How to Install DokuWiki with Nginx and Let's encrypt SSL on CentOS 8
DokuWiki is a simple to use and highly versatile Open Source wiki software that doesn't require a database. It is loved by users for its clean and readable syntax. The ease of maintenance, backup, and integration makes it an administrator's favorite. Built-in access controls and authentication connectors make DokuWiki especially useful in the enterprise context and a large number of plugins contributed by its vibrant community allow for a broad range of use cases beyond a traditional wiki. This tutorial will show you how to install DokuWiki on a fresh CentOS 8 server.
Requirements
Make sure your server meets the following requirements.
- Web server software supporting PHP (Apache, NGINX, IIS, Lighttpd, LiteSpeed)
- PHP version 5.6 or later, newer versions are highly recommended.
Prerequisites
- A CentOS 8 operating system.
- A non-root user with
sudoprivileges.
Initial Steps
Check your CentOS version:
cat /etc/centos-release
# CentOS Linux release 8.0.1905 (Core)
Set up the timezone:
timedatectl list-timezones
sudo timedatectl set-timezone 'Region/City'
Update your operating system packages (software). This is an important first step because it ensures you have the latest updates and security fixes for your operating system's default software packages:
sudo dnf update -y
Install some essential packages that are necessary for basic administration of the CentOS operating system:
sudo dnf install -y curl wget vim git unzip socat bash-completion epel-release
Step 1 - Install PHP and PHP extensions
Install PHP and required PHP extensions:
sudo dnf install -y php php-cli php-fpm php-gd php-xml php-zip
To show PHP compiled in modules, you can run:
php -m
ctype
curl
exif
fileinfo
. . .
. . .
Check the PHP version:
php --version
# PHP 7.2.11-1-(cli) (built: Oct 26 2019 14:14:18) ( NTS )
# Copyright (c) 1997-2018 The PHP Group
# Zend Engine v3.3.11, Copyright (c) 1998-2018 Zend Technologies
# with Zend OPcache v7.3.11-1~deb10u1, Copyright (c) 1999-2018, by Zend Technologies
Start and enable PHP-FPM service:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm.service
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm.service
Step 2 - Install acme.sh client and obtain Let's Encrypt certificate ( optional )
Securing your site with HTTPS is not necessary, but it is a good practice to secure your site traffic. To obtain a TLS certificate from Let's Encrypt we will use acme.sh client. Acme.sh is a simple UNIX shell software for obtaining TLS certificates from Let's Encrypt with zero dependencies.
Download and install acme.sh:
sudo su - root
git clone https://github.com/Neilpang/acme.sh.git
cd acme.sh
./acme.sh --install --accountemail [email protected]
source ~/.bashrc
cd ~
Check acme.sh version:
acme.sh --version
# v2.8.2
Obtain RSA and ECC/ECDSA certificates for your domain/hostname:
# RSA 2048
acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength 2048
# ECDSA
acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength ec-256
If you want fake certificates for testing, you can add --staging flag to the above commands.
After running the above commands, your certificates and keys will be in:
- For RSA:
/home/username/example.comdirectory. - For ECC/ECDSA:
/home/username/example.com_eccdirectory.
To list your issued certs you can run:
acme.sh --list
Create a directory to store your certs. We will use the /etc/letsencrypt directory.
mkdir -p /etc/letsecnrypt/example.comsudo mkdir -p /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc
Install/copy certificates to /etc/letsencrypt directory.
# RSA
acme.sh --install-cert -d example.com --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/fullchain.pem --reloadcmd "sudo systemctl reload nginx.service"
# ECC/ECDSA
acme.sh --install-cert -d example.com --ecc --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/fullchain.pem --reloadcmd "sudo systemctl reload nginx.service"
All the certificates will be automatically renewed every 60 days.
After obtaining certs exit from root user and return to regular sudo user:
exit
Step 3 - Install and configure Nginx
DokuWiki will run on any web server that supports PHP. In this tutorial, we will use Nginx. If you prefer Apache or another web server, you can use that instead of Nginx.
Download and install NGINX from the CentOS repository:
sudo dnf install -y nginx
Check the Nginx version:
sudo nginx -v
# nginx version: nginx/1.14.2
Configure Nginx:
sudo vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/dokuwiki.conf
Copy/paste the following Nginx configuration and save it:
server {
listen [::]:443 ssl;
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:80;
listen 80;
# RSA
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/private.key;
# ECC
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/private.key;
server_name wiki.example.com;
root /var/www/dokuwiki;
index index.html index.htm index.php doku.php;
client_max_body_size 15M;
client_body_buffer_size 128K;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ @dokuwiki;
}
location ^~ /conf/ { return 403; }
location ^~ /data/ { return 403; }
location ~ /\.ht { deny all; }
location @dokuwiki {
rewrite ^/_media/(.*) /lib/exe/fetch.php?media=$1 last;
rewrite ^/_detail/(.*) /lib/exe/detail.php?media=$1 last;
rewrite ^/_export/([^/]+)/(.*) /doku.php?do=export_$1&id=$2 last;
rewrite ^/(.*) /doku.php?id=$1 last;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
}Check the Nginx configuration:
sudo nginx -t
Reload Nginx:
sudo systemctl reload nginx.service
Step 4 - Install DokuWiki
Create a document root directory:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/dokuwiki
Navigate to the document root:
cd /var/www/dokuwiki
Download the newest stable release of DokuWiki from the DokuWiki download page:
sudo wget https://download.dokuwiki.org/src/dokuwiki/dokuwiki-stable.tgz
Unpack DokuWiki tarball:
sudo tar xvf dokuwiki-stable.tgz
sudo rm dokuwiki-stable.tgz
sudo mv dokuwiki-2018-04-22b/* . && mv dokuwiki-2018-04-22b/.* .
sudo rmdir dokuwiki-2018-04-22b/
Change ownership of the /var/www/dokuwiki directory to www-data:
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/dokuwiki
Run sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf and set user and group to nginx. Initially, it will be set to user and group apache.
sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
Restart php7.3-fpm.service:
sudo systemctl restart php7.3-fpm.service
Open the DokuWiki setup script, install.php, in your browser and setup DokuWiki. The setup script checks for the availability of required PHP functions and checks for needed file permissions. It also creates an initial administrator account and an initial ACL policy. To run the installer, open http://wiki.example.com/install.php in the browser and follow the instructions.
Step 5 - Access DokuWiki Web Interface
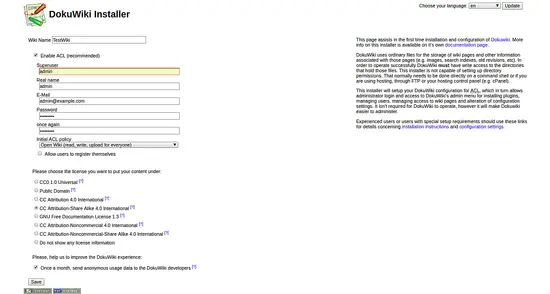
Open your web browser and type the URL http://example.com/install.php. You will be redirected to the following page:
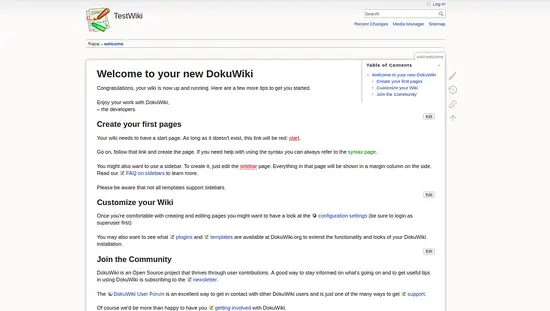
Provide all the required information like superuser name, email, password. Then, click on the Save button. Once the installation has been completed successfully, you should see the following page:
Now, click on your new DokuWiki. You should see the following page:
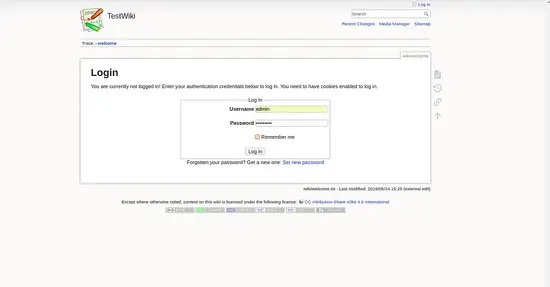
Now, click on the login button. You will be redirected to the following page:
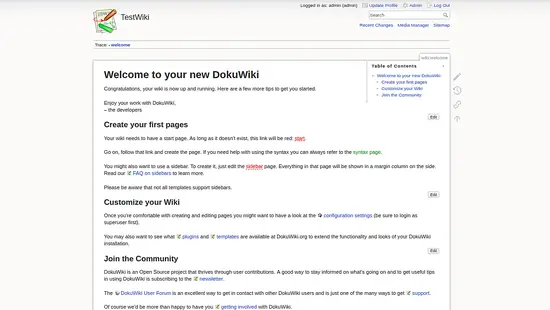
Now, provide your Admin username and password. Then, click on the Log In button. You should see the DokuWiki dashboard in the following page:
After a successful configuration, delete the install.php file from the DokuWiki root directory:
sudo rm /var/www/dokuwiki/install.php
Congratulations! You have successfully installed and configured DokuWiki on CentOS 8 server. You can now create your own wiki site easily using DokuWiki.