure SELinux and FirewallD for Nextcloud
- Step 8 - Nextcloud Installation Wizard
- Reference
Nextcloud is a free (Open Source) Dropbox-like software, a fork of the ownCloud project. Nextcloud is written in PHP and JavaScript, it supports many database systems such as, MySQL/MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle Database and SQLite. In order to keep your files synchronized between Desktop and your own server, Nextcloud provides applications for Windows, Linux and Mac desktops and a mobile app for android and iOS. Nextcloud is not just a dropbox clone, it provides additional features like Calendar, Contacts, Schedule tasks, and streaming media with Ampache.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure the latest Nextcloud 10 release on a CentOS 7 server. I will run Nextcloud with a Nginx web server and PHP7-FPM and use MariaDB as the database system.
Prerequisite
- CentOS 7 64bit
- Root privileges on the server
Step 1 - Install Nginx and PHP7-FPM on CentOS 7
Before we start with the Nginx and php7-fpm installation, we have to add the EPEL package repository. Install it with this yum command.
yum -y install epel-release
Now install Nginx from the EPEL repository.
yum -y install nginx
Then we have to add another repository for php7-fpm. There are several repositories available on the net that provide PHP 7 packages, I will use webtatic here.
Add the PHP7-FPM webtatic repository:
rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
Next, install PHP7-FPM and some additional packages for the Nextcloud installation.
yum -y install php70w-fpm php70w-cli php70w-gd php70w-mcrypt php70w-mysql php70w-pear php70w-xml php70w-mbstring php70w-pdo php70w-json php70w-pecl-apcu php70w-pecl-apcu-devel
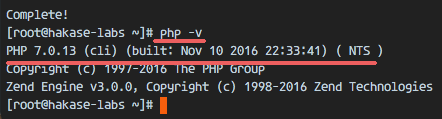
Finally, check the PHP version from server terminal to verify that PHP installed correctly.
php -v
Step 2 - Configure PHP7-FPM
In this step, we will configure php-fpm to run with Nginx. Php7-fpm will run under user nginx and listen on port 9000.
Edit the default php7-fpm configuration file with vim.
vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
In line 8 and 10, change user and group to 'nginx'.
user = nginx
group = nginx
In line 22, make sure php-fpm is running under server port.
listen = 127.0.0.1:9000
Uncomment line 366-370 to activate the php-fpm system environment variables.
env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME
env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin
env[TMP] = /tmp
env[TMPDIR] = /tmp
env[TEMP] = /tmp
Save the file and exit the vim editor.
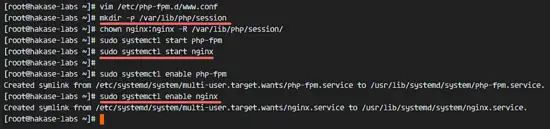
Next, create a new directory for the session path in the '/var/lib/' directory, and change the owner to the 'nginx' user.
mkdir -p /var/lib/php/session
chown nginx:nginx -R /var/lib/php/session/
Now start php-fpm and Nginx, then enable the services to start at boot time.
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
sudo systemctl enable nginx
PHP7-FPM configuration is done.
Step 3 - Install and Configure MariaDB
I will use MariaDB for the Nextcloud database. Install the mariadb-server package from the CentOS repository with yum.
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
Start the MariaDB service and add it to run at boot time.
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
Now configure the MariaDB root password.
mysql_secure_installation
Type in your root password when requested.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
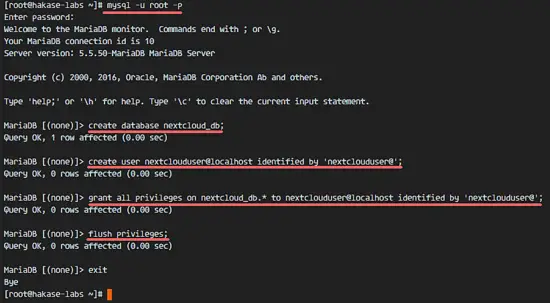
The MariaDB root password has been set, now we can login to the mysql shell to create a new database and a new user for Nextcloud. I will create a new database named 'nextcloud_db' and a user 'nextclouduser' with password 'nextclouduser@'. Choose a secure password for your installation!
mysql -u root -p
Type Password
Type in the mysql query below to create a new database and a new user.
create database nextcloud_db;
create user nextclouduser@localhost identified by 'nextclouduser@';
grant all privileges on nextcloud_db.* to nextclouduser@localhost identified by 'nextclouduser@';
flush privileges;
The nextcloud_db database with user 'nextclouduser' has been created.
Step 4 - Generate a Self-signed SSL Certificate for Nextcloud
In this tutorial, I will run nextcloud with a https connection for the client. You can use free SSL such as let's encrypt or create self signed SSL certificate. I will create my own self-signed SSL certificate file with the OpenSSL command.
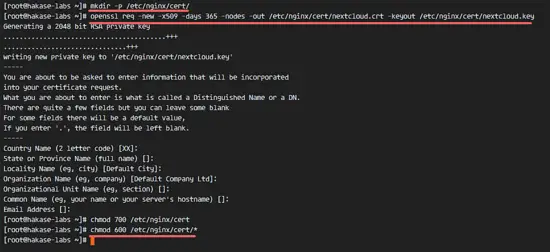
Create a new directory for the SSL file.
mkdir -p /etc/nginx/cert/
And generate a new SSL certificate file with the the openssl command below.
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -nodes -out /etc/nginx/cert/nextcloud.crt -keyout /etc/nginx/cert/nextcloud.key
Finally, change the permission of all certificate files to 600 with chmod.
chmod 700 /etc/nginx/cert
chmod 600 /etc/nginx/cert/*
Step 5 - Download and Install Nextcloud
We will download Nextcloud with wget directly to the server, so we have to install wget first. Additionally, we need the unzip program. Install both applications with yum.
yum -y install wget unzip
Go to the /tmp directory and download latest stable Nextcloud 10 version from the Nextcloud web site with wget.
cd /tmp
wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-10.0.2.zip
Extract the nextcloud zip file and move it's content to the '/usr/share/nginx/html/' directory.
unzip nextcloud-10.0.2.zip
mv nextcloud/ /usr/share/nginx/html/
Next, go to the Nginx web root directory and create a new 'data' directory for Nextcloud.
cd /usr/share/nginx/html/
mkdir -p nextcloud/data/
Change the owner of the 'nextcloud' directory to the 'nginx' user and group.
chown nginx:nginx -R nextcloud/
Step 6 - Configure Nextcloud Virtual Host in Nginx
In step 5 we've downloaded the Nextcloud source code and configured it to run under the Nginx web server. But we still need to configure a virtual host for Nextcloud. Create a new virtual host configuration file 'nextcloud.conf' in the Nginx 'conf.d' directory.
cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
vim nextcloud.conf
Paste the Nextcloud virtual host configuration below.
upstream php-handler {
server 127.0.0.1:9000;
#server unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name cloud.nextcloud.co;
# enforce https
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name cloud.nextcloud.co;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/cert/nextcloud.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/cert/nextcloud.key;
# Add headers to serve security related headers
# Before enabling Strict-Transport-Security headers please read into this
# topic first.
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000;
includeSubDomains; preload;";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Robots-Tag none;
add_header X-Download-Options noopen;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies none;
# Path to the root of your installation
root /usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/;
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# The following 2 rules are only needed for the user_webfinger app.
# Uncomment it if you're planning to use this app.
#rewrite ^/.well-known/host-meta /public.php?service=host-meta last;
#rewrite ^/.well-known/host-meta.json /public.php?service=host-meta-json
# last;
location = /.well-known/carddav {
return 301 $scheme://$host/remote.php/dav;
}
location = /.well-known/caldav {
return 301 $scheme://$host/remote.php/dav;
}
# set max upload size
client_max_body_size 512M;
fastcgi_buffers 64 4K;
# Disable gzip to avoid the removal of the ETag header
gzip off;
# Uncomment if your server is build with the ngx_pagespeed module
# This module is currently not supported.
#pagespeed off;
error_page 403 /core/templates/403.php;
error_page 404 /core/templates/404.php;
location / {
rewrite ^ /index.php$uri;
}
location ~ ^/(?:build|tests|config|lib|3rdparty|templates|data)/ {
deny all;
}
location ~ ^/(?:\.|autotest|occ|issue|indie|db_|console) {
deny all;
}
location ~ ^/(?:index|remote|public|cron|core/ajax/update|status|ocs/v[12]|updater/.+|ocs-provider/.+|core/templates/40[34])\.php(?:$|/) {
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param HTTPS on;
#Avoid sending the security headers twice
fastcgi_param modHeadersAvailable true;
fastcgi_param front_controller_active true;
fastcgi_pass php-handler;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_request_buffering off;
}
location ~ ^/(?:updater|ocs-provider)(?:$|/) {
try_files $uri/ =404;
index index.php;
}
# Adding the cache control header for js and css files
# Make sure it is BELOW the PHP block
location ~* \.(?:css|js)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$uri$is_args$args;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=7200";
# Add headers to serve security related headers (It is intended to
# have those duplicated to the ones above)
# Before enabling Strict-Transport-Security headers please read into
# this topic first.
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000;
includeSubDomains; preload;";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Robots-Tag none;
add_header X-Download-Options noopen;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies none;
# Optional: Don't log access to assets
access_log off;
}
location ~* \.(?:svg|gif|png|html|ttf|woff|ico|jpg|jpeg)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$uri$is_args$args;
# Optional: Don't log access to other assets
access_log off;
}
}
Save the file and exit vim.
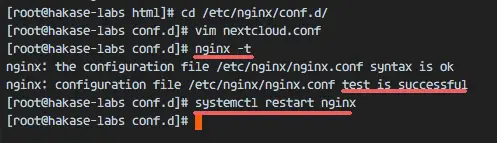
Now test the Nginx configuration to ensure that there are no error,s- Then restart the service.
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
Step 7 - Configure SELinux and FirewallD for Nextcloud
In this tutorial, we will leave SELinux on in enforcing mode, so we need a new package SELinux management tools to configure SELinux for Nextcloud.
Install the SELinux management tools with this command.
yum -y install policycoreutils-python-utils
Then execute the commands below as root user to allow Nextcloud to run under SELinux. Remember to change the Nextcloud directory in case you use a different directory.
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/data(/.*)?'
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/config(/.*)?'
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/apps(/.*)?'
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/assets(/.*)?'
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/.htaccess'
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/.user.ini'
restorecon -Rv '/usr/share/nginx/html/nextcloud/'
Next, we will enable the firewalld service and open the HTTP and HTTPS ports for Nextcloud.
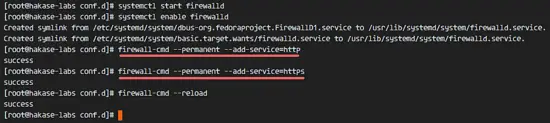
Start firewalld and enable it to start at boot time.
systemctl start firewalld
systemctl enable firewalld
Now open the HTTP and HTTPS ports with the firewall-cmd command, then reload the firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
firewall-cmd --reload
All the server configuration is done.
Step 8 - Nextcloud Installation Wizard
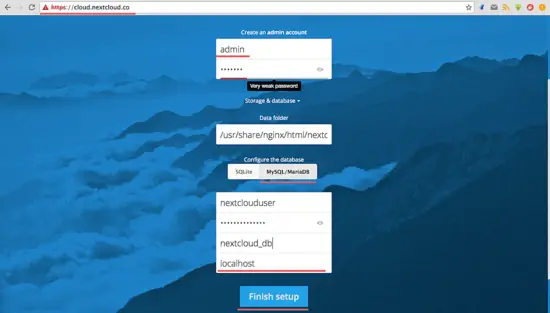
Open your web browser and type in your Nextcloud domain name, mine is: cloud.nextcloud.co. You will be redirected to the secure https connection.
Type in your desired admin user name and password, and then type in your database credentials. Click 'Finish Setup'.
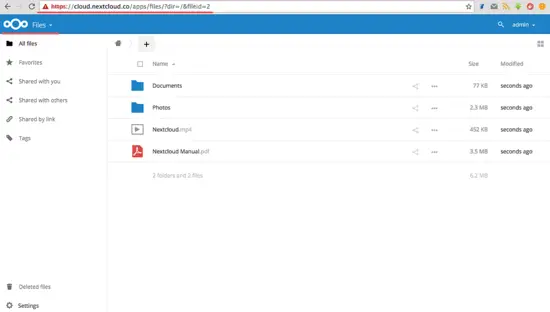
The Nextcloud Admin Dashboard (File Manager) appears.
Nextcloud User Settings.
Admin Settings.
Nextcloud has been installed with Nginx, PHP7-FPM, and MariaDB on a CentOS 7 Server.