How to use Bash file test operators in Linux
File Test Operators are used in Linux to check and verify attributes of files like ownership or if they are a symlink. Every Test operator has a specific purpose. The most important operators are -e and -s. In this article, you will learn to test files using the if statement followed by some important test operators in Linux.
In this article we will cover the following test operators:
- If -e test operator
- If -s test operator
- If -d test operator
- If -h test operator
- If -r test operator
- If -O test operator
Use of if -e Operator
The key aim of using the if-e test operator in Centos 8 is to verify if the specific file resides in the directory or not. So if you want to verify the existence of a file using if-e, you have to follow the steps below:
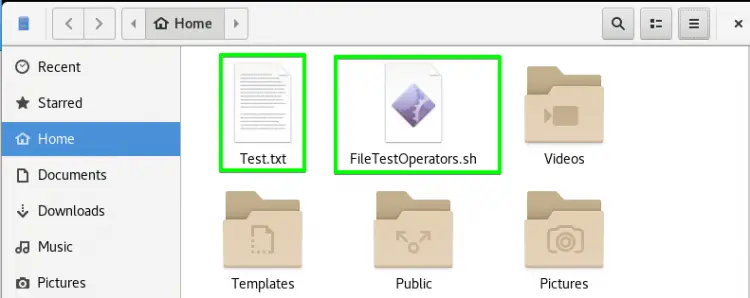
Create two new files with the names Test.txt and FileTestOperators.sh respectively. Extension .sh belongs to the bash file. You may create both in the home directory directly, or with the following command:
$ touch Test.txt
$ touch FileTestOperators.sh
If you want to authenticate whether or not the file is created, use the following command:
$ ls -l Test.txt
You can see both the files are created in the home directory.
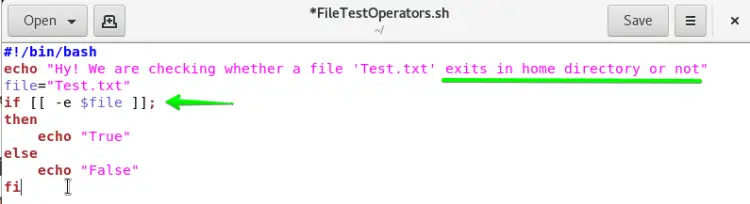
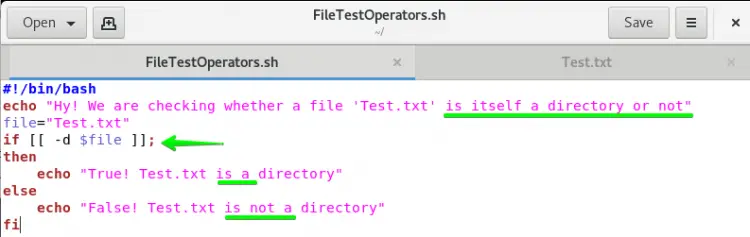
Open the file FileTestOperators.sh and write down the script in it as shown in the below image. We have initialized a variable file and passed the Test.txt file as a value to it. In the If statement, we have the -e operator used to confirm the existence of file Test.txt using variable file.
Run the below-mentioned command to check the existence of the file:
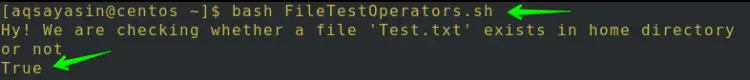
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As the file exists in the directory, so the output will be True.
Use of if -s Operator
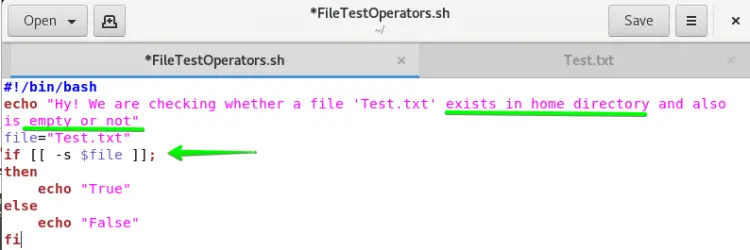
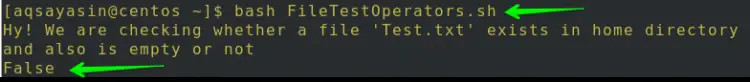
The purpose of using the if-s test operator in Centos 8 is to verify if the specified file exists and is empty or not. So if you want to verify it using if-e, you have to follow the steps below:
We will be using the same files with a minor change in the file FileTestOperators.sh. You just have to change the -s operator instead of -e in the if statement.
Run the below-mentioned command to check whether the file is empty or not:
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As the file is empty, so the output generated by the -s operator is False
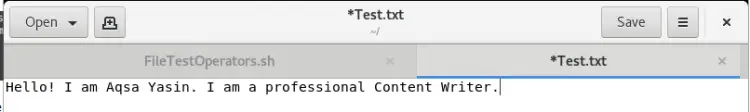
Now you have to add some text in the file Test.txt to alter the result, as shown in the below image.
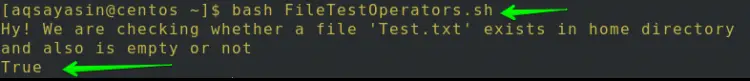
Again run the below-mentioned command:
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As the file is not empty this time, so the output generated by the -s operator will be True as shown in the image.
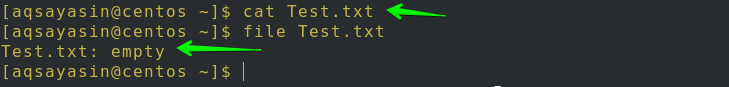
You can also use the following two commands to verify that file is empty:
$ cat Test.txt
$ file Test.txt
Use of if -d Operator
The aim of using the if-d test operator in Centos 8 is to verify that the specific file is itself a directory or not. So if you want to check it using if-d, you should follow the below-mentioned steps:
Here, again we are using the same both files with a slight change in the FileTestOperators.sh bash file. We have to change the -s operator with the -d operator in the if statement as shown in the below image.
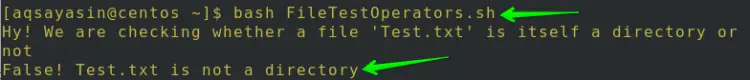
So, runs the below-mentioned command to check whether the file is a directory or not:
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As we know the Test.txt file is not a directory that is why the -d operator outputs False Test.txt is not a directory as shown in the below image.
Use of if -h Operator
The if-h test operator is used to check whether the file is a symbolic (soft) link or not. So if you want to verify the existence of a file using if-h, you have to go through the following steps:
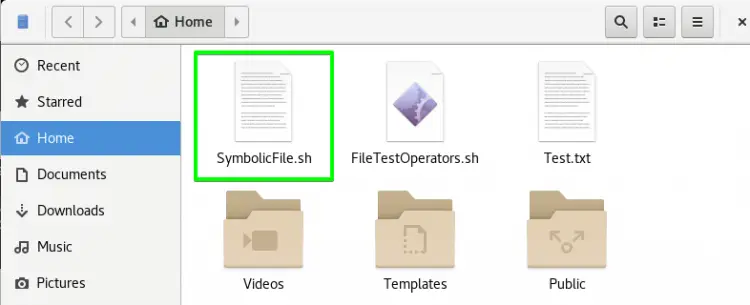
Create a new file with the name SymbolicFile.sh. You may create it in the home directory directly, or with the following command:
$ touch SymbolicFile.sh
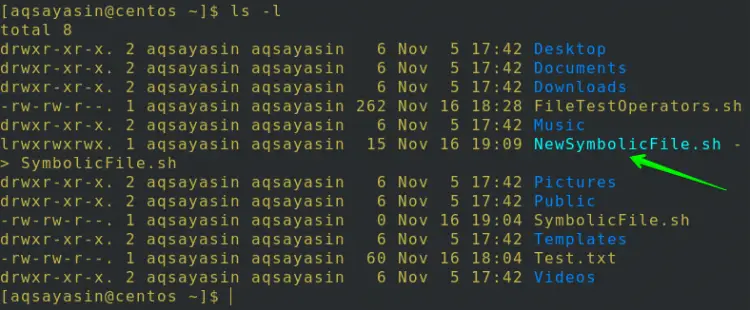
You can see the SymbolicFile.sh file in the home directory as shown in the below image.
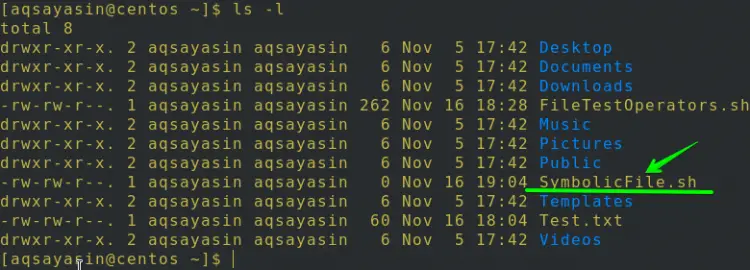
You can list all the directories and files using the ls command. You can see the SymbolicFile.sh file is also listed as shown in the image.
$ ls –l
Create a symbolic link using a simple link command. In this command, -s refers to a soft link, SymbolicFile.sh is a file whose link will be created, and NewSymbolicFile.sh is a symbolic link.
$ ln -s SymbolicFile.sh NewSymbolicFile.sh
Again list all the directories and files. You can see a soft link has been created.
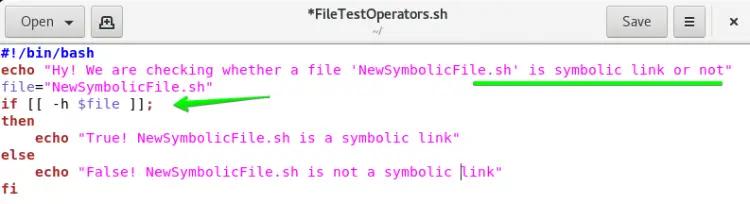
So, again we are using FileTestOperators.sh bash file with a slight change.Change -d operator with -h operator in the if statement. This time we have to change a file name as well. We have to use a file that is a symbolic link itself e.g. NewSymbolicFile.sh.
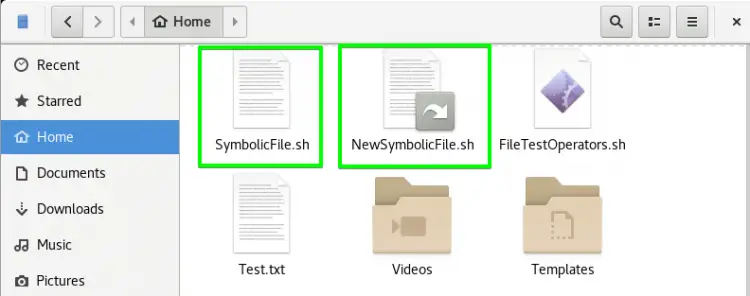
You can see both files in the below image.
Now run the below command:
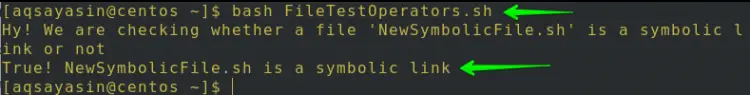
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As we know the NewSymbolicFile.sh file is a symbolic link, that is why the -h operator outputs True NewSymbolicFile.sh is a symbolic link as shown in the below image.
Use of if -r Operator
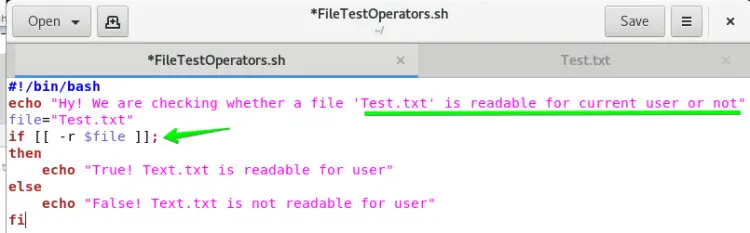
The if -r test operator is used to check the readability of the file e.g. the file is readable or not. So if you want to check it using if-r, you have to follow these steps:
Again, we are using Test.txt and FileTestOperators.sh bash file with a slight change. Change -h operator with -r operator in the if statement and assign Test.txt file as a value to variable file.
Now run the below command:
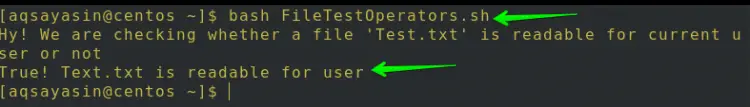
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As we know that the Test.txt file is readable so the -r operator outputs True! Test.txt is readable.
Note: Use -w and -x operators respectively to verify whether the file is writable and executable or not.
Use of if -O Operator
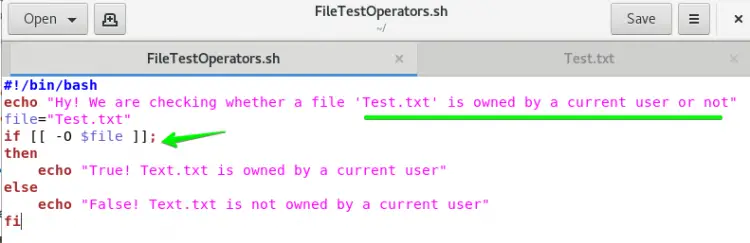
The purpose of the if -O test operator is used to check whether the file is owned by a current user or not. So to verify it using if-O, you have to go through these steps:
Again, we are using Test.txt and FileTestOperators.sh bash file with a little change. Change -r operator with -O operator in the if statement and assign Test.txt file as a value to variable file.
Now run the below command:
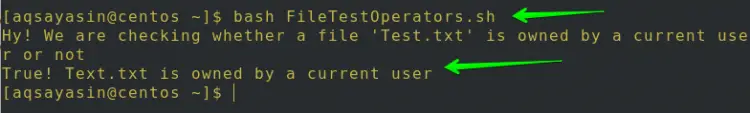
$ bash FileTestOperators.sh
As we know that the Test.txt file is already owned by the current user so the -O operator outputs True Test.txt is owned by a current user.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned about the most important and different file test operators and their working in Centos 8. I hope you are now able to create files, checking the existence of files, checking the readability of files, checking ownership of files, and making soft links. Users can feel themself at ease after following this article thoroughly.